Циррус (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин) Таблетки
В двух двойных слепых, плацебо-контролируемые испытания (n = 2094) у которых 701 пациент с сезонным аллергическим ринитом лечился циррусом (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин) Таблетки (цетиризин гидрохлорид 5 мг и псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид 120 мг) два раза в день в течение двух недель, процент пациентов, которые вышли преждевременно из-за нежелательных явлений, составил 2,0% в Cirrus (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин) группа, по сравнению с 1,1% в группе плацебо. Все побочные эффекты, о которых сообщалось более чем 1% пациентов в группе Cirrus (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин), перечислены в таблице 1.
ТАБЛИЦА 1. КРАТКОВЫЕ ОПЫТЫ, ОТЧЕТНЫЕ У ПАЦИЕНТОВ, НАМЕРЕННЫХ 12 ЛЕТ И СТАРЫХ В СЕЗОННЫХ АЛЛЕРГИЧЕСКИХ РИНИТИКАХ ТРААЛОВ Cirrus (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин) ТАБЛЕТКИ С ЦЕНАМИ 1% ИЛИ БОЛЬШОЙ (ПЕРЦЕНТНАЯ ИНЦИДЕНЦИЯ)
| РЕКЛАМНЫЙ ОПЫТ | Cirrus | PLACEBO |
| (n = 701) | (n = 696) | |
| Бессонница | 4,0 | 0,6 |
| Сухой рот | 3,6 | 0,4 |
| Усталость | 2.4 | 0,9 |
| Сонливость | 1,9 | 0,1 |
| Фарингит | 1,7 | 1.1 |
| Носовое кровотечение | 1.1 | 0,9 |
| Случайное повреждение | 1.1 | 0,4 |
| Головокружение | 1.1 | 0,1 |
| Синусит | 1,0 | 0,6 |
Таблетки ZYRTEC
Контролируемые и неконтролируемые клинические испытания цетиризина, проведенные в Соединенных Штатах и Канаде, включали более 6000 пациентов в возрасте 12 лет и старше, причем более 3900 получали цетиризин в дозах от 5 до 20 мг в день. Продолжительность лечения варьировалась от 1 недели до 6 месяцев со средним воздействием 30 дней.
Большинство побочных реакций, о которых сообщалось во время терапии цетиризином, были легкими или умеренными. В плацебо-контролируемых исследованиях частота прерываний из-за побочных реакций у пациентов, получавших цетиризин 5 или 10 мг, существенно не отличалась от плацебо (2,9% против. 2,4% соответственно).
Наиболее распространенной побочной реакцией у пациентов в возрасте 12 лет и старше, которая чаще встречалась на цетиризине, чем плацебо, была сонливость. Частота сонливости, связанной с цетиризином, была связана с дозой, 6% в плацебо, 11% в 5 мг и 14% в 10 мг. Прекращение лечения цетиризином было необычным (1,0% на цетиризин против. 0,6% на плацебо). Усталость и сухость во рту также, по-видимому, связаны с лечением побочными реакциями. Не было различий по возрасту, расе, полу или массе тела в отношении частоты побочных реакций.
В таблице 2 перечислены неблагоприятные события у пациентов в возрасте 12 лет и старше, которые были зарегистрированы для цетиризина 5 и 10 мг в контролируемых клинических испытаниях в Соединенных Штатах и были более распространены с цетиризином, чем плацебо.
ТАБЛИЦА 2. КРАТКОВЫЕ ОПЫТЫ, ОТЧЕТНЫЕ У ПАЦИЕНТОВ, НАМЕРЕННЫХ 12 ЛЕТ И СТАРЫХ В ПЛАЦЕБО-КОНТРОЛИРОВАННЫХ ИСКУССТВЕННЫХ СТОРОНАХ ЦЕТИРИЗИНА (МАКСИМАЛЬНАЯ ДОЗА 10 МГ) СКОРОСТЬЮ 2% ИЛИ БОЛЬШОЙ (ПЕРЦЕНТНАЯ ИНЦИДЕНЦИЯ)
| РЕКЛАМНЫЙ ОПЫТ | ЦЕТИРИЗИН | PLACEBO |
| (П = 2034) | (П = 1612) | |
| Сонливость | 13,7 | 6.3 |
| Усталость | 5,9 | 2,6 |
| Сухой рот | 5,0 | 2,3 |
| Фарингит | 2,0 | 1,9 |
| Головокружение | 2,0 | 1.2 |
Кроме того, головная боль и тошнота возникали более чем у 2% пациентов, но чаще встречались у пациентов с плацебо.
Следующие события наблюдались нечасто (менее 2%) у 3982 взрослых и детей в возрасте 12 лет и старше или у 659 пациентов (от 6 до 11 лет), получавших цетиризин в исследованиях в США, включая открытое исследование продолжительностью шесть месяцев. Причинная связь этих нечастых событий с введением цетиризина не установлена.
Автономная нервная система: анорексия, приливы крови, повышенное слюноотделение, задержка мочи.
Сердечно-сосудистые: сердечная недостаточность, гипертония, сердцебиение, тахикардия.
Центральные и периферические нервные системы: ненормальная координация, атаксия, спутанность сознания, дисфония, гиперестезия, гиперкинезия, гипертония, гипестезия, судороги ног, мигрень, миелит, паралич, парестезия, птоз, обморок, тремор, подергивание, головокружение, дефект поля зрения.
Желудочно-кишечный тракт: нарушение функции печени, обострение кариеса зубов, запор, диспепсия, отрыжка, метеоризм, гастрит, геморрой, повышение аппетита, мелена, ректальное кровоизлияние, стоматит, включая язвенный стоматит, изменение цвета языка, отек языка.
Генитуринарный: цистит, дизурия, гематурия, частота мочеиспускания, полиурия, недержание мочи, инфекция мочевыводящих путей.
Слух и вестибуляр: глухота, боль в ухе, ототоксичность, шум в ушах.
Метаболический / Питательный: обезвоживание, сахарный диабет, жажда.
Скелетно-мышечная система: артралгия, артрит, артроз, мышечная слабость, миалгия.
Психиатрический : ненормальное мышление, возбуждение, амнезия, беспокойство, снижение либидо, деперсонализация, депрессия, эмоциональная лабильность, эйфория, нарушение концентрации, бессонница, нервозность, паронирия, расстройство сна.
Дыхательная система: бронхит, одышка, гипервентиляция, увеличение мокроты, пневмония, респираторные заболевания, ринит, синусит, инфекции верхних дыхательных путей.
Репродуктивный: дисменорея, боль в груди у женщин, межменструальное кровотечение, лейкорея, меноррагия, вагинит.
Ретикулоэндотелиальный : лимфаденопатия.
Кожа: прыщи, алопеция, ангионевротический отек, буллезная сыпь, дерматит, сухость кожи, экзема, эритематозная сыпь, фурункулез, гиперкератоз, гипертрихоз, повышенное потоотделение, макулопапулезная сыпь, реакция светочувствительности, токсическая реакция светочувствительности, зуд, пурпура, сыпь, себорея, кожные узлы, крапивница.
Особые чувства: парозмия, потеря вкуса, извращение вкуса.
Видение: слепота, конъюнктивит, боль в глазах, глаукома, потеря приспособления, глазное кровоизлияние, ксерофтальмия.
Тело как целое : случайная травма, астения, боль в спине, боль в груди, увеличение живота, отек лица, лихорадка, генерализованный отек, приливы, увеличение веса, отек ног, недомогание, полип носа, боль, бледность, периорбитальный отек, периферические отеки, суровость.
Случайные случаи преходящего, обратимого повышения печеночной трансаминазы имели место во время терапии цетиризином. Сообщалось о гепатите со значительным повышением уровня трансаминаз и повышенным содержанием билирубина в сочетании с применением цетиризина.
В опыте зарубежного маркетинга или опыте в пострыночный период были зарегистрированы следующие дополнительные редкие, но потенциально тяжелые побочные эффекты: анафилаксия, холестаз, гломерулонефрит, гемолитическая анемия, гепатит, орофациальная дискинезия, тяжелая гипотензия, мертворождение, тромбоцитопения, агрессивная реакция и судороги.
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид
Гидрохлорид псевдоэфедрина может вызывать умеренную стимуляцию ЦНС у гиперчувствительных пациентов.
Может возникнуть нервозность, возбудимость, беспокойство, головокружение, слабость или бессонница. Сообщалось о головной боли, тошноте, сонливости, тахикардии, сердцебиении, прессорной активности и сердечных аритмиях. Симпатомиметические препараты также связаны с другими неблагоприятными эффектами, такими как страх, беспокойство, напряжение, тремор, галлюцинации, судороги, бледность, затрудненное дыхание, дизурия и сердечно-сосудистый коллапс.
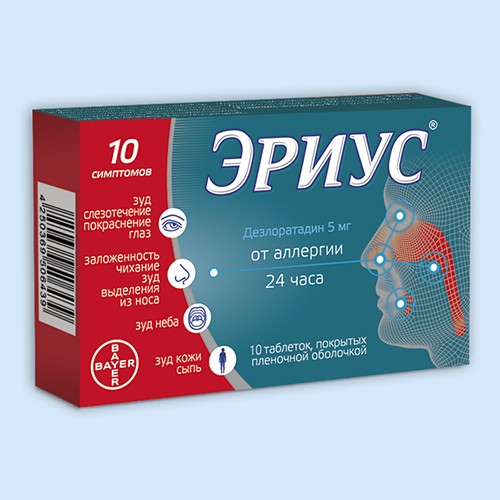
Круглые двояковыпуклые таблетки, покрытые оболочкой светло-голубого цвета, с тиснением.
1 таблетка содержит
действующее вещество: дезлоратадин 5 мг;
вспомогательные вещества: кальция гидрофосфат дигидрат, целлюлоза микрокристаллическая, крахмал кукурузный, тальк;
оболочка: лактозы моногидрат, гидроксипропилметилцеллюлоза, титана диоксид, полиэтиленгликоль, лак алюминиевый голубой FD&C №2, воск карнаубский, воск белый.
Антигистаминные средства для системного применения. Код АТС R06A Х27.
Фармакодинамика
Дезлоратадин – неседативный длительно действующий антигистаминный препарат, обладающий селективным антагонистическим действием на периферические H1-гистаминовые рецепторы. После перорального приема дезлоратадин селективно блокирует периферические H1-гистаминовые рецепторы, так как вещество не проникает через гематоэнцефалический барьер.
Исследования in vitro показали, что дезлоратадин оказывает противоаллергическое действие, в том числе угнетает высвобождение провоспалительных цитокинов, включая ИЛ-4, ИЛ-6, ИЛ-8 и ИЛ-13, из тучных клеток/базофилов человека, а также ингибирует экспрессию молекулы адгезии Р-селектина в эндотелиальных клетках. Клиническое значение этих данных остается неизвестным.
В клинических исследованиях многократных доз ежедневное применение дезлоратадина в дозе менее 20 мг в течение 14 дней не сопровождалось статистически или клинически значимыми изменениями со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы. В клинико-фармакологическом исследовании по применению препарата Эриус в дозе 45 мг/сутки (в 9 раз выше терапевтической дозы) в течение 10 дней не наблюдалось удлинения интервала QTc.
В исследованиях по изучению взаимодействия с кетоконазолом и эритромицином клинически значимых изменений концентрации дезлоратадина в плазме не выявлено.
Эриус не проникает через гематоэнцефалический барьер. В контролируемых клинических исследованиях при применении рекомендуемой дозы 5 мг частота сонливости не превышала таковую в группе плацебо. В ходе клинических исследований Эриус не влиял на психомоторную функцию при приеме дозы не более 7,5 мг.
В исследовании однократной дозы у взрослых дезлоратадин 5 мг не влиял на стандартные параметры работоспособности в условиях полета, в том числе не вызывал усиление субъективной сонливости или не ухудшал способности выполнять задачи полета.
В клинико-фармакологических исследованиях дезлоратадин не усиливал такие эффекты алкоголя, как нарушение психомоторной функции и сонливость. Результаты психомоторных тестов существенно не отличались у пациентов, получавших дезлоратадин и плацебо по отдельности или в сочетании с алкоголем.
У пациентов с аллергическим ринитом Эриус был эффективен для облегчения таких симптомов, как чихание, выделения из носа и зуд, а также зуд и покраснение глаз, слезотечение, зуд неба. Эриус эффективно контролирует симптомы в течение 24 часов. Эффективность таблеток Эриус не была однозначно продемонстрирована в исследованиях у подростков в возрасте 12-17 лет.
Помимо установленной классификации ринита (сезонный и круглогодичный), аллергический ринит можно подразделять на интермиттирующий и персистирующий на основании длительности сохранения симптомов. При интермиттирующем рините симптомы наблюдаются менее 4 дней в неделю или менее 4 недель в году. При персистирующем рините – больше 4 дней в неделю или больше 4 недель в году.
Эриус достаточно эффективно облегчал состояние пациентов с сезонным аллергическим ринитом по результатам суммарного балла опросника качества жизни больных риноконъюнктивитом. Наибольшее улучшение отмечено в области практических проблем и повседневной деятельности, ограниченной присутствием симптомов.
В качестве клинической модели крапивницы изучалась хроническая идиопатическая крапивница на основании сходства их основных патофизиологических механизмов, независимо от этиологии и отсутствия проблем при проспективном наборе пациентов, страдающих хроническим заболеванием. Поскольку выделение гистамина является причинным фактором при всех видах крапивницы, ожидается, что дезлоратадин будет эффективным средством в купировании симптомов других видов крапивницы, в том числе и при хронической идиопатической крапивнице, как указано в клинических рекомендациях.
В двух плацебо-контролируемых шестинедельных испытаниях у пациентов с хронической идиопатической крапивницей Эриус эффективно облегчал зуд и снижал размер и количество высыпаний по окончании первого курса лечения. В каждом исследовании эффект сохранялся в течение 24 часов после приема дозы. Как и в других исследованиях антигистаминных препаратов при хронической идиопатической крапивнице исключалась меньшая часть пациентов, которые считались резистентными к лечению антигистаминными средствами. Облегчение зуда более чем на 50 % наблюдалось у 55 % пациентов, которые получали лечение дезлоратадином, по сравнению с 19 % пациентов, которые получали плацебо. Лечение препаратом Эриус также значительно снижало отрицательное влияние заболевания на сон и активность в течение дня, которое определялось по четырехбалльной шкале, используемой для оценки этих переменных.
Фармакокинетика
Дезлоратадин начинает определяться в плазме в течение 30 минут после приема. Максимальная концентрация дезлоратадина в плазме достигается в среднем через 3 часа, период полувыведения составляет в среднем 27 часов. Степень кумуляции дезлоратадина соответствует его периоду полувыведения (приблизительно 27 часов) и кратности применения (один раз в сутки). Биодоступность дезлоратадина была пропорциональна дозе в диапазоне от 5 до 20 мг.
В исследовании фармакокинетики, в котором демографические особенности пациентов были сопоставимы с таковыми в общей популяции лиц с сезонным аллергическим ринитом, 4 % испытуемых достигали более высоких концентраций дезлоратадина. Этот процент может варьироваться в зависимости от этнического происхождения. Максимальная концентрация дезлоратадина была почти в 3 раза выше примерно через 7 часов с конечной фазой полувыведения, длящейся примерно 89 часов. Профиль безопасности у этих испытуемых не отличался от такового в общей популяции.
Дезлоратадин умеренно (83-87%) связывается с белками плазмы. При применении дезлоратадина в дозе 5-20 мг один раз в сутки в течение 14 дней признаков клинически значимой кумуляции препарата не обнаружено.
Ферменты, обусловливающие метаболизм дезлоратадина, еще не установлены, и поэтому нельзя полностью исключить вероятность взаимодействия с другими лекарственными препаратами. Результаты проведенных исследований in vivo и in vitro показали, что дезлоратадин не угнетает CYP3A4 или CYP2D6 и не является ни субстратом, ни ингибитором Р-гликопротеида.
В исследовании с однократным приемом дезлоратадина в дозе 7,5 мг установлено, что пища (жирный высококалорийный завтрак) или грейпфрутовый сок не влияют на распределение дезлоратадина.
Пациенты с нарушением функции почек
Фармакокинетику дезлоратадина у пациентов с хронической почечной недостаточностью (ХПН) сравнивали с фармакокинетикой у здоровых лиц в одном исследовании однократных доз и в одном исследовании многократных доз. В однодозном исследовании воздействие дезлоратадина было примерно в 2 и 2,5 раза больше у пациентов с легкой/умеренной и тяжелой формой ХПН, соответственно, чем у здоровых лиц. В многодозном исследовании стационарное состояние достигалось после 11-го дня, и по сравнению со здоровыми испытуемыми воздействие дезлоратадина было примерно в 1,5 раза больше у пациентов с легкой и умеренной формой ХПН и примерно в 2,5 раза больше у пациентов с тяжелой формой ХПН. В обоих исследованиях изменения в воздействии (AUC и Сmax) дезлоратадина и 3-гидроксидезлоратадина не были клинически значимыми.
Для облегчения симптомов аллергических ринитов, таких как зуд и покраснение глаз, слезотечение, чихание, зуд и выделения из носа, зуд неба.
Для облегчения симптомов, связанных с крапивницей, таких как зуд и сыпь.
Для облегчения симптомов, связанных с аллергическим ринитом (в том числе интермиттирующим и персистирующим) и крапивницей, Эриус принимают независимо от приема пищи.
Взрослые и дети старше 12 лет: по 1 таблетке 1 раз в сутки.
Терапию интермиттирующего аллергического ринита (симптомы менее 4 дней в неделю или менее 4 недель в году) необходимо проводить с учетом данных анамнеза: прекратить после исчезновения симптомов и возобновить после повторного их появления. При персистирующем аллергическом рините (симптомы более 4 дней в неделю или более 4 недель в году) необходимо продолжать лечение на протяжении всего периода контакта с аллергеном.
Дети
Безопасность и эффективность препарата у детей до 12 лет не установлены. Данные отсутствуют. Опыт клинических испытаний с применением дезлоратадина у подростков от 12 до 17 лет ограничен.
Пожилые пациенты
Безопасность и эффективность у пациентов пожилого возраста не установлены.
Пациенты с нарушением функции почек
У пациентов с тяжелой почечной недостаточностью следует применять с осторожностью.
Пациенты с нарушением функции печени
Данные по применению у пациентов с нарушением функции печени отсутствуют.
Если Вы забыли принять препарат своевременно, примите пропущенную дозу как можно быстрее. Затем продолжайте прием препарата Эриус в обычное время. Принимать двойную дозу таблеток для компенсации пропущенной дозы не следует.
Как и все лекарственные средства, Эриус может вызвать побочные эффекты, хотя не каждый человек испытывает их.
Во время применения препарата Эриус очень редко наблюдались случаи тяжелых аллергических реакций (затрудненное дыхание, свистящее дыхание, зуд, крапивница и отеки). В случае возникновения указанных побочных реакций следует прекратить принимать лекарственное средство и немедленно обратиться к врачу.
Побочные эффекты, наблюдавшиеся в ходе клинических исследований у взрослых, были приблизительно схожи с нежелательными явлениями при приеме плацебо.
Тем не менее, усталость, сухость во рту и головная боль наблюдались чаще, чем при приеме плацебо. Головная боль отмечалась как наиболее частый побочный эффект у подростков.
По результатам клинических исследований препарата Эриус были отмечены следующие побочные эффекты: часто (более чем у 1 человека из 10): усталость, сухость во рту, головная боль.
Взрослые
Во время пострегистрационного применения Эриус были отмечены следующие побочные эффекты: очень редко (не более чем у 1 человека из 10 000): тяжелые аллергические реакции, сыпь, усиленное или нерегулярное сердцебиение, учащенное сердцебиение, боль в желудке, тошнота, рвота, расстройство пищеварения, диарея, головокружение, сонливость, нарушения сна, мышечная боль, галлюцинации, судороги, выраженное беспокойство, воспаление печени, аномальные результаты тестов функции печени; частота неизвестна (исходя из имеющихся данных, частоту возникновения определить невозможно): необычная слабость, пожелтение кожи и/или глаз, повышенная чувствительность кожи к солнцу (даже в пасмурную погоду) и к ультрафиолетовому излучению (например, при посещении солярия), изменение частоты сердцебиения, нестандартное поведение, агрессия, повышенный аппетит, увеличение веса.
Дети
Частота неизвестна: слабое сердцебиение, изменение частоты сердцебиения, нестандартное поведение, агрессия.
Предоставление сообщений о нежелательных реакциях
В случае возникновения каких-либо нежелательных реакций следует проконсультироваться с врачом. Данная рекомендация распространяется на любые возможные нежелательные реакции, в том числе на не перечисленные в листке-вкладыше. Вы также можете сообщить о нежелательных реакциях в национальную информационную базу данных по нежелательным реакциям на лекарственные препараты, включая информацию о неэффективности лекарственных препаратов. Адрес сайта: rceth.by. Сообщая о нежелательных реакциях, вы помогаете получить больше сведений о безопасности препарата.
Повышенная чувствительность к любому из компонентов препарата или лоратадину.
Эффективность и безопасность препарата Эриус в форме таблеток у детей до 12 лет не исследовалась (так как таблетка является неделимой, а доза таблетки рассчитана для детей старше 12 лет).
Дезлоратадин следует назначать с осторожностью пациентам с судорогами в личном или семейном анамнезе и, главным образом, маленьким детям, которые более предрасположены к возникновению судорог при лечении дезлоратадином. Лечащий врач может рассмотреть необходимость прекращения приема дезлоратадина пациентами, которые испытывают судороги в ходе лечения. Таблетки содержат лактозу, поэтому препарат не применяют у пациентов с врожденной непереносимостью галактозы, недостаточностью лактазы лопарей и мальабсорбцией глюкозы-галактозы.
Если Вы планируете иметь ребенка, беременны (или предполагаете, что беременны) либо кормите грудью, посоветуйтесь с врачом или фармацевтом, прежде чем принимать Эриус.
Если Вы беременны или кормите ребенка грудью, принимать Эриус не рекомендуется.
В рекомендуемой дозе Эриус не повлияет на способность управлять транспортным средством или другими механизмами. Несмотря на то, что большинство людей не испытывают сонливости, не рекомендуется заниматься деятельностью, требующей умственного напряжения, такой как управление транспортом или другими механизмами, пока не определена индивидуальная реакция на лекарственный препарат.
Клинически значимых изменений в плазменной концентрации дезлоратадина при неоднократном совместном применении с кетоконазолом, эритромицином, азитромицином, флюоксетином, циметидином обнаружено не было. Взаимодействие с другими лекарственными средствами не известно.
В клинико-фармакологическом исследовании прием таблеток Эриус одновременно с алкоголем не усиливал неблагоприятное влияние алкоголя на психомоторную функцию. Однако в постмаркетинговый период сообщалось о случаях непереносимости алкоголя и интоксикации. Поэтому рекомендуется соблюдать осторожность, если алкоголь принимается одновременно с препаратом.
Дети
Исследования взаимодействия проводились только у взрослых.
Если Вы принимаете какие-либо лекарственные средства, проконсультируйтесь с врачом относительно возможности применения препарата.
Препарат следует принимать в соответствии с рекомендациями врача. При случайной передозировке не предполагается возникновения серьезных нежелательных явлений.
Могут наблюдаться нежелательные реакции, которые описаны при приеме обычных терапевтических доз, но степень их выраженности в случае передозировки может быть выше.
Если Вы приняли больше таблеток Эриус, чем было рекомендовано, немедленно сообщите об этом своему врачу, фармацевту или другому медицинскому работнику.
Хранить в сухом недоступном для детей месте при температуре не выше 30 °C.
2 года. Не использовать по истечении срока годности, указанного на упаковке.
По 10 таблеток в блистере. 1 блистер с листком-вкладышем помещен в картонную коробку.
Название производителя и адрес
Шеринг-Плау Лабо Н.В.,
Индустрипарк 30, 2220, Хейст-оп-ден-Берг, Бельгия
Владелец регистрационного удостоверения
Байер Консьюмер Кэр АГ,
Петер Мериан-Штрассе 84, 4052 Базель, Швейцария
Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) Tablets
In two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (n = 2094) in which 701 patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis were treated with Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) Tablets (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) twice daily for two weeks, the percent of patients who withdrew prematurely due to adverse events was 2.0% in the Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) group, compared with 1.1% in the placebo group. All adverse events that were reported by greater than 1% of patients in the Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) group are listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1. ADVERSE EXPERIENCES REPORTED IN PATIENTS AGED 12 YEARS AND OLDER IN SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS TRIALS OF Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) TABLETS AT RATES OF 1% OR GREATER (PERCENT INCIDENCE)
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | Cirrus | PLACEBO |
| (n = 701) | (n = 696) | |
| Insomnia | 4.0 | 0.6 |
| Dry Mouth | 3.6 | 0.4 |
| Fatigue | 2.4 | 0.9 |
| Somnolence | 1.9 | 0.1 |
| Pharyngitis | 1.7 | 1.1 |
| Epistaxis | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| Accidental Injury | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| Dizziness | 1.1 | 0.1 |
| Sinusitis | 1.0 | 0.6 |
ZYRTEC Tablets
Controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of cetirizine conducted in the United States and Canada included more than 6000 patients aged 12 years and older, with more than 3900 receiving cetirizine at doses of 5 to 20 mg per day. The duration of treatment ranged from 1 week to 6 months, with a mean exposure of 30 days.
Most adverse reactions reported during therapy with cetirizine were mild or moderate. In placebo-controlled trials, the incidence of discontinuations due to adverse reactions in patients receiving cetirizine 5 mg or 10 mg was not significantly different from placebo (2.9% vs. 2.4%, respectively).
The most common adverse reaction in patients aged 12 years and older that occurred more frequently on cetirizine than placebo was somnolence. The incidence of somnolence associated with cetirizine was dose related, 6% in placebo, 11% at 5 mg and 14% at 10 mg. Discontinuations due to somnolence for cetirizine were uncommon (1.0% on cetirizine vs. 0.6% on placebo). Fatigue and dry mouth also appeared to be treatment-related adverse reactions. There were no differences by age, race, gender or by body weight with regard to the incidence of adverse reactions.
Table 2 lists adverse experiences in patients aged 12 years and older that were reported for cetirizine 5 and 10 mg in controlled clinical trials in the United States and were more common with cetirizine than placebo.
TABLE 2. ADVERSE EXPERIENCES REPORTED IN PATIENTS AGED 12 YEARS AND OLDER IN PLACEBO-CONTROLLED UNITED STATES CETIRIZINE TRIALS (MAXIMUM DOSE OF 10 MG) AT RATES OF 2% OR GREATER (PERCENT INCIDENCE)
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | CETIRIZINE | PLACEBO |
| (n=2034) | (n=1612) | |
| Somnolence | 13.7 | 6.3 |
| Fatigue | 5.9 | 2.6 |
| Dry Mouth | 5.0 | 2.3 |
| Pharyngitis | 2.0 | 1.9 |
| Dizziness | 2.0 | 1.2 |
In addition, headache and nausea occurred in more than 2% of the patients, but were more common in placebo patients.
The following events were observed infrequently (less than 2%), in 3982 adults and children 12 years and older or in 659 pediatric (6 to 11 years) patients who received cetirizine in U.S. trials, including an open study of six months duration. A causal relationship of these infrequent events with cetirizine administration has not been established.
Autonomic Nervous System: anorexia, flushing, increased salivation, urinary retention.
Cardiovascular: cardiac failure, hypertension, palpitation, tachycardia.
Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems: abnormal coordination, ataxia, confusion, dysphonia, hyperesthesia, hyperkinesia, hypertonia, hypoesthesia, leg cramps, migraine, myelitis, paralysis, paresthesia, ptosis, syncope, tremor, twitching, vertigo, visual field defect.
Gastrointestinal: abnormal hepatic function, aggravated tooth caries, constipation, dyspepsia, eructation, flatulence, gastritis, hemorrhoids, increased appetite, melena, rectal hemorrhage, stomatitis including ulcerative stomatitis, tongue discoloration, tongue edema.
Genitourinary: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, micturition frequency, polyuria, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection.
Hearing and Vestibular: deafness, earache, ototoxicity, tinnitus.
Metabolic/Nutritional: dehydration, diabetes mellitus, thirst.
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, arthritis, arthrosis, muscle weakness, myalgia.
Psychiatric: abnormal thinking, agitation, amnesia, anxiety, decreased libido, depersonalization, depression, emotional lability, euphoria, impaired concentration, insomnia, nervousness, paroniria, sleep disorder.
Respiratory System: bronchitis, dyspnea, hyperventilation, increased sputum, pneumonia, respiratory disorder, rhinitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection.
Reproductive: dysmenorrhea, female breast pain, intermenstrual bleeding, leukorrhea, menorrhagia, vaginitis.
Reticuloendothelial: lymphadenopathy.
Skin: acne, alopecia, angioedema, bullous eruption, dermatitis, dry skin, eczema, erythematous rash, furunculosis, hyperkeratosis, hypertrichosis, increased sweating, maculopapular rash, photosensitivity reaction, photosensitivity toxic reaction, pruritus, purpura, rash, seborrhea, skin disorder, skin nodule, urticaria.
Special Senses: parosmia, taste loss, taste perversion.
Vision: blindness, conjunctivitis, eye pain, glaucoma, loss of accommodation, ocular hemorrhage, xerophthalmia.
Body as a Whole: accidental injury, asthenia, back pain, chest pain, enlarged abdomen, face edema, fever, generalized edema, hot flashes, increased weight, leg edema, malaise, nasal polyp, pain, pallor, periorbital edema, peripheral edema, rigors.
Occasional instances of transient, reversible hepatic transaminase elevations have occurred during cetirizine therapy. Hepatitis with significant transaminase elevation and elevated bilirubin in association with the use of cetirizine has been reported.
In foreign marketing experience or experience in the post market period, the following additional rare, but potentially severe adverse events have been reported: anaphylaxis, cholestasis, glomerulonephritis, hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, orofacial dyskinesia, severe hypotension, stillbirth, thrombocytopenia, aggressive reaction and convulsions.
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride may cause mild CNS stimulation in hypersensitive patients.
Nervousness, excitability, restlessness, dizziness, weakness, or insomnia may occur. Headache, nausea, drowsiness, tachycardia, palpitation, pressor activity, and cardiac arrhythmias have been reported. Sympathomimetic drugs have also been associated with other untoward effects such as fear, anxiety, tenseness, tremor, hallucinations, seizures, pallor, respiratory difficulty, dysuria, and cardiovascular collapse.
ZYRTEC-D — cetirizine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride tablet, multilayer, extended release
Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc
———-
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR®
(cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and
pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg)
Extended Release Tablets
For Oral Use
DESCRIPTION
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR™ (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) Extended Release Tablets for oral administration contain 5 mg of cetirizine hydrochloride for immediate release and 120 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride for extended release in a bilayer tablet. Tablets also contain as inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose.
Cetirizine hydrochloride, one of the two active components of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets, is an orally active and selective H1-receptor antagonist. The chemical name is (+/−)- [2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl] ethoxy] acetic acid, dihydrochloride. Cetirizine hydrochloride is a racemic compound with an empirical formula of C21H25ClN2O3•2HCl. The molecular weight is 461.82. Cetirizine hydrochloride is a white, crystalline powder and is water-soluble. The chemical structure is shown below:
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, the other active ingredient of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets, is an adrenergic (vasoconstrictor) agent with the chemical name (1S.2S)-2-methylamino-1-phenyl-1-propanol hydrochloride. The molecular weight is 201.70. The molecular formula is C10H15NO•HCl. Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride occurs as fine, white to off-white crystals or powder, having a faint characteristic odor. It is very soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, and sparingly soluble in chloroform. The chemical structure is shown below:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanisms of Action
Cetirizine, a metabolite of hydroxyzine, is an antihistamine; its principal effects are mediated via selective inhibition of H1 receptors. The antihistaminic activity of cetirizine has been clearly documented in a variety of animal and human models. In vivo and Ex vivo animal models have shown negligible anticholinergic and antiserotonergic activity. In clinical trials, however, dry mouth was more common with cetirizine than with placebo. In vitro receptor binding studies have shown no measurable affinity for other than H1 receptors. Autoradiographic studies with radiolabeled cetirizine in the rat have shown negligible penetration into the brain. Ex vivo experiments in the mouse have shown that systemically administered cetirizine does not significantly occupy cerebral H1 receptors.
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is an orally active sympathomimetic amine and exerts a decongestant action on the nasal mucosa. Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is recognized as an effective agent for the relief of nasal congestion due to allergic rhinitis. Pseudoephedrine produces peripheral effects similar to those of ephedrine and central effects similar to, but less intense than, amphetamines. It has the potential for excitatory side effects.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The bioavailability of cetirizine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride from ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets is not significantly different from that achieved with separate administration of a cetirizine 5 mg tablet and a pseudoephedrine 120 mg extended release caplet. Co-administration of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine does not significantly affect the bioavailability of either component.
Following a single dose of the ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablet, a mean peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 114 ng/mL at a time (Tmax) of 2.2 hours postdose was observed for cetirizine and a mean Cmax of 309 ng/mL at a Tmax of 4.4 hours postdose was observed for pseudoephedrine.
When healthy volunteers were administered multiple doses of the ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablet to reach steady-state concentrations (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg twice daily for seven days), a mean Cmax of 178 ng/mL was observed for cetirizine and 526 ng/mL for pseudoephedrine.
Food had no significant effect on the extent of cetirizine absorption (AUC), but Tmax was delayed by 1.8 hours and Cmax was decreased by 30%. Food had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of pseudoephedrine. ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets may be given with or without food (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Distribution
The mean plasma protein binding of cetirizine is 93%, independent of concentration in the range of 25–1000 ng/mL, which includes the therapeutic plasma levels observed. The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of pseudoephedrine has been reported to be 2.6–3.3 L/kg. No plasma protein binding data in humans are available.
Metabolism
A human mass balance study of cetirizine in 6 healthy male volunteers indicated that 70% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine and 10% in the feces. Approximately 50% of the radioactivity was identified in the urine as unchanged drug. Most of the rapid increase in peak plasma radioactivity was associated with parent drug, suggesting low first pass metabolism. Cetirizine is metabolized to a limited extent by oxidative O-dealkylation to a metabolite with negligible antihistaminic activity. The enzyme or enzymes responsible for this metabolism have not been identified.
One to seven percent of the pseudoephedrine dose appeared to be metabolized to norpseudoephedrine by N-demethylation after a single dose.
Elimination
After administration of the ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablet, the mean elimination half-life of cetirizine was 7.9 hours and the mean elimination half-life of pseudoephedrine was 6.0 hours.
It was reported that 0.4–0.7% of the pseudoephedrine dose was estimated to be excreted in the breast milk over 24 hours after a single dose. The pattern of the relative milk/plasma drug concentration profile showed that pseudoephedrine concentrations in milk were 2- to 3-fold higher than those in plasma.
Drug Interactions
Pharmacokinetic interaction trials with cetirizine in adults were conducted with pseudoephedrine, antipyrine, ketoconazole, erythromycin and azithromycin. No interactions were observed. In a multiple dose study of theophylline (400 mg once daily for 3 days) and cetirizine (20 mg once daily for 3 days), a 16% decrease in the clearance of cetirizine was observed. The disposition of theophylline was not altered by concomitant cetirizine administration.
Special Populations
Pediatrics
Although cetirizine pharmacokinetics have been studied in children, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets contain 120 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, which exceeds the recommended dose for patients less than 12 years of age. Therefore, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are not recommended for patients under 12 years of age.
Geriatrics
Following a single, 10-mg oral dose of cetirizine, the elimination half-life was prolonged by 50% and the apparent total body clearance was 40% lower in 16 geriatric subjects with a mean age of 77 years compared to 14 adult subjects with a mean age of 53 years. The decrease in cetirizine clearance in these elderly volunteers may be related to decreased renal function.
The pharmacokinetics of pseudoephedrine has not been adequately studied in geriatric subjects.
Gender
The effect of gender on cetirizine or pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics has not been adequately studied.
Race
The effect of race on cetirizine or pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics has not been adequately studied.
Renal Impairment
The kinetics of cetirizine were studied following multiple, oral, 10-mg daily doses of cetirizine for 7 days in 7 normal volunteers (creatinine clearance 89–128 mL/min), 8 patients with mild renal function impairment (creatinine clearance 42–77 mL/min) and 7 patients with moderate renal function impairment (creatinine clearance 11–31 mL/min). The pharmacokinetics of cetirizine were similar in patients with mild impairment and normal volunteers. Moderately impaired patients had a 3-fold increase in half-life and a 70% decrease in clearance compared to normal volunteers.
Patients on hemodialysis (n=5) given a single, 10-mg dose of cetirizine had a 3-fold increase in half life and a 70% decrease in clearance compared to normal volunteers. Less than 10% of the administered dose was removed during the single dialysis session.
About 55–75% of an administered dose of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is excreted unchanged in the urine; the remainder is apparently metabolized in the liver. Therefore, pseudoephedrine may accumulate in patients with renal insufficiency.
Dosing adjustment is necessary in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment and in patients on dialysis (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Hepatic Impairment
Sixteen patients with chronic liver diseases (hepatocellular, cholestatic, and biliary cirrhosis), given 10 or 20 mg of cetirizine as a single, oral dose had a 50% increase in half-life along with a corresponding 40% decrease in clearance compared to 16 healthy subjects.
The effect of hepatic impairment on pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Dosing adjustment may be necessary in patients with hepatic impairment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Pharmacodynamics
Trials in 69 adult normal volunteers (aged 20–61 years) showed that cetirizine at doses of 5 and 10 mg inhibited the skin wheal and flare caused by the intradermal injection of histamine. The onset of this activity after a single 10-mg dose occurred within 20 minutes in 50% of subjects and within one hour in 95% of subjects; this activity persisted for at least 24 hours. The effects of intradermal injection of various other mediators or histamine releasers were also inhibited by cetirizine. In mildly asthmatic subjects, cetirizine at 5 to 20 mg blocked bronchoconstriction due to nebulized histamine, with virtually total blockade after a 20 mg dose. In trials conducted for up to 12 hours following cutaneous antigen challenge, the late phase recruitment of eosinophils, neutrophils and basophils, components of the allergic inflammatory response, was inhibited by cetirizine at a dose of 20 mg. The clinical significance of these findings is not known.
In four clinical trials in healthy adult males, no clinically significant mean increases in QTc were observed in cetirizine treated subjects. In the first study, a placebo-controlled crossover trial, cetirizine was given at doses up to 60 mg per day, 6 times the maximum clinical dose, for 1 week, and no significant mean QTc prolongation occurred. In the second study, a crossover trial, cetirizine 20 mg and erythromycin (500 mg every 8 hours) were given alone and in combination. There was no significant effect on QTc with the combination or with cetirizine alone. In the third trial, also a crossover study, cetirizine 20 mg and ketoconazole (400 mg per day) were given alone and in combination. Cetirizine caused a mean increase in QTc of 9.1 msec from baseline after 10 days of therapy. Ketoconazole also increased QTc by 8.3 msec. The combination caused an increase of 17.4 msec, equal to the sum of the individual effects. Thus, there was no significant drug interaction on QTc with the combination of cetirizine and ketoconazole. In the fourth study, a placebo-controlled parallel trial, cetirizine 20 mg was given alone or in combination with azithromycin (500 mg as a single dose on the first day followed by 250 mg once daily). There was no significant increase in QTc with cetirizine 20 mg alone or in combination with azithromycin.
In a six-week, placebo-controlled study of 186 patients (aged 12–64 years) with allergic rhinitis and mild to moderate asthma, cetirizine 10 mg once daily improved rhinitis symptoms and did not alter pulmonary function. This study supports the safety of administering cetirizine to allergic rhinitis patients with mild to moderate asthma.
Clinical Trials
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets
Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials (n=1094 and n=1000) comparing ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) to active control and placebo for two weeks in patients 12 years and older with seasonal allergic rhinitis were conducted in the United States. In the two trials, 390 patients were aged 12 to 17 years. The primary efficacy measure in both trials was the mean change from baseline in the subject-rated Total Symptom Severity Complex (TSSC) score, which included the following symptoms: sneezing, runny nose, itchy nose, itchy eyes, watery eyes, postnasal drip, and nasal congestion. In both trials patients who received ZYRTEC-D showed a significant reduction in the TSSC score compared to those who received placebo.
Zyrtec Tablets
Nine multicenter, randomized, double-blind, clinical trials comparing cetirizine 5 to 20 mg to placebo in patients 12 years and older with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis were conducted in the United States. Five of these showed significant reductions in symptoms of allergic rhinitis, 3 in seasonal allergic rhinitis (1 to 4 weeks in duration) and 2 in perennial allergic rhinitis for up to 8 weeks in duration. In general, the 10 mg dose was more effective than the 5 mg dose and the 20 mg dose gave no added effect. Some of these trials included pediatric patients aged 12 to 16 years.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets should be administered when both the antihistaminic properties of cetirizine hydrochloride and the nasal decongestant properties of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride are desired.
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are indicated for the relief of nasal and non-nasal symptoms associated with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and children 12 years of age and older.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients or to hydroxyzine.
Due to its pseudoephedrine component, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma or urinary retention, and in patients receiving monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor therapy or within fourteen (14) days of stopping such treatment (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions section). It is also contraindicated in patients with severe hypertension, or severe coronary artery disease, and in those who have shown hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to its components, to adrenergic agents, or to other drugs of similar chemical structures. Manifestations of patient idiosyncrasy to adrenergic agents include insomnia, dizziness, weakness, tremor, or arrhythmias.
WARNINGS
Sympathomimetic amines should be used judiciously and sparingly in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic heart disease, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, renal impairment, or prostatic hypertrophy (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Sympathomimetic amines may produce central nervous system stimulation with convulsions or cardiovascular collapse with accompanying hypotension. The elderly are more likely to have adverse reactions to sympathomimetic amines.
PRECAUTIONS
Due to its pseudoephedrine component, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic heart disease, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, renal impairment, or prostatic hypertrophy (see WARNINGS and CONTRAINDICATIONS). Patients with decreased renal function should be given a lower initial dose (one tablet per day) because they have reduced elimination of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
In clinical trials, the occurrence of somnolence has been reported in some patients taking cetirizine or ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets; due caution should therefore be exercised when driving a car or operating potentially dangerous machinery after taking ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets. Concurrent use of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets with alcohol or other CNS depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of CNS performance may occur.
Drug Interactions
Cetirizine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride do not influence the pharmacokinetics of each other when administered concomitantly.
No clinically significant drug interactions have been found with cetirizine and theophylline at a low dose, azithromycin, ketoconazole, or erythromycin. There was a small decrease in the clearance of cetirizine caused by a 400 mg dose of theophylline; it is possible that larger theophylline doses could have a greater effect.
Due to the pseudoephedrine component, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients taking monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors and for 14 days after stopping use of an MAO inhibitor. Concomitant use with antihypertensive drugs that interfere with sympathetic activity (e.g., methyldopa, mecamylamine, and reserpine) may reduce their antihypertensive effects. Increased ectopic pacemaker activity can occur when pseudoephedrine is used concomitantly with digitalis. Care should be taken in the administration of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets concomitantly with other sympathomimetic amines because combined effects on the cardiovascular system may be harmful to the patient (see WARNINGS).
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
There are no carcinogenicity trials of pseudoephedrine and cetirizine in combination.
Cetirizine
In a 2-year study in rats, cetirizine was not carcinogenic at dietary doses up to 20 mg/kg (approximately 15 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). In a 2-year study in mice, cetirizine caused an increased incidence of benign liver tumors in males at a dietary dose of 16 mg/kg (approximately 6 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). No increase in the incidence of liver tumors was observed in mice at a dietary dose of 4 mg/kg (approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). The clinical significance of these findings during long-term use of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets is not known.
Pseudoephedrine
Two-year studies in rats and mice conducted under the auspices of the National Toxicology Program (NTP) demonstrated no evidence of carcinogenic potential with ephedrine sulfate, a structurally related drug with pharmacological properties similar to pseudoephedrine, at dietary doses up to 10 and 27 mg/kg, respectively (approximately 1/3 and 1/2, respectively, the maximum recommended daily dose of pseudoephedrine in adults on a mg/m2 basis).
Cetirizine was not mutagenic in the Ames test or mouse lymphoma test and not clastogenic in the human lymphocyte assay or the in vivo rodent micronucleus test. Likewise, the combination of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine in a 1:24 ratio was not mutagenic or clastogenic in these tests. However, the Ames and mouse lymphoma assays did not strictly adhere to test standards.
In a reproductive toxicity study in rats, combination oral doses of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine up to 6/154 mg/kg (approximately 5 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis) had no effect on fertility.
Pregnancy Category C
In rats, the combination of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine caused developmental toxicity when administered orally at 6/154 mg/kg (approximately 5 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). When rats were dosed throughout pregnancy with oral doses of cetirizine/pseudoephedrine, 6/154 mg/kg increased the number of fetal skeletal malformations (rib distortions) and variants (unossified sternebrae). When dosing was continued through lactation, 6/154 mg/kg also decreased the viability and weight gain of offspring. These effects were not observed at 1.6/38 mg/kg (approximately equivalent to the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). No embryofetal toxicity was observed when rabbits were dosed throughout organogenesis with oral doses of cetirizine/pseudoephedrine of up to 6/154 mg/kg (approximately 10 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). Because there are no adequate and well-controlled trials in pregnant women, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
In rats the combination of cetirizine/pseudoephedrine decreased the viability and weight gain of offspring when administered orally to dams throughout pregnancy and lactation at 6/154 mg/kg (approximately 5 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). This effect was not observed at 1.6/38 mg/kg (approximately equivalent to the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). For cetirizine administered alone, studies in dogs indicate that approximately 3% of the dose is excreted in milk, and cetirizine has been reported to be excreted in human breast milk. For pseudoephedrine administered alone, 0.4–0.7% of the dose has been reported to be excreted in human breast milk.
Because cetirizine and pseudoephedrine are excreted in milk, use of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets in nursing mothers is not recommended.
Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, although the elderly are more likely to have adverse reactions to sympathomimetic amines. In general, dosing in an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
The cetirizine and pseudoephedrine components of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Cetirizine
Of the total number of subjects in clinical trials of cetirizine alone, 186 were 65 years and over, while 39 were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. With regard to efficacy, clinical trials of cetirizine for each approved indication did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients.
Pediatric Use
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets contain 120 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride in an extended release formulation. This dose of pseudoephedrine exceeds the recommended dose for pediatric patients under 12 years of age. Therefore, clinical trials of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets have not been conducted in patients under 12 years of age.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets
In two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (n=2094) in which 701 patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis were treated with ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) twice daily for two weeks, the percent of patients who withdrew prematurely due to adverse events was 2.0% in the ZYRTEC-D group, compared with 1.1% in the placebo group. All adverse events that were reported by greater than 1% of patients in the ZYRTEC-D group are listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1. ADVERSE EXPERIENCES REPORTED IN PATIENTS AGED 12 YEARS AND OLDER IN SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS TRIALS OF ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR EXTENDED RELEASE TABLETS AT RATES OF 1% OR GREATER (PERCENT INCIDENCE)
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | ZYRTEC-D (n=701) |
PLACEBO (n=696) |
|---|---|---|
| Insomnia | 4.0 | 0.6 |
| Dry Mouth | 3.6 | 0.4 |
| Fatigue | 2.4 | 0.9 |
| Somnolence | 1.9 | 0.1 |
| Pharyngitis | 1.7 | 1.1 |
| Epistaxis | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| Accidental Injury | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| Dizziness | 1.1 | 0.1 |
| Sinusitis | 1.0 | 0.6 |
ZYRTEC Tablets
Controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of cetirizine conducted in the United States and Canada included more than 6000 patients aged 12 years and older, with more than 3900 receiving cetirizine at doses of 5 to 20 mg per day. The duration of treatment ranged from 1 week to 6 months, with a mean exposure of 30 days.
Most adverse reactions reported during therapy with cetirizine were mild or moderate. In placebo-controlled trials, the incidence of discontinuations due to adverse reactions in patients receiving cetirizine 5 mg or 10 mg was not significantly different from placebo (2.9% vs. 2.4%, respectively).
The most common adverse reaction in patients aged 12 years and older that occurred more frequently on cetirizine than placebo was somnolence. The incidence of somnolence associated with cetirizine was dose related, 6% in placebo, 11% at 5 mg and 14% at 10 mg. Discontinuations due to somnolence for cetirizine were uncommon (1.0% on cetirizine vs. 0.6% on placebo). Fatigue and dry mouth also appeared to be treatment-related adverse reactions. There were no differences by age, race, gender or by body weight with regard to the incidence of adverse reactions.
Table 2 lists adverse experiences in patients aged 12 years and older that were reported for cetirizine 5 and 10 mg in controlled clinical trials in the United States and were more common with cetirizine than placebo.
TABLE 2. ADVERSE EXPERIENCES REPORTED IN PATIENTS AGED 12 YEARS AND OLDER IN PLACEBO-CONTROLLED UNITED STATES CETIRIZINE TRIALS (MAXIMUM DOSE OF 10 MG) AT RATES OF 2% OR GREATER (PERCENT INCIDENCE)
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | CETIRIZINE (n=2034) |
PLACEBO (n=1612) |
|---|---|---|
| Somnolence | 13.7 | 6.3 |
| Fatigue | 5.9 | 2.6 |
| Dry Mouth | 5.0 | 2.3 |
| Pharyngitis | 2.0 | 1.9 |
| Dizziness | 2.0 | 1.2 |
In addition, headache and nausea occurred in more than 2% of the patients, but were more common in placebo patients.
The following events were observed infrequently (less than 2%), in 3982 adults and children 12 years and older or in 659 pediatric (6 to 11 years) patients who received cetirizine in U.S. trials, including an open study of six months duration. A causal relationship of these infrequent events with cetirizine administration has not been established.
Autonomic Nervous System: anorexia, flushing, increased salivation, urinary retention.
Cardiovascular: cardiac failure, hypertension, palpitation, tachycardia.
Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems: abnormal coordination, ataxia, confusion, dysphonia, hyperesthesia, hyperkinesia, hypertonia, hypoesthesia, leg cramps, migraine, myelitis, paralysis, paresthesia, ptosis, syncope, tremor, twitching, vertigo, visual field defect.
Gastrointestinal: abnormal hepatic function, aggravated tooth caries, constipation, dyspepsia, eructation, flatulence, gastritis, hemorrhoids, increased appetite, melena, rectal hemorrhage, stomatitis including ulcerative stomatitis, tongue discoloration, tongue edema.
Genitourinary: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, micturition frequency, polyuria, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection.
Hearing and Vestibular: deafness, earache, ototoxicity, tinnitus.
Metabolic/Nutritional: dehydration, diabetes mellitus, thirst.
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, arthritis, arthrosis, muscle weakness, myalgia.
Psychiatric: abnormal thinking, agitation, amnesia, anxiety, decreased libido, depersonalization, depression, emotional lability, euphoria, impaired concentration, insomnia, nervousness, paroniria, sleep disorder.
Respiratory System: bronchitis, dyspnea, hyperventilation, increased sputum, pneumonia, respiratory disorder, rhinitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection.
Reproductive: dysmenorrhea, female breast pain, intermenstrual bleeding, leukorrhea, menorrhagia, vaginitis.
Reticuloendothelial: lymphadenopathy.
Skin: acne, alopecia, angioedema, bullous eruption, dermatitis, dry skin, eczema, erythematous rash, furunculosis, hyperkeratosis, hypertrichosis, increased sweating, maculopapular rash, photosensitivity reaction, photosensitivity toxic reaction, pruritus, purpura, rash, seborrhea, skin disorder, skin nodule, urticaria.
Special Senses: parosmia, taste loss, taste perversion.
Vision: blindness, conjunctivitis, eye pain, glaucoma, loss of accommodation, ocular hemorrhage, xerophthalmia.
Body as a Whole: accidental injury, asthenia, back pain, chest pain, enlarged abdomen, face edema, fever, generalized edema, hot flashes, increased weight, leg edema, malaise, nasal polyp, pain, pallor, periorbital edema, peripheral edema, rigors.
Occasional instances of transient, reversible hepatic transaminase elevations have occurred during cetirizine therapy. Hepatitis with significant transaminase elevation and elevated bilirubin in association with the use of cetirizine has been reported.
In foreign marketing experience or experience in the post market period, the following additional rare, but potentially severe adverse events have been reported: anaphylaxis, cholestasis, glomerulonephritis, hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, orofacial dyskinesia, severe hypotension, stillbirth, thrombocytopenia, aggressive reaction and convulsions.
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride may cause mild CNS stimulation in hypersensitive patients. Nervousness, excitability, restlessness, dizziness, weakness, or insomnia may occur. Headache, nausea, drowsiness, tachycardia, palpitation, pressor activity, and cardiac arrhythmias have been reported. Sympathomimetic drugs have also been associated with other untoward effects such as fear, anxiety, tenseness, tremor, hallucinations, seizures, pallor, respiratory difficulty, dysuria, and cardiovascular collapse.
OVERDOSAGE
Information regarding acute overdosage is limited to experience with cetirizine alone and the marketing history of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride.
Overdosage has been reported with cetirizine. In one adult patient who took 150 mg of cetirizine, the patient was somnolent but did not display any other clinical signs or abnormal blood chemistry or hematology results. In an 18-month-old pediatric patient who took an overdose of cetirizine (approximately 180 mg), restlessness and irritability were observed initially; this was followed by drowsiness. Should overdose occur, treatment should be symptomatic or supportive, taking into account any concomitantly ingested medications. There is no known specific antidote to cetirizine. Cetirizine is not effectively removed by dialysis, and dialysis will be ineffective unless a dialyzable agent has been concomitantly ingested. The acute minimal lethal oral doses in mice and rats were 237 and 562 mg/kg, respectively (approximately 95 and 460 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). In rodents, the target of acute toxicity was the central nervous system, and the target of multiple-dose toxicity was the liver.
In large doses, sympathomimetics may give rise to giddiness, headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, thirst, tachycardia, precordial pain, palpitations, difficulty in micturition, muscular weakness and tenseness, anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Many patients can present a toxic psychosis with delusions and hallucinations. Some may develop cardiac arrhythmias, circulatory collapse, convulsions, coma and respiratory failure.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults and Children 12 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dose of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets is one tablet twice daily for adults and children 12 years of age and older. ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets may be given with or without food.
Dose Adjustment for Renal and Hepatic Impairment
In patients with decreased renal function (creatinine clearance 11–31 mL/min), patients on hemodialysis (creatinine clearance less than 7 mL/min), and in hepatically impaired patients, a dose of one tablet once daily is recommended (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS).
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets should be swallowed whole, and should not be broken or chewed.
HOW SUPPLIED
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are white, round, biconvex, bilayer tablets containing 5 mg cetirizine hydrochloride in an immediate release layer and 120 mg pseudoephedrine hydrochloride in an extended release layer. ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are supplied in high-density polyethylene bottles of 100 tablets fitted with polypropylene child-resistant closures (NDC 0069-1630-66).
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are engraved with ZYRTEC-D on one side.
STORAGE
Store at 20–25°C (68–77°F); excursions permitted to 15–30°C (59–86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]
Rx only
Cetirizine is licensed from UCB Pharma, Inc.
LAB-0038-5.0
Циррус (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин) Таблетки
В двух двойных слепых, плацебо-контролируемые испытания (n = 2094) у которых 701 пациент с сезонным аллергическим ринитом лечился циррусом (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин) Таблетки (цетиризин гидрохлорид 5 мг и псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид 120 мг) два раза в день в течение двух недель, процент пациентов, которые вышли преждевременно из-за нежелательных явлений, составил 2,0% в Cirrus (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин) группа, по сравнению с 1,1% в группе плацебо. Все побочные эффекты, о которых сообщалось более чем 1% пациентов в группе Cirrus (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин), перечислены в таблице 1.
ТАБЛИЦА 1. КРАТКОВЫЕ ОПЫТЫ, ОТЧЕТНЫЕ У ПАЦИЕНТОВ, НАМЕРЕННЫХ 12 ЛЕТ И СТАРЫХ В СЕЗОННЫХ АЛЛЕРГИЧЕСКИХ РИНИТИКАХ ТРААЛОВ Cirrus (цетиризин, псевдоэфедрин) ТАБЛЕТКИ С ЦЕНАМИ 1% ИЛИ БОЛЬШОЙ (ПЕРЦЕНТНАЯ ИНЦИДЕНЦИЯ)
| РЕКЛАМНЫЙ ОПЫТ | Cirrus | PLACEBO |
| (n = 701) | (n = 696) | |
| Бессонница | 4,0 | 0,6 |
| Сухой рот | 3,6 | 0,4 |
| Усталость | 2.4 | 0,9 |
| Сонливость | 1,9 | 0,1 |
| Фарингит | 1,7 | 1.1 |
| Носовое кровотечение | 1.1 | 0,9 |
| Случайное повреждение | 1.1 | 0,4 |
| Головокружение | 1.1 | 0,1 |
| Синусит | 1,0 | 0,6 |
Таблетки ZYRTEC
Контролируемые и неконтролируемые клинические испытания цетиризина, проведенные в Соединенных Штатах и Канаде, включали более 6000 пациентов в возрасте 12 лет и старше, причем более 3900 получали цетиризин в дозах от 5 до 20 мг в день. Продолжительность лечения варьировалась от 1 недели до 6 месяцев со средним воздействием 30 дней.
Большинство побочных реакций, о которых сообщалось во время терапии цетиризином, были легкими или умеренными. В плацебо-контролируемых исследованиях частота прерываний из-за побочных реакций у пациентов, получавших цетиризин 5 или 10 мг, существенно не отличалась от плацебо (2,9% против. 2,4% соответственно).
Наиболее распространенной побочной реакцией у пациентов в возрасте 12 лет и старше, которая чаще встречалась на цетиризине, чем плацебо, была сонливость. Частота сонливости, связанной с цетиризином, была связана с дозой, 6% в плацебо, 11% в 5 мг и 14% в 10 мг. Прекращение лечения цетиризином было необычным (1,0% на цетиризин против. 0,6% на плацебо). Усталость и сухость во рту также, по-видимому, связаны с лечением побочными реакциями. Не было различий по возрасту, расе, полу или массе тела в отношении частоты побочных реакций.
В таблице 2 перечислены неблагоприятные события у пациентов в возрасте 12 лет и старше, которые были зарегистрированы для цетиризина 5 и 10 мг в контролируемых клинических испытаниях в Соединенных Штатах и были более распространены с цетиризином, чем плацебо.
ТАБЛИЦА 2. КРАТКОВЫЕ ОПЫТЫ, ОТЧЕТНЫЕ У ПАЦИЕНТОВ, НАМЕРЕННЫХ 12 ЛЕТ И СТАРЫХ В ПЛАЦЕБО-КОНТРОЛИРОВАННЫХ ИСКУССТВЕННЫХ СТОРОНАХ ЦЕТИРИЗИНА (МАКСИМАЛЬНАЯ ДОЗА 10 МГ) СКОРОСТЬЮ 2% ИЛИ БОЛЬШОЙ (ПЕРЦЕНТНАЯ ИНЦИДЕНЦИЯ)
| РЕКЛАМНЫЙ ОПЫТ | ЦЕТИРИЗИН | PLACEBO |
| (П = 2034) | (П = 1612) | |
| Сонливость | 13,7 | 6.3 |
| Усталость | 5,9 | 2,6 |
| Сухой рот | 5,0 | 2,3 |
| Фарингит | 2,0 | 1,9 |
| Головокружение | 2,0 | 1.2 |
Кроме того, головная боль и тошнота возникали более чем у 2% пациентов, но чаще встречались у пациентов с плацебо.
Следующие события наблюдались нечасто (менее 2%) у 3982 взрослых и детей в возрасте 12 лет и старше или у 659 пациентов (от 6 до 11 лет), получавших цетиризин в исследованиях в США, включая открытое исследование продолжительностью шесть месяцев. Причинная связь этих нечастых событий с введением цетиризина не установлена.
Автономная нервная система: анорексия, приливы крови, повышенное слюноотделение, задержка мочи.
Сердечно-сосудистые: сердечная недостаточность, гипертония, сердцебиение, тахикардия.
Центральные и периферические нервные системы: ненормальная координация, атаксия, спутанность сознания, дисфония, гиперестезия, гиперкинезия, гипертония, гипестезия, судороги ног, мигрень, миелит, паралич, парестезия, птоз, обморок, тремор, подергивание, головокружение, дефект поля зрения.
Желудочно-кишечный тракт: нарушение функции печени, обострение кариеса зубов, запор, диспепсия, отрыжка, метеоризм, гастрит, геморрой, повышение аппетита, мелена, ректальное кровоизлияние, стоматит, включая язвенный стоматит, изменение цвета языка, отек языка.
Генитуринарный: цистит, дизурия, гематурия, частота мочеиспускания, полиурия, недержание мочи, инфекция мочевыводящих путей.
Слух и вестибуляр: глухота, боль в ухе, ототоксичность, шум в ушах.
Метаболический / Питательный: обезвоживание, сахарный диабет, жажда.
Скелетно-мышечная система: артралгия, артрит, артроз, мышечная слабость, миалгия.
Психиатрический : ненормальное мышление, возбуждение, амнезия, беспокойство, снижение либидо, деперсонализация, депрессия, эмоциональная лабильность, эйфория, нарушение концентрации, бессонница, нервозность, паронирия, расстройство сна.
Дыхательная система: бронхит, одышка, гипервентиляция, увеличение мокроты, пневмония, респираторные заболевания, ринит, синусит, инфекции верхних дыхательных путей.
Репродуктивный: дисменорея, боль в груди у женщин, межменструальное кровотечение, лейкорея, меноррагия, вагинит.
Ретикулоэндотелиальный : лимфаденопатия.
Кожа: прыщи, алопеция, ангионевротический отек, буллезная сыпь, дерматит, сухость кожи, экзема, эритематозная сыпь, фурункулез, гиперкератоз, гипертрихоз, повышенное потоотделение, макулопапулезная сыпь, реакция светочувствительности, токсическая реакция светочувствительности, зуд, пурпура, сыпь, себорея, кожные узлы, крапивница.
Особые чувства: парозмия, потеря вкуса, извращение вкуса.
Видение: слепота, конъюнктивит, боль в глазах, глаукома, потеря приспособления, глазное кровоизлияние, ксерофтальмия.
Тело как целое : случайная травма, астения, боль в спине, боль в груди, увеличение живота, отек лица, лихорадка, генерализованный отек, приливы, увеличение веса, отек ног, недомогание, полип носа, боль, бледность, периорбитальный отек, периферические отеки, суровость.
Случайные случаи преходящего, обратимого повышения печеночной трансаминазы имели место во время терапии цетиризином. Сообщалось о гепатите со значительным повышением уровня трансаминаз и повышенным содержанием билирубина в сочетании с применением цетиризина.
В опыте зарубежного маркетинга или опыте в пострыночный период были зарегистрированы следующие дополнительные редкие, но потенциально тяжелые побочные эффекты: анафилаксия, холестаз, гломерулонефрит, гемолитическая анемия, гепатит, орофациальная дискинезия, тяжелая гипотензия, мертворождение, тромбоцитопения, агрессивная реакция и судороги.
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид
Гидрохлорид псевдоэфедрина может вызывать умеренную стимуляцию ЦНС у гиперчувствительных пациентов.
Может возникнуть нервозность, возбудимость, беспокойство, головокружение, слабость или бессонница. Сообщалось о головной боли, тошноте, сонливости, тахикардии, сердцебиении, прессорной активности и сердечных аритмиях. Симпатомиметические препараты также связаны с другими неблагоприятными эффектами, такими как страх, беспокойство, напряжение, тремор, галлюцинации, судороги, бледность, затрудненное дыхание, дизурия и сердечно-сосудистый коллапс.
Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) Tablets
In two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (n = 2094) in which 701 patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis were treated with Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) Tablets (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) twice daily for two weeks, the percent of patients who withdrew prematurely due to adverse events was 2.0% in the Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) group, compared with 1.1% in the placebo group. All adverse events that were reported by greater than 1% of patients in the Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) group are listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1. ADVERSE EXPERIENCES REPORTED IN PATIENTS AGED 12 YEARS AND OLDER IN SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS TRIALS OF Cirrus (cetirizine, pseudoephedrine) TABLETS AT RATES OF 1% OR GREATER (PERCENT INCIDENCE)
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | Cirrus | PLACEBO |
| (n = 701) | (n = 696) | |
| Insomnia | 4.0 | 0.6 |
| Dry Mouth | 3.6 | 0.4 |
| Fatigue | 2.4 | 0.9 |
| Somnolence | 1.9 | 0.1 |
| Pharyngitis | 1.7 | 1.1 |
| Epistaxis | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| Accidental Injury | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| Dizziness | 1.1 | 0.1 |
| Sinusitis | 1.0 | 0.6 |
ZYRTEC Tablets
Controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of cetirizine conducted in the United States and Canada included more than 6000 patients aged 12 years and older, with more than 3900 receiving cetirizine at doses of 5 to 20 mg per day. The duration of treatment ranged from 1 week to 6 months, with a mean exposure of 30 days.
Most adverse reactions reported during therapy with cetirizine were mild or moderate. In placebo-controlled trials, the incidence of discontinuations due to adverse reactions in patients receiving cetirizine 5 mg or 10 mg was not significantly different from placebo (2.9% vs. 2.4%, respectively).
The most common adverse reaction in patients aged 12 years and older that occurred more frequently on cetirizine than placebo was somnolence. The incidence of somnolence associated with cetirizine was dose related, 6% in placebo, 11% at 5 mg and 14% at 10 mg. Discontinuations due to somnolence for cetirizine were uncommon (1.0% on cetirizine vs. 0.6% on placebo). Fatigue and dry mouth also appeared to be treatment-related adverse reactions. There were no differences by age, race, gender or by body weight with regard to the incidence of adverse reactions.
Table 2 lists adverse experiences in patients aged 12 years and older that were reported for cetirizine 5 and 10 mg in controlled clinical trials in the United States and were more common with cetirizine than placebo.
TABLE 2. ADVERSE EXPERIENCES REPORTED IN PATIENTS AGED 12 YEARS AND OLDER IN PLACEBO-CONTROLLED UNITED STATES CETIRIZINE TRIALS (MAXIMUM DOSE OF 10 MG) AT RATES OF 2% OR GREATER (PERCENT INCIDENCE)
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | CETIRIZINE | PLACEBO |
| (n=2034) | (n=1612) | |
| Somnolence | 13.7 | 6.3 |
| Fatigue | 5.9 | 2.6 |
| Dry Mouth | 5.0 | 2.3 |
| Pharyngitis | 2.0 | 1.9 |
| Dizziness | 2.0 | 1.2 |
In addition, headache and nausea occurred in more than 2% of the patients, but were more common in placebo patients.
The following events were observed infrequently (less than 2%), in 3982 adults and children 12 years and older or in 659 pediatric (6 to 11 years) patients who received cetirizine in U.S. trials, including an open study of six months duration. A causal relationship of these infrequent events with cetirizine administration has not been established.
Autonomic Nervous System: anorexia, flushing, increased salivation, urinary retention.
Cardiovascular: cardiac failure, hypertension, palpitation, tachycardia.
Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems: abnormal coordination, ataxia, confusion, dysphonia, hyperesthesia, hyperkinesia, hypertonia, hypoesthesia, leg cramps, migraine, myelitis, paralysis, paresthesia, ptosis, syncope, tremor, twitching, vertigo, visual field defect.
Gastrointestinal: abnormal hepatic function, aggravated tooth caries, constipation, dyspepsia, eructation, flatulence, gastritis, hemorrhoids, increased appetite, melena, rectal hemorrhage, stomatitis including ulcerative stomatitis, tongue discoloration, tongue edema.
Genitourinary: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, micturition frequency, polyuria, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection.
Hearing and Vestibular: deafness, earache, ototoxicity, tinnitus.
Metabolic/Nutritional: dehydration, diabetes mellitus, thirst.
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, arthritis, arthrosis, muscle weakness, myalgia.
Psychiatric: abnormal thinking, agitation, amnesia, anxiety, decreased libido, depersonalization, depression, emotional lability, euphoria, impaired concentration, insomnia, nervousness, paroniria, sleep disorder.
Respiratory System: bronchitis, dyspnea, hyperventilation, increased sputum, pneumonia, respiratory disorder, rhinitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection.
Reproductive: dysmenorrhea, female breast pain, intermenstrual bleeding, leukorrhea, menorrhagia, vaginitis.
Reticuloendothelial: lymphadenopathy.
Skin: acne, alopecia, angioedema, bullous eruption, dermatitis, dry skin, eczema, erythematous rash, furunculosis, hyperkeratosis, hypertrichosis, increased sweating, maculopapular rash, photosensitivity reaction, photosensitivity toxic reaction, pruritus, purpura, rash, seborrhea, skin disorder, skin nodule, urticaria.
Special Senses: parosmia, taste loss, taste perversion.
Vision: blindness, conjunctivitis, eye pain, glaucoma, loss of accommodation, ocular hemorrhage, xerophthalmia.
Body as a Whole: accidental injury, asthenia, back pain, chest pain, enlarged abdomen, face edema, fever, generalized edema, hot flashes, increased weight, leg edema, malaise, nasal polyp, pain, pallor, periorbital edema, peripheral edema, rigors.
Occasional instances of transient, reversible hepatic transaminase elevations have occurred during cetirizine therapy. Hepatitis with significant transaminase elevation and elevated bilirubin in association with the use of cetirizine has been reported.
In foreign marketing experience or experience in the post market period, the following additional rare, but potentially severe adverse events have been reported: anaphylaxis, cholestasis, glomerulonephritis, hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, orofacial dyskinesia, severe hypotension, stillbirth, thrombocytopenia, aggressive reaction and convulsions.
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride may cause mild CNS stimulation in hypersensitive patients.
Nervousness, excitability, restlessness, dizziness, weakness, or insomnia may occur. Headache, nausea, drowsiness, tachycardia, palpitation, pressor activity, and cardiac arrhythmias have been reported. Sympathomimetic drugs have also been associated with other untoward effects such as fear, anxiety, tenseness, tremor, hallucinations, seizures, pallor, respiratory difficulty, dysuria, and cardiovascular collapse.
ZYRTEC-D — cetirizine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride tablet, multilayer, extended release
Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc
———-
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR®
(cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and
pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg)
Extended Release Tablets
For Oral Use
DESCRIPTION
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR™ (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) Extended Release Tablets for oral administration contain 5 mg of cetirizine hydrochloride for immediate release and 120 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride for extended release in a bilayer tablet. Tablets also contain as inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose.
Cetirizine hydrochloride, one of the two active components of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets, is an orally active and selective H1-receptor antagonist. The chemical name is (+/−)- [2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl] ethoxy] acetic acid, dihydrochloride. Cetirizine hydrochloride is a racemic compound with an empirical formula of C21H25ClN2O3•2HCl. The molecular weight is 461.82. Cetirizine hydrochloride is a white, crystalline powder and is water-soluble. The chemical structure is shown below:
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, the other active ingredient of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets, is an adrenergic (vasoconstrictor) agent with the chemical name (1S.2S)-2-methylamino-1-phenyl-1-propanol hydrochloride. The molecular weight is 201.70. The molecular formula is C10H15NO•HCl. Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride occurs as fine, white to off-white crystals or powder, having a faint characteristic odor. It is very soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, and sparingly soluble in chloroform. The chemical structure is shown below:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanisms of Action
Cetirizine, a metabolite of hydroxyzine, is an antihistamine; its principal effects are mediated via selective inhibition of H1 receptors. The antihistaminic activity of cetirizine has been clearly documented in a variety of animal and human models. In vivo and Ex vivo animal models have shown negligible anticholinergic and antiserotonergic activity. In clinical trials, however, dry mouth was more common with cetirizine than with placebo. In vitro receptor binding studies have shown no measurable affinity for other than H1 receptors. Autoradiographic studies with radiolabeled cetirizine in the rat have shown negligible penetration into the brain. Ex vivo experiments in the mouse have shown that systemically administered cetirizine does not significantly occupy cerebral H1 receptors.
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is an orally active sympathomimetic amine and exerts a decongestant action on the nasal mucosa. Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is recognized as an effective agent for the relief of nasal congestion due to allergic rhinitis. Pseudoephedrine produces peripheral effects similar to those of ephedrine and central effects similar to, but less intense than, amphetamines. It has the potential for excitatory side effects.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The bioavailability of cetirizine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride from ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets is not significantly different from that achieved with separate administration of a cetirizine 5 mg tablet and a pseudoephedrine 120 mg extended release caplet. Co-administration of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine does not significantly affect the bioavailability of either component.
Following a single dose of the ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablet, a mean peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 114 ng/mL at a time (Tmax) of 2.2 hours postdose was observed for cetirizine and a mean Cmax of 309 ng/mL at a Tmax of 4.4 hours postdose was observed for pseudoephedrine.
When healthy volunteers were administered multiple doses of the ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablet to reach steady-state concentrations (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg twice daily for seven days), a mean Cmax of 178 ng/mL was observed for cetirizine and 526 ng/mL for pseudoephedrine.
Food had no significant effect on the extent of cetirizine absorption (AUC), but Tmax was delayed by 1.8 hours and Cmax was decreased by 30%. Food had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of pseudoephedrine. ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets may be given with or without food (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Distribution
The mean plasma protein binding of cetirizine is 93%, independent of concentration in the range of 25–1000 ng/mL, which includes the therapeutic plasma levels observed. The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of pseudoephedrine has been reported to be 2.6–3.3 L/kg. No plasma protein binding data in humans are available.
Metabolism
A human mass balance study of cetirizine in 6 healthy male volunteers indicated that 70% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine and 10% in the feces. Approximately 50% of the radioactivity was identified in the urine as unchanged drug. Most of the rapid increase in peak plasma radioactivity was associated with parent drug, suggesting low first pass metabolism. Cetirizine is metabolized to a limited extent by oxidative O-dealkylation to a metabolite with negligible antihistaminic activity. The enzyme or enzymes responsible for this metabolism have not been identified.
One to seven percent of the pseudoephedrine dose appeared to be metabolized to norpseudoephedrine by N-demethylation after a single dose.
Elimination
After administration of the ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablet, the mean elimination half-life of cetirizine was 7.9 hours and the mean elimination half-life of pseudoephedrine was 6.0 hours.
It was reported that 0.4–0.7% of the pseudoephedrine dose was estimated to be excreted in the breast milk over 24 hours after a single dose. The pattern of the relative milk/plasma drug concentration profile showed that pseudoephedrine concentrations in milk were 2- to 3-fold higher than those in plasma.
Drug Interactions
Pharmacokinetic interaction trials with cetirizine in adults were conducted with pseudoephedrine, antipyrine, ketoconazole, erythromycin and azithromycin. No interactions were observed. In a multiple dose study of theophylline (400 mg once daily for 3 days) and cetirizine (20 mg once daily for 3 days), a 16% decrease in the clearance of cetirizine was observed. The disposition of theophylline was not altered by concomitant cetirizine administration.
Special Populations
Pediatrics
Although cetirizine pharmacokinetics have been studied in children, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets contain 120 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, which exceeds the recommended dose for patients less than 12 years of age. Therefore, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are not recommended for patients under 12 years of age.
Geriatrics
Following a single, 10-mg oral dose of cetirizine, the elimination half-life was prolonged by 50% and the apparent total body clearance was 40% lower in 16 geriatric subjects with a mean age of 77 years compared to 14 adult subjects with a mean age of 53 years. The decrease in cetirizine clearance in these elderly volunteers may be related to decreased renal function.
The pharmacokinetics of pseudoephedrine has not been adequately studied in geriatric subjects.
Gender
The effect of gender on cetirizine or pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics has not been adequately studied.
Race
The effect of race on cetirizine or pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics has not been adequately studied.
Renal Impairment
The kinetics of cetirizine were studied following multiple, oral, 10-mg daily doses of cetirizine for 7 days in 7 normal volunteers (creatinine clearance 89–128 mL/min), 8 patients with mild renal function impairment (creatinine clearance 42–77 mL/min) and 7 patients with moderate renal function impairment (creatinine clearance 11–31 mL/min). The pharmacokinetics of cetirizine were similar in patients with mild impairment and normal volunteers. Moderately impaired patients had a 3-fold increase in half-life and a 70% decrease in clearance compared to normal volunteers.
Patients on hemodialysis (n=5) given a single, 10-mg dose of cetirizine had a 3-fold increase in half life and a 70% decrease in clearance compared to normal volunteers. Less than 10% of the administered dose was removed during the single dialysis session.
About 55–75% of an administered dose of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is excreted unchanged in the urine; the remainder is apparently metabolized in the liver. Therefore, pseudoephedrine may accumulate in patients with renal insufficiency.
Dosing adjustment is necessary in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment and in patients on dialysis (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Hepatic Impairment
Sixteen patients with chronic liver diseases (hepatocellular, cholestatic, and biliary cirrhosis), given 10 or 20 mg of cetirizine as a single, oral dose had a 50% increase in half-life along with a corresponding 40% decrease in clearance compared to 16 healthy subjects.
The effect of hepatic impairment on pseudoephedrine pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Dosing adjustment may be necessary in patients with hepatic impairment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Pharmacodynamics
Trials in 69 adult normal volunteers (aged 20–61 years) showed that cetirizine at doses of 5 and 10 mg inhibited the skin wheal and flare caused by the intradermal injection of histamine. The onset of this activity after a single 10-mg dose occurred within 20 minutes in 50% of subjects and within one hour in 95% of subjects; this activity persisted for at least 24 hours. The effects of intradermal injection of various other mediators or histamine releasers were also inhibited by cetirizine. In mildly asthmatic subjects, cetirizine at 5 to 20 mg blocked bronchoconstriction due to nebulized histamine, with virtually total blockade after a 20 mg dose. In trials conducted for up to 12 hours following cutaneous antigen challenge, the late phase recruitment of eosinophils, neutrophils and basophils, components of the allergic inflammatory response, was inhibited by cetirizine at a dose of 20 mg. The clinical significance of these findings is not known.
In four clinical trials in healthy adult males, no clinically significant mean increases in QTc were observed in cetirizine treated subjects. In the first study, a placebo-controlled crossover trial, cetirizine was given at doses up to 60 mg per day, 6 times the maximum clinical dose, for 1 week, and no significant mean QTc prolongation occurred. In the second study, a crossover trial, cetirizine 20 mg and erythromycin (500 mg every 8 hours) were given alone and in combination. There was no significant effect on QTc with the combination or with cetirizine alone. In the third trial, also a crossover study, cetirizine 20 mg and ketoconazole (400 mg per day) were given alone and in combination. Cetirizine caused a mean increase in QTc of 9.1 msec from baseline after 10 days of therapy. Ketoconazole also increased QTc by 8.3 msec. The combination caused an increase of 17.4 msec, equal to the sum of the individual effects. Thus, there was no significant drug interaction on QTc with the combination of cetirizine and ketoconazole. In the fourth study, a placebo-controlled parallel trial, cetirizine 20 mg was given alone or in combination with azithromycin (500 mg as a single dose on the first day followed by 250 mg once daily). There was no significant increase in QTc with cetirizine 20 mg alone or in combination with azithromycin.
In a six-week, placebo-controlled study of 186 patients (aged 12–64 years) with allergic rhinitis and mild to moderate asthma, cetirizine 10 mg once daily improved rhinitis symptoms and did not alter pulmonary function. This study supports the safety of administering cetirizine to allergic rhinitis patients with mild to moderate asthma.
Clinical Trials
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets
Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials (n=1094 and n=1000) comparing ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) to active control and placebo for two weeks in patients 12 years and older with seasonal allergic rhinitis were conducted in the United States. In the two trials, 390 patients were aged 12 to 17 years. The primary efficacy measure in both trials was the mean change from baseline in the subject-rated Total Symptom Severity Complex (TSSC) score, which included the following symptoms: sneezing, runny nose, itchy nose, itchy eyes, watery eyes, postnasal drip, and nasal congestion. In both trials patients who received ZYRTEC-D showed a significant reduction in the TSSC score compared to those who received placebo.
Zyrtec Tablets
Nine multicenter, randomized, double-blind, clinical trials comparing cetirizine 5 to 20 mg to placebo in patients 12 years and older with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis were conducted in the United States. Five of these showed significant reductions in symptoms of allergic rhinitis, 3 in seasonal allergic rhinitis (1 to 4 weeks in duration) and 2 in perennial allergic rhinitis for up to 8 weeks in duration. In general, the 10 mg dose was more effective than the 5 mg dose and the 20 mg dose gave no added effect. Some of these trials included pediatric patients aged 12 to 16 years.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets should be administered when both the antihistaminic properties of cetirizine hydrochloride and the nasal decongestant properties of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride are desired.
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are indicated for the relief of nasal and non-nasal symptoms associated with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and children 12 years of age and older.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients or to hydroxyzine.
Due to its pseudoephedrine component, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma or urinary retention, and in patients receiving monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor therapy or within fourteen (14) days of stopping such treatment (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions section). It is also contraindicated in patients with severe hypertension, or severe coronary artery disease, and in those who have shown hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to its components, to adrenergic agents, or to other drugs of similar chemical structures. Manifestations of patient idiosyncrasy to adrenergic agents include insomnia, dizziness, weakness, tremor, or arrhythmias.
WARNINGS
Sympathomimetic amines should be used judiciously and sparingly in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic heart disease, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, renal impairment, or prostatic hypertrophy (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Sympathomimetic amines may produce central nervous system stimulation with convulsions or cardiovascular collapse with accompanying hypotension. The elderly are more likely to have adverse reactions to sympathomimetic amines.
PRECAUTIONS
Due to its pseudoephedrine component, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic heart disease, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, renal impairment, or prostatic hypertrophy (see WARNINGS and CONTRAINDICATIONS). Patients with decreased renal function should be given a lower initial dose (one tablet per day) because they have reduced elimination of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
In clinical trials, the occurrence of somnolence has been reported in some patients taking cetirizine or ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets; due caution should therefore be exercised when driving a car or operating potentially dangerous machinery after taking ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets. Concurrent use of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets with alcohol or other CNS depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of CNS performance may occur.
Drug Interactions
Cetirizine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride do not influence the pharmacokinetics of each other when administered concomitantly.
No clinically significant drug interactions have been found with cetirizine and theophylline at a low dose, azithromycin, ketoconazole, or erythromycin. There was a small decrease in the clearance of cetirizine caused by a 400 mg dose of theophylline; it is possible that larger theophylline doses could have a greater effect.
Due to the pseudoephedrine component, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are contraindicated in patients taking monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors and for 14 days after stopping use of an MAO inhibitor. Concomitant use with antihypertensive drugs that interfere with sympathetic activity (e.g., methyldopa, mecamylamine, and reserpine) may reduce their antihypertensive effects. Increased ectopic pacemaker activity can occur when pseudoephedrine is used concomitantly with digitalis. Care should be taken in the administration of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets concomitantly with other sympathomimetic amines because combined effects on the cardiovascular system may be harmful to the patient (see WARNINGS).
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
There are no carcinogenicity trials of pseudoephedrine and cetirizine in combination.
Cetirizine
In a 2-year study in rats, cetirizine was not carcinogenic at dietary doses up to 20 mg/kg (approximately 15 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). In a 2-year study in mice, cetirizine caused an increased incidence of benign liver tumors in males at a dietary dose of 16 mg/kg (approximately 6 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). No increase in the incidence of liver tumors was observed in mice at a dietary dose of 4 mg/kg (approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). The clinical significance of these findings during long-term use of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets is not known.
Pseudoephedrine
Two-year studies in rats and mice conducted under the auspices of the National Toxicology Program (NTP) demonstrated no evidence of carcinogenic potential with ephedrine sulfate, a structurally related drug with pharmacological properties similar to pseudoephedrine, at dietary doses up to 10 and 27 mg/kg, respectively (approximately 1/3 and 1/2, respectively, the maximum recommended daily dose of pseudoephedrine in adults on a mg/m2 basis).
Cetirizine was not mutagenic in the Ames test or mouse lymphoma test and not clastogenic in the human lymphocyte assay or the in vivo rodent micronucleus test. Likewise, the combination of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine in a 1:24 ratio was not mutagenic or clastogenic in these tests. However, the Ames and mouse lymphoma assays did not strictly adhere to test standards.
In a reproductive toxicity study in rats, combination oral doses of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine up to 6/154 mg/kg (approximately 5 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis) had no effect on fertility.
Pregnancy Category C
In rats, the combination of cetirizine and pseudoephedrine caused developmental toxicity when administered orally at 6/154 mg/kg (approximately 5 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). When rats were dosed throughout pregnancy with oral doses of cetirizine/pseudoephedrine, 6/154 mg/kg increased the number of fetal skeletal malformations (rib distortions) and variants (unossified sternebrae). When dosing was continued through lactation, 6/154 mg/kg also decreased the viability and weight gain of offspring. These effects were not observed at 1.6/38 mg/kg (approximately equivalent to the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). No embryofetal toxicity was observed when rabbits were dosed throughout organogenesis with oral doses of cetirizine/pseudoephedrine of up to 6/154 mg/kg (approximately 10 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). Because there are no adequate and well-controlled trials in pregnant women, ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
In rats the combination of cetirizine/pseudoephedrine decreased the viability and weight gain of offspring when administered orally to dams throughout pregnancy and lactation at 6/154 mg/kg (approximately 5 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). This effect was not observed at 1.6/38 mg/kg (approximately equivalent to the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). For cetirizine administered alone, studies in dogs indicate that approximately 3% of the dose is excreted in milk, and cetirizine has been reported to be excreted in human breast milk. For pseudoephedrine administered alone, 0.4–0.7% of the dose has been reported to be excreted in human breast milk.
Because cetirizine and pseudoephedrine are excreted in milk, use of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets in nursing mothers is not recommended.
Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, although the elderly are more likely to have adverse reactions to sympathomimetic amines. In general, dosing in an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
The cetirizine and pseudoephedrine components of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Cetirizine
Of the total number of subjects in clinical trials of cetirizine alone, 186 were 65 years and over, while 39 were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. With regard to efficacy, clinical trials of cetirizine for each approved indication did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients.
Pediatric Use
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets contain 120 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride in an extended release formulation. This dose of pseudoephedrine exceeds the recommended dose for pediatric patients under 12 years of age. Therefore, clinical trials of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets have not been conducted in patients under 12 years of age.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets
In two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (n=2094) in which 701 patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis were treated with ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets (cetirizine hydrochloride 5 mg and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 120 mg) twice daily for two weeks, the percent of patients who withdrew prematurely due to adverse events was 2.0% in the ZYRTEC-D group, compared with 1.1% in the placebo group. All adverse events that were reported by greater than 1% of patients in the ZYRTEC-D group are listed in Table 1.
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | ZYRTEC-D (n=701) |
PLACEBO (n=696) |
|---|---|---|
| Insomnia | 4.0 | 0.6 |
| Dry Mouth | 3.6 | 0.4 |
| Fatigue | 2.4 | 0.9 |
| Somnolence | 1.9 | 0.1 |
| Pharyngitis | 1.7 | 1.1 |
| Epistaxis | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| Accidental Injury | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| Dizziness | 1.1 | 0.1 |
| Sinusitis | 1.0 | 0.6 |
ZYRTEC Tablets
Controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials of cetirizine conducted in the United States and Canada included more than 6000 patients aged 12 years and older, with more than 3900 receiving cetirizine at doses of 5 to 20 mg per day. The duration of treatment ranged from 1 week to 6 months, with a mean exposure of 30 days.
Most adverse reactions reported during therapy with cetirizine were mild or moderate. In placebo-controlled trials, the incidence of discontinuations due to adverse reactions in patients receiving cetirizine 5 mg or 10 mg was not significantly different from placebo (2.9% vs. 2.4%, respectively).
The most common adverse reaction in patients aged 12 years and older that occurred more frequently on cetirizine than placebo was somnolence. The incidence of somnolence associated with cetirizine was dose related, 6% in placebo, 11% at 5 mg and 14% at 10 mg. Discontinuations due to somnolence for cetirizine were uncommon (1.0% on cetirizine vs. 0.6% on placebo). Fatigue and dry mouth also appeared to be treatment-related adverse reactions. There were no differences by age, race, gender or by body weight with regard to the incidence of adverse reactions.
Table 2 lists adverse experiences in patients aged 12 years and older that were reported for cetirizine 5 and 10 mg in controlled clinical trials in the United States and were more common with cetirizine than placebo.
| ADVERSE EXPERIENCE | CETIRIZINE (n=2034) |
PLACEBO (n=1612) |
|---|---|---|
| Somnolence | 13.7 | 6.3 |
| Fatigue | 5.9 | 2.6 |
| Dry Mouth | 5.0 | 2.3 |
| Pharyngitis | 2.0 | 1.9 |
| Dizziness | 2.0 | 1.2 |
In addition, headache and nausea occurred in more than 2% of the patients, but were more common in placebo patients.
The following events were observed infrequently (less than 2%), in 3982 adults and children 12 years and older or in 659 pediatric (6 to 11 years) patients who received cetirizine in U.S. trials, including an open study of six months duration. A causal relationship of these infrequent events with cetirizine administration has not been established.
Autonomic Nervous System: anorexia, flushing, increased salivation, urinary retention.
Cardiovascular: cardiac failure, hypertension, palpitation, tachycardia.
Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems: abnormal coordination, ataxia, confusion, dysphonia, hyperesthesia, hyperkinesia, hypertonia, hypoesthesia, leg cramps, migraine, myelitis, paralysis, paresthesia, ptosis, syncope, tremor, twitching, vertigo, visual field defect.
Gastrointestinal: abnormal hepatic function, aggravated tooth caries, constipation, dyspepsia, eructation, flatulence, gastritis, hemorrhoids, increased appetite, melena, rectal hemorrhage, stomatitis including ulcerative stomatitis, tongue discoloration, tongue edema.
Genitourinary: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, micturition frequency, polyuria, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection.
Hearing and Vestibular: deafness, earache, ototoxicity, tinnitus.
Metabolic/Nutritional: dehydration, diabetes mellitus, thirst.
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, arthritis, arthrosis, muscle weakness, myalgia.
Psychiatric: abnormal thinking, agitation, amnesia, anxiety, decreased libido, depersonalization, depression, emotional lability, euphoria, impaired concentration, insomnia, nervousness, paroniria, sleep disorder.
Respiratory System: bronchitis, dyspnea, hyperventilation, increased sputum, pneumonia, respiratory disorder, rhinitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection.
Reproductive: dysmenorrhea, female breast pain, intermenstrual bleeding, leukorrhea, menorrhagia, vaginitis.
Reticuloendothelial: lymphadenopathy.
Skin: acne, alopecia, angioedema, bullous eruption, dermatitis, dry skin, eczema, erythematous rash, furunculosis, hyperkeratosis, hypertrichosis, increased sweating, maculopapular rash, photosensitivity reaction, photosensitivity toxic reaction, pruritus, purpura, rash, seborrhea, skin disorder, skin nodule, urticaria.
Special Senses: parosmia, taste loss, taste perversion.
Vision: blindness, conjunctivitis, eye pain, glaucoma, loss of accommodation, ocular hemorrhage, xerophthalmia.
Body as a Whole: accidental injury, asthenia, back pain, chest pain, enlarged abdomen, face edema, fever, generalized edema, hot flashes, increased weight, leg edema, malaise, nasal polyp, pain, pallor, periorbital edema, peripheral edema, rigors.
Occasional instances of transient, reversible hepatic transaminase elevations have occurred during cetirizine therapy. Hepatitis with significant transaminase elevation and elevated bilirubin in association with the use of cetirizine has been reported.
In foreign marketing experience or experience in the post market period, the following additional rare, but potentially severe adverse events have been reported: anaphylaxis, cholestasis, glomerulonephritis, hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, orofacial dyskinesia, severe hypotension, stillbirth, thrombocytopenia, aggressive reaction and convulsions.
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride may cause mild CNS stimulation in hypersensitive patients. Nervousness, excitability, restlessness, dizziness, weakness, or insomnia may occur. Headache, nausea, drowsiness, tachycardia, palpitation, pressor activity, and cardiac arrhythmias have been reported. Sympathomimetic drugs have also been associated with other untoward effects such as fear, anxiety, tenseness, tremor, hallucinations, seizures, pallor, respiratory difficulty, dysuria, and cardiovascular collapse.
OVERDOSAGE
Information regarding acute overdosage is limited to experience with cetirizine alone and the marketing history of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride.
Overdosage has been reported with cetirizine. In one adult patient who took 150 mg of cetirizine, the patient was somnolent but did not display any other clinical signs or abnormal blood chemistry or hematology results. In an 18-month-old pediatric patient who took an overdose of cetirizine (approximately 180 mg), restlessness and irritability were observed initially; this was followed by drowsiness. Should overdose occur, treatment should be symptomatic or supportive, taking into account any concomitantly ingested medications. There is no known specific antidote to cetirizine. Cetirizine is not effectively removed by dialysis, and dialysis will be ineffective unless a dialyzable agent has been concomitantly ingested. The acute minimal lethal oral doses in mice and rats were 237 and 562 mg/kg, respectively (approximately 95 and 460 times the maximum recommended daily dose in adults on a mg/m2 basis). In rodents, the target of acute toxicity was the central nervous system, and the target of multiple-dose toxicity was the liver.
In large doses, sympathomimetics may give rise to giddiness, headache, nausea, vomiting, sweating, thirst, tachycardia, precordial pain, palpitations, difficulty in micturition, muscular weakness and tenseness, anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia. Many patients can present a toxic psychosis with delusions and hallucinations. Some may develop cardiac arrhythmias, circulatory collapse, convulsions, coma and respiratory failure.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults and Children 12 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dose of ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets is one tablet twice daily for adults and children 12 years of age and older. ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets may be given with or without food.
Dose Adjustment for Renal and Hepatic Impairment
In patients with decreased renal function (creatinine clearance 11–31 mL/min), patients on hemodialysis (creatinine clearance less than 7 mL/min), and in hepatically impaired patients, a dose of one tablet once daily is recommended (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS).
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets should be swallowed whole, and should not be broken or chewed.
HOW SUPPLIED
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are white, round, biconvex, bilayer tablets containing 5 mg cetirizine hydrochloride in an immediate release layer and 120 mg pseudoephedrine hydrochloride in an extended release layer. ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are supplied in high-density polyethylene bottles of 100 tablets fitted with polypropylene child-resistant closures (NDC 0069-1630-66).
ZYRTEC-D 12 HOUR Extended Release Tablets are engraved with ZYRTEC-D on one side.
STORAGE
Store at 20–25°C (68–77°F); excursions permitted to 15–30°C (59–86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]
Rx only
Cetirizine is licensed from UCB Pharma, Inc.
LAB-0038-5.0
- Overview
- Uses
- Side-effects
- Precautions
- Interactions
- Contraindications
Overview
Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet works by blocking and inhibiting the action of histamine; causing narrowing of the blood vessels and reduces swelling in the nasal passages;
Detailed information related to Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet’s uses, composition, dosage, side effects and reviews is listed below.
Uses
Side-effects
Precautions
Before using Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet, inform your doctor about your current list of medications, over the counter products (e.g. vitamins, herbal supplements, etc.), allergies, pre-existing diseases, and current health conditions (e.g. pregnancy, upcoming surgery, etc.). Some health conditions may make you more susceptible to the side-effects of the drug. Take as directed by your doctor or follow the direction printed on the product insert. Dosage is based on your condition. Tell your doctor if your condition persists or worsens. Important counseling points are listed below.
- Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until you know how this medication affects you
- Avoid taking this drug too close to bedtime
- Breast-feeding
- Do not use continuously or more than the recommended duration
- Kidney disease
- Limit caffeine use while taking this medication
- Liver disease
- May cause jitteriness, dizziness, shortness of breath, anxiety
- Plan to become pregnant
- Pregnant
Interactions with Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet
If you use other drugs or over the counter products at the same time, the effects of Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet may change. This may increase your risk for side-effects or cause your drug not to work properly. Tell your doctor about all the drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements you are using, so that you doctor can help you prevent or manage drug interactions. Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet may interact with the following drugs and products:
- Aripiprazole
- Cardiac glycosides
- Chlorpheniramine
- Clemastine
- Diphenhydramine
- Fentanyl
- Quinidine
- Tricyclic antidepressants
When not to use Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet
- Allergic
- Allergic reactions
- Hypertension
- Phaeochromocytoma
Composition and Active Ingredients
Packages and Strengths
Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet is available in the following packages and strengths
Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet — Packages: Oral 5, 120mg in Blister x 14 (Shelf life: 36 months/Store below 25C)
Frequently asked Questions
-
Is Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet safe to use when pregnant?
- Cetirizine Dihydrochloride: Please consult with your doctor for case-specific recommendations.
- Pseudoephedrine: No
-
Is Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet safe while breastfeeding?
- Cetirizine Dihydrochloride: Please discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
- Pseudoephedrine: Please discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
-
Is it safe to drive or operate heavy machinery when using this product?
If you experience drowsiness, dizziness, hypotension or a headache as side-effects when using Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet medicine then it may not be safe to drive a vehicle or operate heavy machinery. One should not drive a vehicle if using the medicine makes you drowsy, dizzy or lowers your blood-pressure extensively. Pharmacists also advise patients not to drink alcohol with medicines as alcohol intensifies drowsiness side-effects. Please check for these effects on your body when using Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet. Always consult with your doctor for recommendations specific to your body and health conditions.
-
Is this medicine or product addictive or habit forming?
Most medicines don’t come with a potential for addiction or abuse. Usually, the government’s categorizes medicines that can be addictive as controlled substances. Examples include schedule H or X in India and schedule II-V in the US. Please consult the product package to make sure that the medicine does not belong to such special categorizations of medicines. Lastly, do not self-medicate and increase your body’s dependence to medicines without the advice of a doctor.
-
Can i stop using this product immediately or do I have to slowly wean off the use?
Some medicines need to be tapered or cannot be stopped immediately because of rebound effects. Please consult with your doctor for recommendations specific to your body, health and other medications that you may be using.
Other important Information on Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet
Missing a dose
In case you miss a dose, use it as soon as you notice. If it is close to the time of your next dose, skip the missed dose and resume your dosing schedule. Do not use extra dose to make up for a missed dose. If you are regularly missing doses, consider setting an alarm or asking a family member to remind you. Please consult your doctor to discuss changes in your dosing schedule or a new schedule to make up for missed doses, if you have missed too many doses recently.
Overdosage of Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet
- Do not use more than prescribed dose. Taking more medication will not improve your symptoms; rather they may cause poisoning or serious side-effects. If you suspect that you or anyone else who may have overdosed of Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet, please go to the emergency department of the closest hospital or nursing home. Bring a medicine box, container, or label with you to help doctors with necessary information.
- Do not give your medicines to other people even if you know that they have the same condition or it seems that they may have similar conditions. This may lead to overdosage.
- Please consult your physician or pharmacist or product package for more information.
Storage of Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet
- Store medicines at room temperature, away from heat and direct light. Do not freeze medicines unless required by package insert. Keep medicines away from children and pets.
- Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into drainage unless instructed to do so. Medication discarded in this manner may contaminate the environment. Please consult your pharmacist or doctor for more details on how to safely discard Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet.
Expired Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet
- Taking a single dose of expired Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet is unlikely to produce an adverse event. However, please discuss with your primary health provider or pharmacist for proper advice or if you feel unwell or sick. Expired drug may become ineffective in treating your prescribed conditions. To be on the safe side, it is important not to use expired drugs. If you have a chronic illness that requires taking medicine constantly such as heart condition, seizures, and life-threatening allergies, you are much safer keeping in touch with your primary health care provider so that you can have a fresh supply of unexpired medications.
Dosage Information
Please consult your physician or pharmacist or refer to the product package.
Cite this page
Page URL
HTML Link
APA Style Citation
- Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet — Product — TabletWise.com. (n.d.). Retrieved October 10, 2023, from https://www.tabletwise.com/saudiarabia/cirrus-5-120mg-tablet
MLA Style Citation
- «Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet — Product — TabletWise.com» Tabletwise.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 Oct. 2023.
Chicago Style Citation
- «Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet — Product — TabletWise.com» Tabletwise. Accessed October 10, 2023. https://www.tabletwise.com/saudiarabia/cirrus-5-120mg-tablet.
Last updated date
This page was last updated on 9/27/2020.
This page provides information for Cirrus 5-120Mg Tablet Product in English.
-
Hay Fever
Each spring, summer, and fall, trees, weeds, and grasses release …
-
Allergy
An allergy is a reaction by your immune system to something that …
-
Hives
Hives are red and sometimes itchy bumps on your skin. An …
-
Cold
An acute inflammatory process that affects the nasopharynx. It …
Эриус® (Aerius®) инструкция по применению
📜 Инструкция по применению Эриус®
💊 Состав препарата Эриус®
✅ Применение препарата Эриус®
📅 Условия хранения Эриус®
⏳ Срок годности Эриус®
Описание лекарственного препарата
Эриус®
(Aerius®)
Основано на листке-вкладыше препарата, утверждено компанией-производителем
и подготовлено для электронного издания справочника Видаль 2023 года.
Дата обновления: 2023.06.30
Владелец регистрационного удостоверения:
Контакты для обращений:
БАЙЕР АГ
(Германия)
Код ATX:
R06AX27
(Дезлоратадин)
Лекарственная форма
| Эриус® |
Таб., покр. пленочной оболочкой, 5 мг: 10 или 20 шт. рег. №: ЛП-(001060)-(РГ-RU) Предыдущий рег. №: П N014704/02 |
Форма выпуска, упаковка и состав
препарата Эриус®
Таблетки, покрытые пленочной оболочкой голубого цвета, круглые, двояковыпуклые; с одной стороны таблетки имеется небольшое углубление в центре, другая сторона гладкая.
Вспомогательные вещества: кальция гидрофосфата дигидрат, целлюлоза микрокристаллическая 102, крахмал кукурузный, тальк.
Состав оболочки: опадрай II голубой 32В10817 (лактозы моногидрат, гипромеллоза, титана диоксид, макрогол, FD&C голубой #2/индигокармин алюминиевый лак), воск карнаубский.
10 шт. — блистеры (1) — пачки картонные с контролем первого вскрытия.
10 шт. — блистеры (2) — пачки картонные с контролем первого вскрытия.
Фармакологическое действие
Антигистаминный препарат длительного действия. Является первичным активным метаболитом лоратадина. Ингибирует каскад реакций аллергического воспаления, в т.ч. высвобождение провоспалительных цитокинов, включая интерлейкины ИЛ-4, ИЛ-6, ИЛ-8, ИЛ-13, высвобождение провоспалительных хемокинов (RANTES), продукцию супероксидных анионов активированными полиморфно-ядерными нейтрофилами, адгезию и хемотаксис эозинофилов, выделение молекул адгезии, таких как P-селектин, IgE — опосредованное высвобождение гистамина, простагландина D2 и лейкотриена С4. Таким образом, предупреждает развитие и облегчает течение аллергических реакций, обладает противозудным и антиэкссудативным действием, уменьшает проницаемость капилляров, предупреждает развитие отека тканей, спазма гладкой мускулатуры.
Препарат не оказывает воздействия на ЦНС, практически не обладает седативным эффектом (не вызывает сонливости) и не влияет на скорость психомоторных реакций. В клинико-фармакологических исследованиях применения дезлоратадина в рекомендуемой терапевтической дозе не отмечалось удлинения интервала QT на ЭКГ.
Действие препарата Эриус® начинается в течение 30 мин после приема внутрь и продолжается в течение 24 ч.
Фармакокинетика
Всасывание
После приема препарата внутрь дезлоратадин хорошо всасывается из ЖКТ. Определяется в плазме крови через 30 минут после приема внутрь. Cmax достигается в среднем через 3 ч после приема.
Распределение
Связывание дезлоратадина с белками плазмы составляет 83-87%. При применении у взрослых и подростков в течение 14 дней в дозе от 5 мг до 20 мг 1 раз/сут признаков клинически значимой кумуляции дезлоратадина не выявлено. Одновременный прием пищи или одновременное употребление грейпфрутового сока не влияет на распределение дезлоратадина (при приеме в дозе 7.5 мг 1 раз/сут). Не проникает через ГЭБ.
Метаболизм
Интенсивно метаболизируется в печени путем гидроксилирования с образованием 3-ОН-дезлоратадина, соединенного с глюкуронидом. Дезлоратадин не является ингибитором CYP3A4 и CYP2D6 и не является субстратом или ингибитором Р-гликопротеина.
Выведение
Лишь небольшая часть принятой внутрь дозы выводится почками (<2%) и через кишечник (<7%).
T1/2 — 20-30 ч (в среднем — 27 ч).
Показания препарата
Эриус®
- аллергический ринит (устранение или облегчение чиханья, заложенности носа, выделения слизи из носа, зуда в носу, зуда неба, зуда и покраснения глаз, слезотечения);
- крапивница (уменьшение или устранение кожного зуда, сыпи).
Режим дозирования
Для приема внутрь.
Таблетку следует проглатывать целиком, не разжевывая, и запивать водой.
Препарат желательно принимать регулярно в одно и то же время суток, независимо от времени приема пищи.
Взрослым и подросткам от 12 лет — по 1 таблетке (5 мг) 1 раз/сут.
При лечении сезонного аллергического ринита (наличие симптомов продолжительностью менее 4 дней в неделю или менее 4 недель в году) необходимо оценивать течение заболевания. После исчезновения симптомов прием препарата следует прекратить. При повторном возникновении симптомов лечение можно возобновить.
При круглогодичном аллергическом рините (наличие симптомов продолжительностью более 4 дней в неделю и более 4 недель в году) предполагается длительное лечение в течение всего периода контакта с аллергеном.
При крапивнице применять при наличии симптомов, индивидуальная продолжительность терапии определяется врачом.
Побочное действие
Наиболее часто встречающиеся побочные эффекты (≥1/100 до <1/10), частота которых была несколько выше, чем при приеме плацебо: повышенная повышенная утомляемость (1.2%), сухость во рту (0.8%) и головная боль (0.6%).
У детей в возрасте 12-17 лет, по результатам клинических исследований, наиболее часто встречающимся побочным эффектом являлась головная боль (5.9%), частота которой была не выше, чем при приеме плацебо (6.9%).
Информация о побочных эффектах представлена по результатам клинических исследований и наблюдений пострегистрационного периода.
Нежелательные реакции перечислены по системно-органным классам с указанием частоты согласно следующей классификации: очень часто (≥1/10), часто (от ≥1/100 до <1/10), нечасто (от ≥1/1000 до <1/100), редко (от ≥1/10 000 до <1/1000), очень редко (<1/10 000), частота неизвестна (по имеющимся данным установить частоту возникновения не представлялось возможным).
Со стороны психики: очень редко — галлюцинации; частота неизвестна — аномальное поведение, агрессия.
Со стороны нервной системы: часто — головная боль; очень редко — головокружение, сонливость, бессонница, психомоторная гиперактивность, судороги.
Со стороны печени и желчевыводящих путей: очень редко — повышение активности ферментов печени, повышение концентрации билирубина, гепатит; частота неизвестна — желтуха.
Со стороны пищеварительной системы: часто — сухость во рту; очень редко — боль в животе, тошнота, рвота, диспепсия, диарея, повышение аппетита.
Со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы: очень редко — тахикардия, сердцебиение; частота неизвестна — удлинение интервала QT.
Со стороны костно-мышечной системы: очень редко — миалгия.
Со стороны кожи и подкожных тканей: частота неизвестна — фотосенсибилизация.
Общие расстройства: часто — повышенная утомляемость; очень редко — анафилаксия, ангионевротический отек, одышка, зуд, сыпь, в т.ч. крапивница; частота неизвестна — астения.
Лабораторные и инструментальные данные: повышение массы тела.
Пострегистрационный период
Дети: частота неизвестна — удлинение интервала QT, аритмия, брадикардия, аномальное поведение, агрессия.
Если отмечаются указанные в инструкции нежелательные реакции, или они усугубляются, или отмечаются любые другие нежелательные реакции, не указанные в инструкции, пациент должен сообщить об этом врачу.
Противопоказания к применению
- повышенная чувствительность к дезлоратадину, другим компонентам препарата или лоратадину;
- беременность;
- период грудного вскармливания;
- детский возраст до 12 лет.
С осторожностью: почечная недостаточность тяжелой степени, судороги в анамнезе.
Применение при беременности и кормлении грудью
Беременность
Назначение препарата Эриус® при беременности противопоказано в связи с отсутствием клинических данных о безопасности его применения в данный период.
Период грудного вскармливания
Дезлоратадин выделяется с грудным молоком, поэтому применение препарата Эриус® в период грудного вскармливания противопоказано.
Применение при нарушениях функции почек
С осторожностью следует применять препарат при почечной недостаточности тяжелой степени.
Применение у детей
Противопоказано применение у детей в возрасте до 12 лет.
Особые указания
Исследований эффективности препарата Эриус® при ринитах инфекционной этиологии не проводилось.
Необходимо соблюдать осторожность при применении препарата Эриус® у пациентов с судорогами в анамнезе, особенно у пациентов детского возраста. Следует прекратить применение препарата в случае развития судорог.
Пациентам с редко встречающейся наследственной непереносимостью галактозы, дефицитом лактазы лопарей или глюкозо-галактозной мальабсорбцией не следует принимать этот препарат.
Влияние на способность к управлению транспортными средствами и механизмами
Следует принимать во внимание потенциальную возможность развития таких побочных эффектов, как головокружение и сонливость. При появлении описанных нежелательных явлений следует воздержаться от выполнения указанных видов деятельности.
Передозировка
Симптомы: прием дозы, превышающей рекомендованную в 5 раз, не приводил к появлению каких-либо симптомов.
В ходе клинических исследований ежедневное применение у взрослых и подростков дезлоратадина в дозе до 20 мг в течение 14 дней не сопровождалось статистически или клинически значимыми изменениями со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы. В клинико-фармакологическом исследовании применение дезлоратадина в дозе 45 мг/сут (в 9 раз выше рекомендуемой) в течение 10 дней не вызывало удлинения интервала QT и не сопровождалось появлением серьезных побочных эффектов.
Лечение: при случайном приеме внутрь большого количества препарата пациент должен незамедлительно обратиться к врачу. Проводится промывание желудка, прием активированного угля; при необходимости — симптоматическая терапия. Дезлоратадин не выводится при гемодиализе, эффективность перитонеального диализа не установлена.
Лекарственное взаимодействие
Не выявлено клинически значимого взаимодействия в исследованиях при совместном применении с азитромицином, кетоконазолом, эритромицином, флуоксетином и циметидином.
Одновременный прием пищи или употребление грейпфрутового сока не оказывает влияния на эффективность препарата.
Эриус® не усиливает действие алкоголя на ЦНС. Тем не менее, во время пострегистрационного применения были зарегистрированы случаи непереносимости алкоголя и алкогольного опьянения, поэтому дезлоратадин одновременно с алкоголем следует применять с осторожностью.
Условия хранения препарата Эриус®
Препарат следует хранить в недоступном для детей месте при температуре не выше 30°С.
Срок годности препарата Эриус®
Срок годности — 2 года.
Условия реализации
Препарат отпускают без рецепта.
Контакты для обращений
БАЙЕР АГ
(Германия)

|
|
Организация, принимающая |
Если вы хотите разместить ссылку на описание этого препарата — используйте данный код
Аналоги препарата
Блогир-3®
(BELUPO, Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics, Хорватия)
Дезал
(ACTAVIS GROUP PTC ehf., Исландия)
Дезлоратадин
(ТАТХИМФАРМПРЕПАРАТЫ, Россия)
Дезлоратадин
(СИНТЕЗ, Россия)
Дезлоратадин
(Березовский фармацевтический завод, Россия)
Дезлоратадин
(БИОКОМ, Россия)
Дезлоратадин
(РИФ, Россия)
Дезлоратадин
(БРАЙТ ВЭЙ, Россия)
Дезлоратадин Велфарм
(АТОЛЛ, Россия)
Дезлоратадин ВП
(VETPROM, Болгария)
Все аналоги