1 таблетка содержит: эрготамина тартрат 1 мг кофеин 100 мг.
Комбинированный препарат, купирует приступы мигрени и головной боли сосудистого генеза. Эрготамин нормализаует тонус расширенных экстракраниальных артерий. Кофеин ускоряет и увеличивает всасывание эрготамина в кишечнике.
Фармакокинетика
После приема внутрь около 62% эрготамина всасывается в ЖКТ . Максимальная концентрация в плазме достигается через 2 ч после приема внутрь. Связывание с белками плазмы — 98%. Эрготамин метаболизируется в печени с образованием фармакологически активных метаболитов. Выводится эрготамин преимущественно с желчью как в неизмененном виде, так и в виде метаболитов. Выведение носит двухфазный характер, периоды полувыведения 2.7 ч и 21 ч для I и II фазы соответственно.
После приема препарата внутрь кофеин всасывается быстро и почти полностью. Связывание с белками плазмы составляет 35%. Кофеин практически полностью метаболизируется в организме. Метаболиты выводятся, главным образом, с мочой. Период полувыведения составляет около 3.5 ч.
Острые приступы мигрени и сходные с ними приступы головных болей сосудистого генеза.
Кафергот следует принимать в самом начале приступа. Для первого приема рекомендуется доза в 2 таб. Если через 30 мин улучшения состояния не наступает, следует принять еще 1 таб. Прием препарата можно повторять и далее с интервалом в 30 мин, не превышая максимальной суточной дозы.
При последующих приступах первоначальную дозу можно увеличить до 3 таб., в зависимости от суммарной дозы, принимавшейся во время предыдущих приступов.
Максимальная суточная доза — 6 мг эрготамина тартрата (6 таб.).
Максимальная недельная доза — 10 мг эрготамина тартрата (10 таб.).
Тошнота, рвота, аллергические реакции, повышение артериального давления. При длительном применении — слабость и боль в конечностях, тремор, кардиалгия, тахикардия, брадикардия, фиброзные изменения плевры и забрюшинного пространства. Передозировка. Симптомы: сонливость, спутанность сознания, тахикардия, головокружение, парестезии, угнетение дыхательного центра, кома. Лечение: промывание желудка, активированный уголь, симптоматическая терапия.
— повышенная чувствительность к одному из компонентов препарата;
— нарушение периферического кровообращения;
— облитерирующие заболевания сосудов;
— ИБС или тяжелая артериальная гипертония;
— печеночная или почечная недостаточность;
— сепсис;
— беременность, лактация.
Особые указания:
При появлении таких симптомов, как онемение кончиков пальцев кистей или стоп, прием препарата следует немедленно прекратить и обратиться к врачу.
Кафергот применяется для лечения острого приступа мигрени, его не следует использовать для профилактики приступов или принимать часто в течение длительного времени.
Передозировка:
Симптомы: тошнота, рвота, сонливость, спутанность сознания, тахикардия, головокружение, парастезии и боли в конечностях, угнетение дыхания, кома.
Лечение: промывание желудка, прием активированного угля, симптоматическая терапия, при атрериальном спазме — вазодилататоры типа нитропруссида натрия.
Лекарственное взаимодействие:
Одновременный прием олеандомицина, эритромицина или джозамицина вместе с эрготамином может привести к повышению концентрации эрготамина в плазме.
Имеются сообщения о нескольких случаях вазоспазма у больных, получавших одновременно эрготамин и пропранолол.
Таблетки в упаковке по 20 шт.
При комнатной температуре в защищенном от света месте.
Близким по составу препаратом является Авамигран (Avamigran).
Производитель — Novartis.
Инструкция составлена коллективом авторов и редакторов сайта Piluli. Список авторов справочника лекарств представлен на странице редакции сайта: Редакция сайта.
Описание препарата «Кафергот» на данной странице является упрощённой и дополненной версией официальной инструкции по применению. Перед приобретением или использованием препарата вы должны проконсультироваться с врачом и ознакомиться с утверждённой производителем аннотацией.
Информация о препарате предоставлена исключительно с ознакомительной целью и не должна быть использована как руководство к самолечению. Только врач может принять решение о назначении препарата, а также определить дозы и способы его применения.
Количество просмотров: 26233.
Кафергот
Группы препарата:
- Сердечно-сосудистые лекарственные средства
- Лекарственные средства, улучшающие мозговое кровообращение
Наименование
Кафергот (Cafergot)
Фармакологическое действие
Комбинированный препарат, купирует приступы мигрени и головной боли сосудистого генеза. Эрготамин нормализаует тонус расширенных экстракраниальных артерий. Кофеин ускоряет и увеличивает всасывание эрготамина в кишечнике.
Фармакокинетика
После приема внутрь около 62% эрготамина всасывается в ЖКТ . Максимальная концентрация в плазме достигается через 2 ч после приема внутрь. Связывание с белками плазмы — 98%. Эрготамин метаболизируется в печени с образованием фармакологически активных метаболитов. Выводится эрготамин преимущественно с желчью как в неизмененном виде, так и в виде метаболитов. Выведение носит двухфазный характер, периоды полувыведения 2.7 ч и 21 ч для I и II фазы соответственно.
После приема препарата внутрь кофеин всасывается быстро и почти полностью. Связывание с белками плазмы составляет 35%. Кофеин практически полностью метаболизируется в организме. Метаболиты выводятся, главным образом, с мочой. Период полувыведения составляет около 3.5 ч.
Показания к применению
Острые приступы мигрени и сходные с ними приступы головных болей сосудистого генеза.
Способ применения
Кафергот следует принимать в самом начале приступа. Для первого приема рекомендуется доза в 2 таб. Если через 30 мин улучшения состояния не наступает, следует принять еще 1 таб. Прием препарата можно повторять и далее с интервалом в 30 мин, не превышая максимальной суточной дозы.
При последующих приступах первоначальную дозу можно увеличить до 3 таб., в зависимости от суммарной дозы, принимавшейся во время предыдущих приступов.
Максимальная суточная доза — 6 мг эрготамина тартрата (6 таб.).
Максимальная недельная доза — 10 мг эрготамина тартрата (10 таб.).
Побочные действия
Тошнота, рвота, аллергические реакции, повышение артериального давления. При длительном применении — слабость и боль в конечностях, тремор, кардиалгия, тахикардия, брадикардия, фиброзные изменения плевры и забрюшинного пространства. Передозировка. Симптомы: сонливость, спутанность сознания, тахикардия, головокружение, парестезии, угнетение дыхательного центра, кома. Лечение: промывание желудка, активированный уголь, симптоматическая терапия.
Противопоказания
— повышенная чувствительность к одному из компонентов препарата;
— нарушение периферического кровообращения;
— облитерирующие заболевания сосудов;
— ИБС или тяжелая артериальная гипертония;
— печеночная или почечная недостаточность;
— сепсис;
— беременность, лактация.
Особые указания:
При появлении таких симптомов, как онемение кончиков пальцев кистей или стоп, прием препарата следует немедленно прекратить и обратиться к врачу.
Кафергот применяется для лечения острого приступа мигрени, его не следует использовать для профилактики приступов или принимать часто в течение длительного времени.
Передозировка:
Симптомы: тошнота, рвота, сонливость, спутанность сознания, тахикардия, головокружение, парастезии и боли в конечностях, угнетение дыхания, кома.
Лечение: промывание желудка, прием активированного угля, симптоматическая терапия, при атрериальном спазме — вазодилататоры типа нитропруссида натрия.
Лекарственное взаимодействие:
Одновременный прием олеандомицина, эритромицина или джозамицина вместе с эрготамином может привести к повышению концентрации эрготамина в плазме.
Имеются сообщения о нескольких случаях вазоспазма у больных, получавших одновременно эрготамин и пропранолол.
Форма выпуска
Таблетки в упаковке по 20 шт.
Условия хранения
При комнатной температуре в защищенном от света месте.
Состав
1 таблетка содержит: эрготамина тартрат 1 мг кофеин 100 мг.
Дополнительно
Близким по составу препаратом является Авамигран (Avamigran).
Производитель — Novartis.
Действующее вещество
Эрготамина тартрат, Кофеин
KAISER FOUNDATION HOSPITALS
CAFERGOT (Ergotamine Tartrate and Caffeine) Tablets, USP1 mg/ 100 mg
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- CAFERGOT DESCRIPTION
- CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- Pharmacokinetics:
- CAFERGOT INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CAFERGOT CONTRAINDICATIONS
- WARNINGS
- Fibrotic Complications:
- PRECAUTIONS
- Information for Patients:
- Drug Interactions:
- Pregnancy:
- Labor and Delivery:
- Nursing Mothers:
- Pediatric Use:
- CAFERGOT ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- OVERDOSAGE
- CAFERGOT DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- HOW SUPPLIED
- CAFERGOT(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) Package Label
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING
Serious and/or life-threatening peripheral ischemia has been associated with the coadministration of CAFERGOT® with potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors including protease inhibitors and macrolide antibiotics. Because CYP 3A4 inhibition elevates the serum levels of CAFERGOT®, the risk for vasospasm leading to cerebral ischemia and/or ischemia of the extremities is increased. Hence, concomitant use of these medications is contraindicated.(See also
CONTRAINDICATIONS
and
WARNINGS
section).
CAFERGOT DESCRIPTION
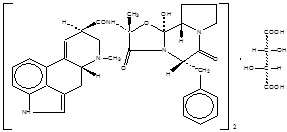
Each tablet for oral administration contains 1 mg ergotamine tartrate, USP, and 100 mg caffeine, USP.
ERGOTAMINE TARTRATE:
(C33H35N5O5)2• C4H6O6 M.W. 1313.41
Ergotaman-3’, 6’, 18-trione, 12’-hydroxy-2’-methyl-5’-(phenyl-methyl)-, (5’α), [R-(R*, R*)]-2,3-dihydroxy-butanedioate (2:1) (salt)
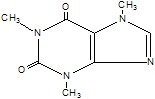
CAFFEINE:
C8H10N4O2 (anhydrous) M.W. 194.19
1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl-
Inactive ingredients include black iron oxide, compressible sugar, iron oxide red, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium starch glycolate, talc, titanium dioxide and yellow iron oxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ergotamine is an alpha adrenergic blocking agent with a direct stimulating effect on the smooth muscle of peripheral and cranial blood vessels and produces depression of central vasomotor centers. The compound also has the properties of serotonin antagonism. In comparison to hydrogenated ergotamine, the adrenergic blocking actions are less pronounced and vasoconstrictive actions are greater.
Caffeine, also a cranial vasoconstrictor, is added to further enhance the vasoconstrictive effect without the necessity of increasing ergotamine dosage.
Many migraine patients experience excessive nausea and vomiting during attacks, making it impossible for them to retain any oral medication. In such cases, therefore, the only practical means of medication is through the rectal route where medication may reach the cranial vessels directly, evading the splanchnic vasculature and the liver.
Pharmacokinetics:
Interactions: Pharmacokinetic interactions (increased blood levels of ergotamine) have been reported in patients treated orally with ergotamine and macrolide antibiotics (e.g., troleandomycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin), and in patients treated orally with ergotamine and protease inhibitors (e.g. ritonavir) presumably due to inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A metabolism of ergotamine (See CONTRAINDICATIONS). Ergotamine has also been shown to be an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 3A catalyzed reactions. No pharmacokinetic interactions involving other cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are known.
CAFERGOT INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) are indicated as therapy to abort or prevent vascular headache; e.g., migraine, migraine variants or so-called «histaminic cephalalgia».
CAFERGOT CONTRAINDICATIONS
Coadministration of ergotamine with potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors (ritonavir, nelfinavir, indinavir, erythromycin, clarithromycin, and troleandomycin) has been associated with acute ergot toxicity (ergotism) characterized by vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions), with some cases resulting in amputation. There have been rare reports of cerebral ischemia in patients on protease inhibitor therapy when CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) was coadministered, at least one resulting in death. Because of the increased risk of ergotism and other serious vasospastic adverse events, ergotamine use is contraindicated with these drugs and other potent inhibitors of CYP 3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole) (see WARNINGS: CYP 3A4 Inhibitors).
CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this product, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Peripheral vascular disease, coronary heart disease, hypertension, impaired hepatic or renal function and sepsis.
Hypersensitivity to any of the components.
WARNINGS
CYP 3A4 Inhibitors (e.g. Macrolide Antibiotics and Protease Inhibitors): Coadministration of ergotamine with potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors such as protease inhibitors or macrolide antibiotics has been associated with serious adverse events; for this reason, these drugs should not be given concomitantly with ergotamine (See
CONTRAINDICATIONS
). While these reactions have not been reported with less potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors, there is a potential risk for serious toxicity including vasospasm when these drugs are used with ergotamine. Examples of less potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors include: saquinavir, nefazodone, fluconazole, fluoxetine, grapefruit juice, fluvoxamine, zileuton, metronidazole, and clotrimazole. These lists are not exhaustive, and the prescriber should consider the effects on CYP 3A4 of other agents being considered for concomitant use with ergotamine.
Fibrotic Complications:
There have been a few reports of patients on ergotamine and caffeine therapy developing retroperitoneal and/or pleuropulmonary fibrosis. There have also been rare reports of fibrotic thickening of the aortic, mitral, tricuspid, and/or pulmonary valves with long-term continuous use of ergotamine and caffeine. Ergotamine tartrate should not be used for chronic daily administration (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
PRECAUTIONS
General:
Although signs and symptoms of ergotism rarely develop even after long term intermittent use, care should be exercised to remain within the limits of recommended dosage.
Ergotism is manifested by intense arterial vasoconstriction, producing signs and symptoms of peripheral vascular ischemia. Ergotamine induces vasoconstriction by a direct action on vascular smooth muscle. In chronic intoxication with ergot derivatives, headache, intermittent claudication, muscle pains, numbness, coldness, and pallor of the digits may occur. If the condition is allowed to progress untreated, gangrene can result.
While most cases of ergotism associated with ergotamine treatment result from frank overdosage, some cases have involved apparent hypersensitivity. There are few reports of ergotism among patients taking doses within the recommended limits or for brief periods of time. In rare instances, patients, particularly those who have used the medication indiscriminately over long periods of time, may display withdrawal symptoms consisting of rebound headache upon discontinuation of the drug.
Information for Patients:
Patients should be advised that two tablets of CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) should be taken at the first sign of a migraine headache. No more than 6 tablets should be taken for any single migraine attack. No more than 10 tablets should be taken during any 7-day period. Administration of ergotamine and caffeine tablets should not exceed the dosing guidelines and should not be used for chronic daily administration (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) should be used only for migraine headaches. It is not effective for other types of headaches and it lacks analgesic properties. Patients should be advised to report to the physician immediately any of the following: numbness and tingling of the fingers and toes, muscle pains in the arms and legs, weakness in the legs, pain in the chest or temporary speeding or slowing of the heart rate, swelling or itching.
Drug Interactions:
CYP 3A4 Inhibitors (e.g. Macrolide Antibiotics and Protease Inhibitors):
See CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS
CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) should not be administered with other vasoconstrictors. Use with sympathomimetics (pressor agents) may cause extreme elevation of blood pressure. The beta-blocker Inderal (propranolol) has been reported to potentiate the vasoconstrictive action of CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) by blocking the vasodilating property of epinephrine. Nicotine may provoke vasoconstriction in some patients, predisposing to a greater ischemic response to ergot therapy.
The blood levels of ergotamine-containing drugs are reported to be elevated by the concomitant administration of macrolide antibiotics and vasospastic reactions have been reported with therapeutic doses of the ergotamine-containing drugs when coadministered with these antibiotics.
Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects:
Pregnancy Category X: There are no studies on the placental transfer or teratogenicity of the combined products of CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP). Caffeine is known to cross the placenta and has been shown to be teratogenic in animals. Ergotamine crosses the placenta in small amounts, although it does not appear to be embryotoxic in this quantity. However, prolonged vasoconstriction of the uterine vessels and/or increased myometrial tone leading to reduced myometrial and placental blood flow may have contributed to fetal growth retardation observed in animals. (See
CONTRAINDICATIONS
)
Nonteratogenic Effects: CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the oxytocic effects of ergotamine. (See
CONTRAINDICATIONS
)
Labor and Delivery:
CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) is contraindicated in labor and delivery due to its oxytocic effect which is maximal in the third trimester. (See
CONTRAINDICATIONS
)
Nursing Mothers:
Ergot drugs are known to inhibit prolactin but there are no reports of decreased lactation with CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP). Ergotamine is excreted in breast milk and may cause symptoms of vomiting, diarrhea, weak pulse and unstable blood pressure in nursing infants. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP), a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use:
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
CAFERGOT ADVERSE REACTIONS
Cardiovascular: Vasoconstrictive complications of a serious nature may occur at times. These include ischemia, cyanosis, absence of pulse, cold extremities, gangrene, precordial distress and pain, EKG changes and muscle pains. Although these effects occur most commonly with long-term therapy at relatively high doses, they have also been reported with short-term or normal doses. Other cardiovascular adverse effects include transient tachycardia or bradycardia and hypertension.
Gastrointestinal: Nausea and vomiting
Neurological: Paresthesias, numbness, weakness, and vertigo
Allergic: Localized edema and itching.
Fibrotic Complications: (see WARNINGS).
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
There have been reports of drug abuse and psychological dependence in patients on CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) therapy. Due to the chronicity of vascular headaches, it is imperative that patients be advised not to exceed recommended dosages with long-term use to avoid ergotism. (See
PRECAUTIONS)
OVERDOSAGE
The toxic effects of an acute overdosage of CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) are due primarily to the ergotamine component. The amount of caffeine is such that its toxic effects will be overshadowed by those of ergotamine. Symptoms include vomiting; numbness, tingling, pain and cyanosis of the extremities associated with diminished or absent peripheral pulses; hypertension or hypotension; drowsiness, stupor, coma, convulsions and shock. A case has been reported of reversible bilateral papillitis with ring scotomata in a patient who received five times the recommended daily adult dose over a period of 14 days.
Treatment consists of removal of the offending drug by induction of emesis, gastric lavage, and catharsis. Maintenance of adequate pulmonary ventilation, correction of hypotension, and control of convulsions and blood pressure are important considerations. Treatment of peripheral vasospasm should consist of warmth, but not heat, and protection of the ischemic limbs. Vasodilators may be beneficial but caution must be exercised to avoid aggravating an already existent hypotension.
CAFERGOT DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Procedure: For the best results, dosage should start at the first sign of an attack. Adults: Take 2 tablets at the start of attack; 1 additional tablet every ½ hour, if needed for full relief (maximum 6 tablets per attack, 10 per week).
Maximum Adult Dosage: Total dose for any one attack should not exceed 6 tablets. Total weekly dosage should not exceed 10 tablets. Ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets should not be used for chronic daily administration. In carefully selected patients, with due consideration of maximum dosage recommendations, administration of the drug at bedtime may be an appropriate short-term preventive measure.
HOW SUPPLIED
CAFERGOT®(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) for oral administration are available as:
1 mg/100 mg: round tablets, film coated beige, debossed SZ 183 on one side and plain on the reverse side and supplied as:
Box of 30 Unit-Dose Tablets NDC 0179-0089-70
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) (see USP controlled room temperature).
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
Manufactured by:
SANDOZ INC.
Princeton, NJ 08540
Repackaged by:
KAISER FOUNDATION HOSPITALS
Livermore, CA 94551
CAFERGOT(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine tablets, USP) Package Label

CAFERGOT
Ergotamine Tartrate and Caffeine TABLET
Product Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Human prescription drug label | Item Code (Source) | NDC:0179-0089(NDC:0781-5405) |
| Route of Administration | ORAL | DEA Schedule |
Active Ingredient/Active Moiety |
||
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Basis of Strength | Strength |
| ERGOTAMINE TARTRATE ERGOTAMINE | 1 mg | |
| CAFFEINE | 100 mg |
Inactive Ingredients |
|
|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Strength |
| FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE | |
| ferric oxide red | |
| MAGNESIUM STEARATE | |
| cellulose, microcrystalline | |
| polyethylene glycol | |
| POLYVINYL ALCOHOL | |
| SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO | |
| talc | |
| titanium dioxide | |
| FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW |
Product Characteristics |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Size | Imprint Code | Shape |
| WHITE (Beige) | 10 mm | SZ;183 | ROUND |
Packaging |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Item Code | Package Description | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| 1 | NDC:0179-0089-70 | 30 in 1 BOX, UNIT-DOSE |
Marketing Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| ANDA | ANDA084294 | 2011-04-21 |
Cafergot Prescribing Information
Package insert / product label
Generic name: ergotamine tartrate and caffeine
Dosage form: Suppositories
Drug class: Antimigraine agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 24, 2023.
On This Page
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Indications and Usage
- Contraindications
- Warnings
- Precautions
- Patient Counseling Information
- Drug Interactions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Abuse and Dependence
- Overdosage
- Dosage and Administration
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
WARNING
Serious and/or life-threatening peripheral ischemia has been associated with the coadministration of CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) with potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors including protease inhibitors and macrolide antibiotics. Because CYP 3A4 inhibition elevates the serum levels of CAFERGOT, the risk for vasospasm leading to cerebral ischemia and/or ischemia of the extremities is increased. Hence, concomitant use of these medications is contraindicated. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS)
CAFERGOT®
(ergotamine tartrate and caffeine)
SUPPOSITORIES, USP
Rx only
Cafergot Description
CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) Suppository
ergotamine tartrate USP……………………………………………………………2 mg
caffeine USP…………………………………………………………………….100 mg
Inactive Ingredients: cocoa butter NF and tartaric acid NF.
CAFERGOT suppositories are sealed in foil to afford protection from cocoa butter leakage. If an unavoidable period of exposure to heat softens the suppository, it should be chilled in ice-cold water to solidify it before removing the foil.
Cafergot — Clinical Pharmacology
Ergotamine is an alpha adrenergic blocking agent with a direct stimulating effect on the smooth muscle of peripheral and cranial blood vessels and produces depression of central vasomotor centers. The compound also has the properties of serotonin antagonism. In comparison to hydrogenated ergotamine, the adrenergic blocking actions are less pronounced and vasoconstrictive actions are greater.
Caffeine, also a cranial vasoconstrictor, is added to further enhance the vasoconstrictive effect without the necessity of increasing ergotamine dosage.
Many migraine patients experience excessive nausea and vomiting during attacks, making it impossible for them to retain any oral medication. In such cases, therefore, the only practical means of medication is through the rectal route where medication may reach the cranial vessels directly, evading the splanchnic vasculature and the liver.
Pharmacokinetics
Interactions
Pharmacokinetic interactions (increased blood levels of ergotamine) have been reported in patients treated orally with ergotamine and macrolide antibiotics (e.g., troleandomycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin), and in patients treated orally with ergotamine and protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir) presumably due to inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A metabolism of ergotamine (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Ergotamine has also been shown to be an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 3A catalyzed reactions. No pharmacokinetic interactions involving other cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are known.
Indications and Usage for Cafergot
CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine)
Indicated as therapy to abort or prevent vascular headache, e.g., migraine, migraine variants or so-called “histaminic cephalalgia”.
Contraindications
Coadministration of ergotamine with potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors (ritonavir, nelfinavir, indinavir, erythromycin, clarithromycin, and troleandomycin) has been associated with acute ergot toxicity (ergotism) characterized by vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions), with some cases resulting in amputation. There have been rare reports of cerebral ischemia in patients on protease inhibitor therapy when CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) was coadministered, at least one resulting in death. Because of the increased risk for ergotism and other serious vasospastic adverse events, ergotamine use is contraindicated with these drugs and other potent inhibitors of CYP 3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole) (see WARNINGS: CYP 3A4 Inhibitors).
CAFERGOT may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. CAFERGOT is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this product, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Peripheral vascular disease, coronary heart disease, hypertension, impaired hepatic or renal function and sepsis.
Hypersensitivity to any of the components.
Warnings
CYP 3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., Macrolide Antibiotics and Protease Inhibitors)
Coadministration of ergotamine with potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors such as protease inhibitors or macrolide antibiotics has been associated with serious adverse events; for this reason, these drugs should not be given concomitantly with ergotamine (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). While these reactions have not been reported with less potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors, there is a potential risk for serious toxicity including vasospasm when these drugs are used with ergotamine. Examples of less potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors include: saquinavir, nefazodone, fluconazole, fluoxetine, grapefruit juice, fluvoxamine, zileuton, metronidazole, and clotrimazole. These lists are not exhaustive, and the prescriber should consider the effects on CYP 3A4 of other agents being considered for concomitant use with ergotamine.
Fibrotic Complications
There have been a few reports of patients on CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) therapy developing retroperitoneal and/or pleuropulmonary fibrosis. There have also been rare reports of fibrotic thickening of the aortic, mitral, tricuspid, and/or pulmonary valves with long-term continuous use of CAFERGOT. CAFERGOT suppositories should not be used for chronic daily administration (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Precautions
General
Although signs and symptoms of ergotism rarely develop even after long term intermittent use of the rectally administered drug, care should be exercised to remain within the limits of recommended dosage.
Ergotism is manifested by intense arterial vasoconstriction, producing signs and symptoms of peripheral vascular ischemia. Ergotamine induces vasoconstriction by a direct action on vascular smooth muscle. In chronic intoxication with ergot derivatives, headache, intermittent claudication, muscle pains, numbness, coldness and pallor of the digits may occur. If the condition is allowed to progress untreated, gangrene can result.
While most cases of ergotism associated with ergotamine treatment result from frank overdosage, some cases have involved apparent hypersensitivity. There are few reports of ergotism among patients taking doses within the recommended limits or for brief periods of time. In rare instances, patients, particularly those who have used the medication indiscriminately over long periods of time, may display withdrawal symptoms consisting of rebound headache upon discontinuation of the drug.
Rare cases of a solitary rectal or anal ulcer have occurred from abuse of ergotamine suppositories usually in higher than recommended doses or with continual use at the recommended dose for many years. Spontaneous healing occurs within usually 4-8 weeks after drug withdrawal.
Information for Patients
Patients should be advised that one suppository of CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) should be taken at the first sign of a migraine headache. No more than 2 suppositories should be taken for any single migraine attack. No more than 5 suppositories should be taken during any 7-day period. Administration of CAFERGOT suppositories should not exceed the dosing guidelines and should not be used for chronic daily administration (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). CAFERGOT should be used only for migraine headaches. It is not effective for other types of headaches and it lacks analgesic properties. Patients should be advised to report to the physician immediately any of the following: numbness or tingling in the fingers and toes, muscle pain in the arms and legs, weakness in the legs, pain in the chest or temporary speeding or slowing of the heart rate, swelling or itching.
Drug Interactions
CYP 3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., Macrolide Antibiotics and Protease Inhibitors)
(See CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS.)
CAFERGOT should not be administered with other vasoconstrictors. Use with sympathomimetics (pressor agents) may cause extreme elevation of blood pressure. The beta-blocker Inderal (propranolol) has been reported to potentiate the vasoconstrictive action of CAFERGOT by blocking the vasodilating property of epinephrine. Nicotine may provoke vasoconstriction in some patients, predisposing to a greater ischemic response to ergot therapy.
The blood levels of ergotamine-containing drugs are reported to be elevated by the concomitant administration of macrolide antibiotics and vasospastic reactions have been reported with therapeutic doses of the ergotamine-containing drugs when coadministered with these antibiotics.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category X: There are no studies on the placental transfer or teratogenicity of the combined products of CAFERGOT. Caffeine is known to cross the placenta and has been shown to be teratogenic in animals. Ergotamine crosses the placenta in small amounts, although it does not appear to be embryotoxic in this quantity. However, prolonged vasoconstriction of the uterine vessels and/or increased myometrial tone leading to reduced myometrial and placental blood flow may have contributed to fetal growth retardation observed in animals. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Nonteratogenic Effects
CAFERGOT is contraindicated in pregnancy due to the oxytocic effects of ergotamine. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Labor and Delivery
CAFERGOT is contraindicated in labor and delivery due to its oxytocic effect which is maximal in the third trimester. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Nursing Mothers
Ergot drugs are known to inhibit prolactin but there are no reports of decreased lactation with CAFERGOT. Ergotamine is excreted in breast milk and may cause symptoms of vomiting, diarrhea, weak pulse and unstable blood pressure in nursing infants. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from CAFERGOT, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Cardiovascular: Vasoconstrictive complications of a serious nature may occur at times. These include ischemia, cyanosis, absence of pulse, cold extremities, gangrene, precordial distress and pain, EKG changes and muscle pains. Although these effects occur most commonly with long-term therapy at relatively high doses, they have also been reported with short-term or normal doses. Other cardiovascular adverse effects include transient tachycardia or bradycardia and hypertension.
Gastrointestinal: Nausea and vomiting; rectal or anal ulcer (from overuse of suppositories).
Neurological: paresthesias, numbness, weakness, and vertigo.
Allergic: Localized edema and itching.
Fibrotic Complications: (See WARNINGS.)
Drug Abuse and Dependence
There have been reports of drug abuse and psychological dependence in patients on CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) therapy. Due to the chronicity of vascular headaches, it is imperative that patients be advised not to exceed recommended dosages with long-term use to avoid ergotism. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Overdosage
The toxic effects of an acute overdosage of CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) are due primarily to the ergotamine component. The amount of caffeine is such that its toxic effects will be overshadowed by those of ergotamine. Symptoms include vomiting, numbness, tingling, pain and cyanosis of the extremities associated with diminished or absent peripheral pulses; hypertension or hypotension; drowsiness, stupor, coma, convulsions and shock. A case has been reported of reversible bilateral papillitis with ring scotomata in a patient who received five times the recommended daily adult dose over a period of 14 days.
Treatment consists of removal of the offending drug by enema. Maintenance of adequate pulmonary ventilation, correction of hypotension, and control of convulsions and blood pressure are important considerations. Treatment of peripheral vasospasm should consist of warmth, but not heat, and protection of the ischemic limbs. Vasodilators may be beneficial but caution must be exercised to avoid aggravating an already existent hypotension.
Cafergot Dosage and Administration
Procedure
For the best results, dosage should start at the first sign of an attack.
| RECTALLY | One suppository at start of attack; second suppository after 1 hour, if needed for full relief 1 hr. |
|
 |
 |
Early Aministration Gives Maximum Effectiveness
Maximum Adult Dosage
Rectally
Two suppositories is the maximum dose for an individual attack.
Total weekly dosage should not exceed 5 suppositories. CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) suppositories should not be used for chronic daily administration.
In carefully selected patients, with due consideration of maximum dosage recommendations, administration of the drug at bedtime may be an appropriate short-term preventive measure.
How is Cafergot supplied
CAFERGOT® (ergotamine tartrate and caffeine) Suppositories, USP
Yellowish-white bullet-shaped, cocoa butter base suppositories wrapped in silver colored foil with “CAFERGOT® SUPPOSITORY 78-33 NOVARTIS” printed in fuchsia.
Boxes of 12 (NDC 0078-0033-02).
Store and Dispense
Below 77ºF (25ºC); tight container (sealed foil). Protect from moisture.
T2002-68
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
©Novartis
| CAFERGOT ergotamine tartrate and caffeine suppository |
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
Labeler — Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
Medical Disclaimer
Усиливает действие других средств, содержащих алкалоиды спорыньи и кофеин.
При совместном применении Кофетамина и барбитуратов, примидона, противосудорожных средств — производных гидантоина (фенитоин) возможно усиление метаболизма и увеличение клиренса кофеина.
При совместном применении Кофетамина и циметидина, пероральных контрацептивов, дисульфирама, ципрофлоксацина, норфлоксацина возможно снижение метаболизма кофеина в печени, замедление его выведения и увеличение концентрации в крови.
При совместном применении Кофетамина и средств, вызывающих стимуляцию ЦНС, возможна чрезмерная стимуляция ЦНС.
Кофеин является антагонистом аденозина.
Мексилетин снижает выведение кофеина до 50%; никотин увеличивает скорость выведения кофеина.
Большие дозы кофеина могут вызывать развитие опасных аритмий сердца или выраженного повышения АД на фоне приема ингибиторов МАО (фуразолидон, прокарбазин, селегилин).
Кофеин снижает всасывание препаратов кальция (кальция глюконат, кальция карбонат, комбинация кальция с витамином D) в ЖКТ.
Кофетамин снижает эффект наркотических анальгетиков и снотворных лекарств, увеличивает выведение препаратов лития (лития карбонат) с мочой, ускоряет всасывание, усиливает действие, повышает их токсичность сердечных гликозидов (дигоксин, целанид).
Совместное применение Кофетамина с бета-адреноблокаторами (атенолол, метопролол, небиволол) может приводить к взаимному подавлению терапевтических эффектов; с адренергическими бронхорасширяющими средствами (кленбутерол, сальбутамол, фенотерол) — к дополнительной стимуляции ЦНС и аддитивным токсическим эффектам.
Кофеин может снижать клиренс теофиллина и аминофиллина, увеличивая возможность аддитивных фармакодинамических и токсических эффектов.
Сосудосуживающее действие Кофетамина усиливают альфа-адреностимуляторы, бета-адреноблокаторы, агонисты серотонина (в т.ч. суматриптан) и никотин.
Макролиды (эритромицин, спирамицин, джозамицин, мидекамицин, кларитромицин, азитромицин, рокситромицин) увеличивают токсичность эрготамина.
Cafergot (Oral)
Generic name: ergotamine and caffeine [ er-GOT-a-meen-TAR-trate, KAF-een ]
Drug class: Antimigraine agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 22, 2023.
Uses for Cafergot
Ergotamine and caffeine combination is used to treat or prevent vascular headaches, including migraine, migraine variants, or histaminic cephalalgia. It will not relieve pain other than from migraine headaches.
This medicine is available only with your doctor’s prescription.
Before using Cafergot
In deciding to use a medicine, the risks of taking the medicine must be weighed against the good it will do. This is a decision you and your doctor will make. For this medicine, the following should be considered:
Allergies
Tell your doctor if you have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to this medicine or any other medicines. Also tell your health care professional if you have any other types of allergies, such as to foods, dyes, preservatives, or animals. For non-prescription products, read the label or package ingredients carefully.
Pediatric
Appropriate studies have not been performed on the relationship of age to the effects of ergotamine and caffeine combination in the pediatric population. Safety and efficacy have not been established.
Geriatric
No information is available on the relationship of age to the effects of ergotamine and caffeine combination in geriatric patients.
Breast Feeding
Caffeine
Studies in women suggest that this medication poses minimal risk to the infant when used during breastfeeding.
Ergotamine
There are no adequate studies in women for determining infant risk when using this medication during breastfeeding. Weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks before taking this medication while breastfeeding.
Interactions with Medicines
Although certain medicines should not be used together at all, in other cases two different medicines may be used together even if an interaction might occur. In these cases, your doctor may want to change the dose, or other precautions may be necessary. When you are taking this medicine, it is especially important that your healthcare professional know if you are taking any of the medicines listed below. The following interactions have been selected on the basis of their potential significance and are not necessarily all-inclusive.
Using this medicine with any of the following medicines is not recommended. Your doctor may decide not to treat you with this medication or change some of the other medicines you take.
- Almotriptan
- Amprenavir
- Atazanavir
- Boceprevir
- Clarithromycin
- Cobicistat
- Conivaptan
- Darunavir
- Delavirdine
- Dopamine
- Eletriptan
- Erythromycin
- Fosamprenavir
- Frovatriptan
- Idelalisib
- Indinavir
- Itraconazole
- Ketoconazole
- Letermovir
- Levoketoconazole
- Lopinavir
- Mifepristone
- Naratriptan
- Nefazodone
- Nelfinavir
- Nirmatrelvir
- Posaconazole
- Riociguat
- Ritonavir
- Rizatriptan
- Saquinavir
- Sumatriptan
- Telaprevir
- Telithromycin
- Tipranavir
- Troleandomycin
- Viloxazine
- Voriconazole
- Zolmitriptan
Using this medicine with any of the following medicines is usually not recommended, but may be required in some cases. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
- Abametapir
- Adagrasib
- Alefacept
- Asciminib
- Avacopan
- Azithromycin
- Belzutifan
- Berotralstat
- Capmatinib
- Ceritinib
- Crizotinib
- Dabrafenib
- Eluxadoline
- Enzalutamide
- Erdafitinib
- Fedratinib
- Fexinidazole
- Fluconazole
- Fluvoxamine
- Fosnetupitant
- Givosiran
- Imatinib
- Iobenguane I 131
- Ivacaftor
- Lanreotide
- Lefamulin
- Lenacapavir
- Lorlatinib
- Lumacaftor
- Mavacamten
- Mitotane
- Mobocertinib
- Netupitant
- Octreotide
- Omaveloxolone
- Palbociclib
- Pazopanib
- Peginterferon Alfa-2b
- Phenobarbital
- Pirtobrutinib
- Pixantrone
- Primidone
- Propatyl Nitrate
- Ranolazine
- Ribociclib
- Ritlecitinib
- Selpercatinib
- Sibutramine
- Sotorasib
- Taurursodiol
- Tocilizumab
- Trofinetide
- Tucatinib
- Voxelotor
Using this medicine with any of the following medicines may cause an increased risk of certain side effects, but using both drugs may be the best treatment for you. If both medicines are prescribed together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use one or both of the medicines.
- Nevirapine
- Propranolol
Interactions with Food/Tobacco/Alcohol
Certain medicines should not be used at or around the time of eating food or eating certain types of food since interactions may occur. Using alcohol or tobacco with certain medicines may also cause interactions to occur. The following interactions have been selected on the basis of their potential significance and are not necessarily all-inclusive.
Using this medicine with any of the following is usually not recommended, but may be unavoidable in some cases. If used together, your doctor may change the dose or how often you use this medicine, or give you special instructions about the use of food, alcohol, or tobacco.
- Grapefruit Juice
- Tobacco
Other Medical Problems
The presence of other medical problems may affect the use of this medicine. Make sure you tell your doctor if you have any other medical problems, especially:
- Allergy to aspirin—Use with caution. This medicine contains a yellow dye called tartrazine, which may cause allergic reactions (including asthma) in patients with this condition.
- Heart or blood vessel disease (eg, coronary heart disease, peripheral vascular disease) or
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) or
- Infection (eg, sepsis), severe or
- Kidney disease or
- Liver disease—Should not be used in patients with these conditions.
Proper use of Cafergot
Use this medicine only as directed by your doctor. Do not take more of it, do not take it more often, and do not take it for a longer time than your doctor ordered. If too much of this medicine is taken for a long time, it may become habit-forming (causing serious unwanted effects).
This medicine works best if you take it at the first sign of a migraine headache.
Do not eat grapefruit or drink grapefruit juice while you are using this medicine.
Dosing
The dose of this medicine will be different for different patients. Follow your doctor’s orders or the directions on the label. The following information includes only the average doses of this medicine. If your dose is different, do not change it unless your doctor tells you to do so.
The amount of medicine that you take depends on the strength of the medicine. Also, the number of doses you take each day, the time allowed between doses, and the length of time you take the medicine depend on the medical problem for which you are using the medicine.
- For oral dosage form (tablets):
- For migraine headaches:
- Adults—2 tablets at the first sign of a migraine attack, followed by 1 tablet every 30 minutes if needed. Each tablet contains 1 milligram (mg) ergotamine and 100 mg caffeine. Do not use more than 6 tablets in a day or 10 tablets in a week.
- Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
- For migraine headaches:
Missed Dose
If you miss a dose of this medicine, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule. Do not double doses.
Storage
Store the medicine in a closed container at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct light. Keep from freezing.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Do not keep outdated medicine or medicine no longer needed.
Ask your healthcare professional how you should dispose of any medicine you do not use.
Precautions while using Cafergot
It is very important that your doctor check your progress at regular visits. This will allow your doctor to see if the medicine is working properly and to decide if you should continue to use it.
Using this medicine could harm your unborn baby. Use an effective form of birth control to keep from getting pregnant. Tell your doctor right away if you think you have become pregnant.
Do not use this medicine together with clarithromycin (Biaxin®), erythromycin (Erythrocin®), indinavir (Crixivan®), itraconazole (Sporanox®), ketoconazole (Nizoral®), nelfinavir (Viracept®), ritonavir (Norvir®), or troleandomycin (Tao®).
This medicine may be habit-forming. If you feel that the medicine is not working as well, do not use more than your prescribed dose. Call your doctor for instructions.
If you think you or someone else may have taken an overdose of this medicine, get emergency help at once. Signs of an overdose include: blurred vision, change in consciousness, dizziness, faintness, or lightheadedness when getting up suddenly from a lying position, headache, nervousness, numbness, tingling, pain, and bluish color of the fingernails, lips, skin, palms, or nail beds, loss of consciousness, pale, clammy skin, pounding in the ears, sweating, unusual tiredness or weakness, or vomiting.
This medicine may cause stomach problems (eg, retroperitoneal fibrosis). Check with your doctor right away if you have continuing or severe stomach pain, increased frequency of urination, continuing loss of appetite, lower back pain, continuing or severe nausea and vomiting, or weakness.
Check with your doctor right away if you have chest pain or tightness, or trouble breathing. These may be symptoms of a lung problem (eg, pleuropulmonary fibrosis).
Do not take other medicines unless they have been discussed with your doctor. This includes prescription or nonprescription (over-the-counter [OTC]) medicines and herbal or vitamin supplements.
Side Effects of Cafergot
Along with its needed effects, a medicine may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur:
Incidence not known
- Chest pain, discomfort, or tightness
- cold, pale, or a bluish color skin of the fingers or toes
- continuing loss of appetite
- continuing or severe nausea and vomiting
- continuing or severe stomach pain
- increased frequency of urination
- irregular heartbeat
- itching skin
- lower back pain
- numbness or tingling of the fingers or toes
- pain in the fingers or toes
- pain in arms legs, or lower back, especially pain in calves or heels upon exertion
- sweating
- swelling of hands, ankles, feet, or lower legs
- weakness
- weak or absent pulses in the legs
Get emergency help immediately if any of the following symptoms of overdose occur:
Symptoms of overdose
- Blurred vision
- change or loss of consciousness
- cold clammy skin
- decreased awareness or responsiveness
- dizziness, faintness, or lightheadedness when getting up suddenly from a lying or sitting position
- headache
- nervousness
- numbness, tingling, pain, and bluish color of the fingernails, lips, skin, palms, or nail beds
- pounding in the ears
- seizures
- severe sleepiness
- slow or fast heartbeat
- sweating
- unusual tiredness or weakness
- vomiting
Some side effects may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
Incidence not known
- Burning, crawling, itching, numbness, prickling, «pins and needles», or tingling feelings
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- feeling of constant movement of self or surroundings
- sensation of spinning
Other side effects not listed may also occur in some patients. If you notice any other effects, check with your healthcare professional.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Medical Disclaimer