Ацикловир (Aciclovir) инструкция по применению
📜 Инструкция по применению Ацикловир
💊 Состав препарата Ацикловир
✅ Применение препарата Ацикловир
📅 Условия хранения Ацикловир
⏳ Срок годности Ацикловир
Описание лекарственного препарата
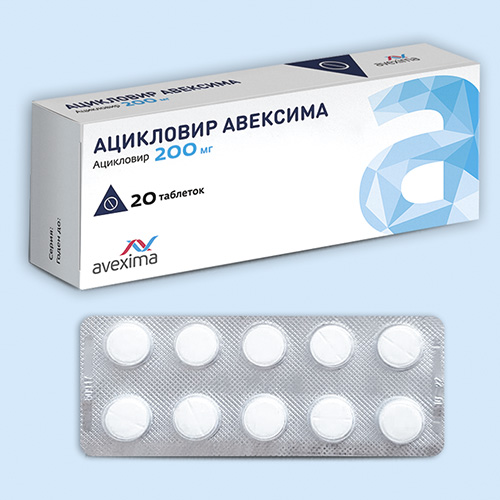
Ацикловир
(Aciclovir)
Основано на официально утвержденной инструкции по применению препарата и подготовлено для электронного издания справочника Видаль 2010 года, дата обновления: 2020.11.16
Владелец регистрационного удостоверения:
Лекарственная форма
| Ацикловир |
Таб. 200 мг: 20 шт. рег. №: ЛП-000199 |
Форма выпуска, упаковка и состав
препарата Ацикловир
10 шт. — упаковки ячейковые контурные (2) — пачки картонные.
Фармакологическое действие
Противовирусный препарат — синтетический аналог ациклического пуринового нуклеозида, обладающего высоко избирательным действием на вирусы герпеса. В инфицированных вирусом клетках под действием вирусной тимидинкиназы происходит фосфорилирование и дальнейшая последовательная трансформация ацикловира в моно-, ди- и трифосфат. Ацикловиртрифосфат встраивается в цепочку вирусной ДНК и блокирует ее синтез посредством конкурентного ингибирования вирусной ДНК-полимеразы.
In vitro ацикловир эффективен против вируса простого герпеса — Herpes simplex 1 и 2 типов; против вируса Varicella zoster, вызывающего ветряную оспу и опоясывающий лишай; более высокие концентрации требуются для ингибирования вируса Эпштейна-Барр. Умеренно активен в отношении цитомегаловируса.
In vivo ацикловир терапевтически и профилактически эффективен, прежде всего, при вирусных инфекциях, вызываемых вирусом Herpes simplex 1 и 2 типов. Предупреждает образование новых элементов сыпи, снижает вероятность кожной диссеминации и висцеральных осложнений, ускоряет образование корок, снижает боль в острой фазе опоясывающего герпеса.
Фармакокинетика
После приема внутрь биологическая доступность составляет 15-30%, при этом создаются дозозависимые концентрации, достаточные для эффективного лечения вирусных заболеваний. Пища не оказывает значительного влияния на всасывание ацикловира. Ацикловир хорошо проникает во многие органы, ткани и жидкости организма. Связывание с белками плазмы составляет 9-33% и не зависит от его концентрации в плазме. Концентрация в спинномозговой жидкости составляет около 50% от его концентрации в плазме. Ацикловир проникает через гематоэнцефалический и плацентарный барьеры, накапливается в грудном молоке. После приема внутрь 1 г/сут концентрация ацикловира в грудном молоке составляет 60-410% от его концентрации в плазме (в организм ребенка с молоком матери ацикловир поступает в дозе 0.3 мг/кг/сут).
Cmax препарата в плазме крови после приема внутрь по 200 мг 5 раз/сут — 0.7 мкг/мл, Cmin— 0.4 мкг/мл; время достижения Cmax в плазме — 1.5-2 ч. Метаболизируется в печени с образованием фармакологически неактивного соединения 9-карбоксиметоксиметилгуанина. Выводится почками путем клубочковой фильтрации и канальцевой секреции: около 84% выводится почками в неизменном виде, 14% — в форме метаболита. Почечный клиренс ацикловира составляет 75-80% от общего плазменного клиренса.T1/2 у взрослых людей с нормальной функцией почек составляет 2-3 ч. У больных с тяжелой почечной недостаточностью T1/2 — 20 ч, при гемодиализе — 5,7 ч, при этом концентрация ацикловира в плазме уменьшается до 60% от исходного значения. Менее 2% ацикловира выводится из организма через кишечник.
Показания препарата
Ацикловир
- лечение инфекций кожи и слизистых оболочек, вызываемых вирусами Herpes simplex 1 и 2 типов, как первичных, так и вторичных, включая генитальный герпес;
- профилактика обострений рецидивирующих инфекций, вызываемых Herpes simplex 1 и 2 типов, у пациентов с нормальным иммунным статусом;
- профилактика первичных и рецидивирующих инфекций, вызываемых вирусами Herpes simplex 1 и 2 типов, у больных с иммунодефицитом;
- в составе комплексной терапии пациентов с выраженным иммунодефицитом: при ВИЧ-инфекции (стадия СПИД, ранние клинические проявления и развернутая клиническая картина) и у пациентов, перенесших трансплантацию костного мозга;
- лечение первичных и рецидивирующих инфекций, вызываемых вирусом Varicella zoster (ветряная оспа, а также опоясывающий лишай — Herpes zoster).
Режим дозирования
Ацикловир принимают во время или сразу после приема пищи и запивают достаточным количеством воды. Режим дозирования устанавливают индивидуально в зависимости от степени тяжести заболевания.
Лечение инфекций кожи и слизистых оболочек, вызываемых Herpes simplex 1 и 2 типов
Взрослые
Ацикловир назначают по 200 мг 5 раз/сут в течение 5 дней с 4-часовым интервалами в течение дня и с 8-часовым интервалом на ночь. В более тяжелых случаях заболевания курс лечения может быть продлен по назначению врача до 10 дней. В составе комплексной терапии при выраженном иммунодефиците, в т.ч. при развернутой клинической картине ВИЧ-инфекции, включая ранние клинические проявления ВИЧ-инфекции и стадию СПИД; после трансплантации костного мозга или при нарушении всасывания из кишечника назначают по 400 мг 5 раз/сут.
Лечение необходимо начинать как можно раньше после возникновения инфекции; при рецидивах ацикловир назначают в продромальном периоде или при проявлении первых элементов сыпи.
Профилактика рецидивов инфекций, вызываемых Herpes simplex 1 и 2 типов у пациентов с нормальным иммунным статусом
Рекомендованная доза составляет по 200 мг 4 раза/сут (каждые 6 ч) или 400 мг 2 раза/сут (каждые 12 ч). В ряде случаев оказываются эффективными более низкие дозы — по 200 мг 3 раза/сут (каждые 8 ч) или 2 раза/сут (каждые 12 ч).
Профилактика инфекций, вызываемых Herpes simplex 1 и 2 типов, у пациентов с иммунодефицитом.
Рекомендуемая доза составляет по 200 мг 4 раза/сут (каждые 6 ч). В случае выраженного иммунодефицита (например, после трансплантации костного мозга) или при нарушении всасывания из кишечника дозу увеличивают до 400 мг 5 раз/сут. Продолжительность профилактического курса терапии определяется длительностью периода существования риска инфицирования.
Лечение инфекций, вызываемых вирусом Varicella zoster (ветряная оспа)
Взрослые
Назначают по 800 мг 5 раз/сут каждые 4 ч днем и с 8-часовым интервалом на ночь. Продолжительность курса лечения 7-10 дней.
Дети
Назначают по 20 мг/кг 4 раза/сут в течение 5 дней (максимальная разовая доза 800 мг), детям от 3-х до 6 лет: по 400 мг 4 раза/сут, старше 6 лет: по 800 мг 4 раза/сут в течение 5 дней.
Лечение необходимо начинать при появлении самых ранних признаков или симптомов ветряной оспы.
Лечение инфекций, вызываемых вирусом Herpes zoster (опоясывающий лишай)
Взрослые
Назначают по 800 мг 4 раза/сут каждые 6 ч в течение 5 дней. Детям в возрасте старше 3 лет препарат назначают в той же дозе, что и взрослым.
Лечение и профилактика инфекций, вызываемых Herpessimplex 1 и 2 типов, пациентов детского возраста с иммунодефицитом и нормальным иммунным статусом.
Дети от 3-х лет до 6 лет — 400 мг раза/сут; старше 6 лет — 800 мг 4 раза/сут. Более точную дозу определяют из расчета 20 мг/кг массы тела, но не более 800 мг раза/сут. Курс лечения составляет 5 дней. Данные о профилактике рецидивов инфекций, вызываемых вирусом простого герпеса, и лечении опоясывающего герпеса у детей с нормальными показателями иммунитета отсутствуют.
Для лечения детей старше 3 лет назначают по 800 мг ацикловира 4 раза/сут каждые 6 ч (как и для лечения взрослых с иммунодефицитом).
В пожилом возрасте происходит снижение клиренса ацикловира в организме параллельно со снижением клиренса креатинина. принимающие большие дозы препарата внутрь, должны получать достаточное количество жидкости. При почечной недостаточности необходимо решить вопрос о снижении дозы препарата.
Необходимо соблюдать осторожность при назначении ацикловира пациентам с почечной недостаточностью. У таких пациентов прием препарата внутрь в рекомендованных дозах с целью лечения и профилактики инфекций, вызываемых вирусом простого герпеса, не приводит к кумуляции препарата до концентраций, превышающих установленные безопасные уровни. Однако, у больных с выраженной почечной недостаточностью (КК меньше 10 мл/мин) дозу ацикловира следует снизить до 200 мг 2 раза/сут с 12-часовыми интервалами.
При лечении инфекций, вызываемых вирусом Varicella zoster, Herpes zoster, a также при лечении пациентов с выраженным иммунодефицитом рекомендуемые дозы составляют:
- терминальная почечная недостаточность (КК менее 10 мл/мин) — по 800 мг 2 раза/сут каждые 12 ч;
- тяжелая почечная недостаточность (КК 10-25 мл/мин) — по 800 мг 3 раза/сут каждые 8 ч.
Побочное действие
Препарат обычно хорошо переносится.
Использована следующая классификация нежелательных реакций в зависимости от частоты встречаемости: очень часто (>1/10), часто (>1/10, <1/100), иногда (>1/1000, <1/100), редко (>1/10 000, <1/1000), очень редко (<1/10 000).
Со стороны пищеварительной системы: часто — тошнота, рвота, диарея; очень редко — гепатит, желтуха, в единичных случаях — абдоминальные боли.
Со стороны системы кроветворения: редко — преходящее незначительное повышение активности ферментов печени, небольшое повышение концентрации мочевины и креатинина, гипербилирубинемия; очень редко — лейкопения, эритропения, анемия, тромбоцитопения.
Со стороны ЦНС: часто — головная боль, головокружение; очень редко — возбуждение, спутанность сознания, тремор, атаксия, дизартрия, галлюцинации, психотические симптомы, судороги, сонливость, энцефалопатия, кома.
Обычно эти побочные эффекты наблюдались у пациентов с почечной недостаточностью или при наличии других провоцирующих факторов, и были, в основном, обратимыми.
Со стороны дыхательной системы: редко — одышка.
Аллергические реакции: анафилактические реакции, кожная сыпь, зуд, крапивница, синдром Лайелла, синдром Стивенса-Джонсона.
Со стороны кожи и подкожной клетчатки: часто — зуд, крапивница, сыпь, в том числе сенсибилизация, редко — алопеция, быстрое диффузное выпадение волос (поскольку такой тип алопеции наблюдается при различных заболеваниях и при терапии многими лекарственными средствами, связь ее с приемом ацикловира не установлена); очень редко синдром Лайелла, синдром Стивенса-Джонсона.
Прочие: часто — утомляемость, лихорадка; редко — периферические отеки, нарушение зрения, лимфаденопатия, миалгия, недомогание.
Противопоказания к применению
- период лактации;
- детский возраст до 3 лет (для данной лекарственной формы).
С осторожностью: беременность; лицам пожилого возраста и пациентам, принимающим большие дозы ацикловира, особенно на фоне дегидратации; нарушение функции почек; неврологические нарушения или неврологические реакции на прием цитотоксических лекарственных средств (в т.ч. в анамнезе).
Применение при беременности и кормлении грудью
Ацикловир проникает через плацентарный барьер и накапливается в грудном молоке. Применение препарата при беременности возможно только в том случае, когда предполагаемая польза для матери превышает потенциальный риск для плода. При необходимости приема ацикловира в период лактации требуется прерывание грудного вскармливания.
Применение при нарушениях функции почек
Принимать с осторожностью при нарушении функции почек.
Необходимо соблюдать осторожность при назначении ацикловира пациентам с почечной недостаточностью. У таких пациентов прием препарата внутрь в рекомендованных дозах с целью лечения и профилактики инфекций, вызываемых вирусом простого герпеса, не приводит к кумуляции препарата до концентраций, превышающих установленные безопасные уровни. Однако, у больных с выраженной почечной недостаточностью (КК меньше 10 мл/мин) дозу ацикловира следует снизить до 200 мг 2 раза/сут с 12-часовыми интервалами.
При лечении инфекций, вызываемых вирусом Varicella zoster, Herpes zoster, a также при лечении пациентов с выраженным иммунодефицитом рекомендуемые дозы составляют:
- терминальная почечная недостаточность (КК менее 10 мл/мин) — по 800 мг 2 раза/сут каждые 12 ч;
- тяжелая почечная недостаточность (КК 10-25 мл/мин) — по 800 мг 3 раза/сут каждые 8 ч.
Применение у детей
Противопоказан детям до 3 лет.
Применение у пожилых пациентов
В пожилом возрасте происходит снижение клиренса ацикловира в организме параллельно со снижением клиренса креатинина. Принимающие большие дозы препарата внутрь, должны получать достаточное количество жидкости. При почечной недостаточности необходимо решить вопрос о снижении дозы препарата.
Особые указания
Ацикловир применяется строго по назначению врача во избежание осложнений у взрослых и детей старше 3-х лет.
Длительность или повторное лечение ацикловиром больных со сниженным иммунитетом может привести в появлению штаммов вирусов, нечувствительных к его действию. У большинства выявленных штаммов вирусов, нечувствительных к ацикловиру, обнаруживается относительная нехватка вирусной тимидинкиназы; были выделены штаммы с измененной тимидинкиназой или с измененной ДНК-полимеразой. In vitro действие ацикловира на изолированные штаммы вируса Herpes simplex может вызвать появление менее чувствительных штаммов.
С осторожностью препарат назначают пациентам с нарушением функции почек, больным пожилого возраста в связи с увеличением периода полувыведения ацикловира.
При применении препарата необходимо обеспечить поступление достаточного количества жидкости.
При приеме препарата следует контролировать функцию почек (концентрацию мочевины крови и креатинина плазмы крови). Ацикловир не предупреждает передачу герпеса половым путем, поэтому в период лечения необходимо воздержаться от половых контактов, даже при отсутствии клинических проявлений. Необходимо информировать пациентов о возможности передачи вируса генитального герпеса в период высыпаний, а также о случаях бессимптомного вирусоносительства.
Влияние на способность к управлению транспортными средствами и механизмами
Нет данных. Однако следует учитывать, что в период лечения ацикловиром может развиваться головокружение, поэтому необходимо соблюдать осторожность при вождении автотранспорта и занятии потенциально опасными видами деятельности, требующими повышенной концентрации внимания и быстроты психомоторных реакций.
Передозировка
Не зарегистрировано случаев передозировки при пероральном приеме ацикловира. Сообщалось о приеме внутрь 20 г ацикловира. Симптомы: ажитация, кома, судороги, летаргия. Возможна преципитация ацикловира в почечных канальцах, если его концентрация превышает растворимость в почечных канальцах (2.5 мг/мл).
Лечение: симптоматическое.
Лекарственное взаимодействие
Одновременное применение с пробенецидом приводит к увеличению среднего T1/2 и снижению клиренса ацикловира.
Усиление эффекта ацикловира отмечается при одновременном назначении иммуностимуляторов.
При одновременном приеме с нефротоксичными препаратами повышается риск развития нарушения функций почек.
Условия хранения препарата Ацикловир
Препарат хранить в сухом, защищенном от света месте при температуре не выше 25°С. Хранить в недоступном для детей месте.
Срок годности препарата Ацикловир
Срок годности — 2 года. Не применять по истечении срока годности.
Условия реализации
Препарат отпускается по рецепту.
Если вы хотите разместить ссылку на описание этого препарата — используйте данный код
Аналоги препарата
Ацикловир
(ОЗОН, Россия)
Ацикловир
(АТОЛЛ, Россия)
Ацикловир
(НОВОСИБХИМФАРМ, Россия)
Ацикловир
(АВВА РУС, Россия)
Ацикловир
(ТАТХИМФАРМПРЕПАРАТЫ, Россия)
Ацикловир
(ИРБИТСКИЙ ХФЗ, Россия)
Ацикловир
(АЛИУМ, Россия)
Ацикловир
(БЕЛМЕДПРЕПАРАТЫ, Республика Беларусь)
Ацикловир
(ЙОДИЛЛИЯ-ФАРМ, Россия)
Ацикловир
(ТЕХНОФАРМ, Россия)
Все аналоги
Состав:
Применение:
Применяется при лечении:
Страница осмотрена фармацевтом Федорченко Ольгой Валерьевной Последнее обновление 2022-04-07
Внимание!
Информация на странице предназначена только для медицинских работников!
Информация собрана в открытых источниках и может содержать значимые ошибки!
Будьте внимательны и перепроверяйте всю информацию с этой страницы!
Топ 20 лекарств с такими-же компонентами:
Топ 20 лекарств с таким-же применением:
Предоставленная в разделе Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
Asiviral
Предоставленная в разделе Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
Aciclovir
Терапевтические показания
Предоставленная в разделе Терапевтические показания Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Терапевтические показания
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
Крем для наружного применения; Драже; Порошок для приготовления раствора для инфузий
Мазь; Таблетки
Острые герпетические заболевания кожи и слизистых оболочек (вызванные вирусом простого герпеса), включая первичный и рецидивирующий герпес половых органов, неонатальный герпес; герпетические инфекции любой локализации у больных с иммунодефицитом (лечение и профилактика); опоясывающий лишай, ветряная оспа.
Для системного применения:
— лечение инфекций кожи и слизистых оболочек, вызванных вирусами Herpes simplex типа I и II (первичные и вторичные, включая генитальный герпес);
— профилактика обострений рецидивирующих инфекций, вызванных вирусами Herpes simplex типа I и II, у пациентов с нормальным иммунным статусом;
— профилактика первичных и рецидивирующих инфекций, вызванных вирусами Herpes simplex типа I и II, у больных с иммунодефицитом;
— в составе комплексной терапии пациентов с выраженным иммунодефицитом: при ВИЧ-инфекции (стадия СПИДа, ранние клинические проявления и развернутая клиническая картина) и у пациентов, перенесших трансплантацию костного мозга;
— лечение первичных и рецидивирующих инфекций, вызванных вирусом Varicella zoster (ветряная оспа, опоясывающий лишай).
Для наружного применения: простой герпес кожи, генитальный герпес (простой и рецидивирующий), лабиальный герпес; опоясывающий лишай и ветряная оспа.
Способ применения и дозы
Предоставленная в разделе Способ применения и дозы Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Способ применения и дозы
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
Крем для наружного применения; Драже; Порошок для приготовления раствора для инфузий
Мазь; Таблетки
Таблетки, покрытые пленочной оболочкой
Внутрь: по 200 мг 4–5 раз в сутки при простом герпесе, герпесе половых органов; по 400 мг 5 раз в сутки для профилактики герпеса у пациентов, которым проводится активная иммуносупрессивная терапия (при трансплантации органов); по 400–800 мг 5 раз в сутки при опоясывающем лишае.
В/в: по 15–30 мг/кг/сут при первичном генитальном герпесе, неонатальном герпесе, опоясывающем лишае, ветряной оспе у больных с врожденным нарушением иммунного ответа или вторичными иммунными дефектами; детям от 3 мес до 12 лет — 250–500 мг/м2 /сут.
Накожно (крем): 5 раз в сутки (каждые 4 ч) наносят на пораженные участки кожи для снижения боли и отека при повторных высыпаниях герпеса на гениталиях и лице.
Внутрь, во время или сразу после приема пищи, запивая достаточным количеством воды. При лечении инфекций кожи и слизистых оболочек, вызванных Herpes simplex I или II, взрослым и детям старше 2 лет — по 200 мг 5 раз в сутки в течение 5 дней с 4 ч интервалами в течении дня и с 8 ч интервалом на ночь (при необходимости курс может быть продлен). В составе комплексной терапии при выраженном иммунодефиците (в т.ч. при развернутой клинической картине ВИЧ-инфекции, включая ранние клинические проявления ВИЧ-инфекции и СПИДа), после трансплантации костного мозга — по 400 мг 5 раз в сутки.
Для профилактики рецидивов инфекций, вызванных Herpes simplex I или II, пациентам с нормальным иммунным статусом и при рецидиве заболевания — по 200 мг 4 раза в сутки каждые 6 ч (максимальная доза — до 400 мг 5 раз в сутки в зависимости от тяжести инфекции).
При лечении инфекций, вызванных Varicella zoster, взрослым и детям массой более 40 кг — по 800 мг 5 раз в сутки каждые 4 ч днем и с 8 ч интервалом на ночь. Продолжительность лечения — 7–10 дней. Детям старше 2 лет — по 20 мг/кг 4 раза в сутки в течение 5 дней.
При лечении инфекций, вызванных Herpes zoster, взрослым — по 800 мг 4 раза в сутки каждые 6 ч днем в течение 5 дней.
При нарушении функции почек при лечении и профилактике инфекций, вызванных Herpes simplex, у больных с Cl креатинина менее 10 мл/мин дозу препарата снижают до 200 мг 2 раза в сутки с 12 ч интервалом.
При лечении и профилактике инфекций, вызванных Varicella zoster, у больных с Cl креатинина менее 10 мл/мин дозу препарата снижают до 800 мг 2 раза в сутки с 12 ч интервалом, при Cl креатинина до 25 мл/мин — по 800 мг 3 раза в сутки с 8 ч интервалом.
Наружно, мазь наносят на пораженную поверхность 5 раз в сутки (через 4 ч). Продолжительность лечения — 5–10 дней.
Наружно. Препарат наносят тонким слоем на пораженные и граничащие с ними участки кожи 5 раз в день (каждые 4 ч, за исключением ночного времени). Крем наносят ватным тампоном либо чистыми руками, чтобы избежать дополнительного инфицирования пораженных участков. Важно начать лечение как можно раньше, желательно при появлении первых признаков и симптомов (в продромальном периоде или при покраснении). Лечение также может начаться на более поздних стадиях (папулы или пузыри).
Терапию следует продолжать до того времени, пока на пузырьках не образуется корка, либо пока они полностью не заживут. Длительность лечения — не менее 5 дней, лечение может быть продолжено до 10 дней. В случае сохранения симптомов заболевания более 10 дней следует обратиться к врачу.
Противопоказания
Предоставленная в разделе Противопоказания Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Противопоказания
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
Крем для наружного применения; Драже; Порошок для приготовления раствора для инфузий
Мазь; Таблетки
Гиперчувствительность.
Гиперчувствительность, в т.ч. к ацикловиру или компонентам препарата, кормление грудью; с осторожностью — дегидратация, почечная недостаточность, неврологические нарушения, в т.ч. в анамнезе.
Побочные эффекты
Предоставленная в разделе Побочные эффекты Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Побочные эффекты
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
Крем для наружного применения; Драже; Порошок для приготовления раствора для инфузий
Мазь; Таблетки
Диспептические явления, головная боль, головокружение, аллергические реакции.
При приеме внутрь.
Со стороны нервной системы и органов чувств: редко — головная боль, слабость; в отдельных случаях — тремор, головокружение, повышенная утомляемость, сонливость, галлюцинации.
Со стороны органов ЖКТ: в единичных случаях — боль в животе, тошнота, рвота, диарея.
Аллергические реакции: кожная сыпь.
Прочие: транзиторное повышение активности ферментов печени; редко — повышение уровня мочевины и креатинина, гипербилирубинемия, лейкопения, эритропения, алопеция, лихорадка.
При наружном применении: возможно покраснение, зуд, шелушение, жжение или покалывание в месте аппликации; в редких случаях — аллергический дерматит.
Передозировка
Предоставленная в разделе Передозировка Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Передозировка
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
Симптомы: при в/в введении — повышение уровня сывороточного креатинина, азота мочевины крови, почечная недостаточность, неврологические симптомы (спутанность сознания, галлюцинации, возбуждение, судороги и кома).
Лечение: гемодиализ значительно усиливает выведение ацикловира из крови и может быть оптимальным методом лечения при его передозировке.
Нет данных о передозировке при использовании в виде глазной мази.
Фармакодинамика
Предоставленная в разделе Фармакодинамика Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Фармакодинамика
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
Обладает высокой специфичностью в отношении вируса простого герпеса (Herpes simplex) типа I и II, вируса, вызывающего ветряную оспу и опоясывающий лишай (Varicella zoster), вируса Эпштейна — Барр и цитомегаловируса.
Фармакокинетика
Предоставленная в разделе Фармакокинетика Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Фармакокинетика
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
При приеме внутрь биодоступность составляет 15–30%, Cmax достигается через 1,5–2 ч. Концентрация после назначения внутрь 200 мг 5 раз в сутки составляет 0,7 мкг/мл. Связывание с белками плазмы составляет 9–33% и не зависит от концентрации ацикловира в плазме. Хорошо проникает во все органы и ткани, включая головной мозг и кожу. Концентрация в спинномозговой жидкости составляет 50% от концентрации в плазме. Проходит через плацентарный барьер, накапливается в грудном молоке. Метаболизируется в печени с образованием фармакологически неактивного производного — 9-карбоксиметоксиметилгуанина. T1/2 у взрослых с нормальной функцией почек — 2–3 ч, при тяжелой почечной недостаточности — 20 ч, у больных при гемодиализе — 5,7 ч (при этом концентрация ацикловира в плазме уменьшается до 60% от исходного значения). Выводится почками (84% — в неизмененном виде, 14% — в виде метаболита), менее 2% — через кишечник. Почечный клиренс составляет 75–80% от общего клиренса.
Фармокологическая группа
Предоставленная в разделе Фармокологическая группа Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Фармокологическая группа
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
- Противовирусное средство [Противовирусные (за исключением ВИЧ) средства]
Взаимодействие
Предоставленная в разделе Взаимодействие Asiviralинформация составлена на основе данных о другом лекарстве с точно таким же составом как лекарство Asiviral. Будьте
внимательны и обязательно уточняйте информацию по разделу Взаимодействие
в инструкции к лекарству Asiviral непосредственно из упаковки или у фармацевта в аптеке.
more…
При приеме внутрь: пробенецид увеличивает средний T1/2 и снижает клиренс ацикловира, нефротоксичные препараты повышают риск нарушения функции почек. При наружном применении: взаимодействия с др. ЛС не выявлено.
Asiviral цена
У нас нет точных данных по стоимости лекарства.
Однако мы предоставим данные по каждому действующему веществу
Средняя стоимость Aciclovir 800 mg за единицу в онлайн аптеках от 0.69$ до 1.08$, за упаковку от 38$ до 73$.
Средняя стоимость Aciclovir 200 mg за единицу в онлайн аптеках от 0.53$ до 1.2$, за упаковку от 30$ до 40$.
Средняя стоимость Aciclovir 400 mg за единицу в онлайн аптеках от 0.62$ до 0.62$, за упаковку от 35$ до 35$.
Источники:
- https://www.drugs.com/search.php?searchterm=asiviral
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=asiviral
Доступно в странах
Найти в стране:
А
Б
В
Г
Д
Е
З
И
Й
К
Л
М
Н
О
П
Р
С
Т
У
Ф
Х
Ч
Ш
Э
Ю
Я
Components:
Method of action:
Treatment option:
Medically reviewed by Fedorchenko Olga Valeryevna, PharmD. Last updated on 2022-04-07
Attention!
Information on this page is intended only for medical professionals!
Information is collected in open sources and may contain significant errors!
Be careful and double-check all the information on this page!
Top 20 medicines with the same components:
Top 20 medicines with the same treatments:
The information provided in of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Asiviral
The information provided in of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Aciclovir
Therapeutic indications
The information provided in Therapeutic indications of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Therapeutic indications in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Asiviral Tablets are indicated for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections of the skin and mucous membranes including initial and recurrent genital herpes (excluding neonatal HSV and severe HSV infections in immunocompromised children).
Asiviral Tablets are indicated for the suppression (prevention of recurrences) of recurrent herpes simplex infections in immunocompetent patients.
Asiviral Tablets are indicated for the prophylaxis of herpes simplex infections in immunocompromised patients.
Asiviral Tablets are indicated for the treatment of varicella (chickenpox) and herpes zoster (shingles) infections.
Asiviral Tablets are indicated for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections of the skin and mucous membranes including initial and recurrent genital herpes (excluding neonatal HSV and severe HSV infections in immunocompromised children).
Asiviral Tablets are indicated for the suppression (prevention of recurrences) of recurrent herpes simplex infections in immunocompetent patients.
Asiviral Tablets are indicated for the prophylaxis of herpes simplex infections in immunocompromised patients.
Asiviral Tablets are indicated for the treatment of varicella (chickenpox) and herpes zoster (shingles) infections.
Route of administration: Oral.
Dosage (Posology) and method of administration
The information provided in Dosage (Posology) and method of administration of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Dosage (Posology) and method of administration in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Posology
Dosage in adults
Treatment of herpes simplex infections: 200 mg Asiviral should be taken five times daily at approximately four hourly intervals omitting the night time dose. Treatment should continue for 5 days, but in severe initial infections this may have to be extended.
In severely immunocompromised patients (e.g. after marrow transplant) or in patients with impaired absorption from the gut the dose can be doubled to 400 mg Asiviral, or alternatively, intravenous dosing could be considered.
Dosing should begin as early as possible after the start of an infection; for recurrent episodes this should preferably be during the prodromal period or when lesions first appear.
Suppression of herpes simplex infections in immunocompetent patients: 200 mg Asiviral should be taken four times daily at approximately six-hourly intervals.
Many patients may be conveniently managed on a regimen of 400 mg Asiviral twice daily at approximately twelve-hourly intervals.
Dosage titration down to 200 mg Asiviral taken thrice daily at approximately eight-hourly intervals or even twice daily at approximately twelve-hourly intervals may prove effective.
Some patients may experience break-through infection on total daily doses of 800 mg Asiviral.
Therapy should be interrupted periodically at intervals of six to twelve months, in order to observe possible changes in the natural history of the disease.
Prophylaxis of herpes simplex infections in immunocompromised patients: 200 mg Asiviral should be taken four times daily at approximately six-hourly intervals.
In severely immunocompromised patients (e.g. after marrow transplant) or in patients with impaired absorption from the gut, the dose can be doubled to 400 mg Asiviral, or alternatively, intravenous dosing could be considered.
The duration of prophylactic administration is determined by the duration of the period at risk.
Treatment of varicella and herpes zoster infections: 800 mg Asiviral should be taken five times daily at approximately four-hourly intervals, omitting the night time dose. Treatment should continue for seven days.
In severely immunocompromised patients (e.g. after marrow transplant) or in patients with impaired absorption from the gut, consideration should be given to intravenous dosing.
Dosing should begin as early as possible after the start of an infection: Treatment of herpes zoster yields better results if initiated as soon as possible after the onset of the rash. Treatment of chickenpox in immunocompetent patients should begin within 24 hours after onset of the rash.
Paediatric population
Treatment of herpes simplex infections, and prophylaxis of herpes simplex infections in the immunocompromised: Children aged two years and over should be given adult dosages and children below the age of two years should be given half the adult dose.
For treatment on neonatal herpes virus infections, intravenous Asiviral is recommended.
Treatment of varicella infection
6 years and over: 800 mg Asiviral four times daily
2 — 5 years: 400 mg Asiviral four times daily
Under 2 years: 200 mg Asiviral four times daily
Treatment should continue for five days.
Dosing may be more accurately calculated as 20 mg/kg bodyweight (not to exceed 800 mg) Asiviral four times daily.
No specific data are available on the suppression of herpes simplex infections or the treatment of herpes zoster infections in immunocompetent children.
Dosage in the elderly
The possibility of renal impairment in the elderly must be considered and the dosage should be adjusted accordingly (see Dosage in renal impairment below). Adequate hydration of elderly patients taking high oral doses of Asiviral should be maintained.
Dosage in renal impairment
Caution is advised when administering Asiviral to patients with impaired renal function. Adequate hydration should be maintained.
In the management of herpes simplex infections in patients with impaired renal function, the recommended oral doses will not lead to accumulation of Asiviral above levels that have been established safe by intravenous infusion. However for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/minute) an adjustment of dosage to 200 mg Asiviral twice daily at approximately twelve-hourly intervals is recommended.
In the treatment of herpes zoster infections it is recommended to adjust the dosage to 800 mg Asiviral twice daily at approximately twelve hourly intervals for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/minute), and to 800 mg Asiviral three times daily at intervals of approximately eight hours for patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance in the range 10 — 25 ml/minute).
Method of administration:
Oral.
Asiviral tablets may be dispersed in a minimum of 50 ml of water or swallowed whole with a little water. Ensure that patients on high doses of Asiviral are adequately hydrated.
Asiviral tablets may be dispersed in a minimum of 50 ml of water or swallowed whole with a little water. Ensure that patients on high doses of aciclovir are adequately hydrated.
Dosage in adults
Treatment of herpes simplex infections: 200 mg Asiviral should be taken five times daily at approximately four hourly intervals omitting the night time dose. Treatment should continue for 5 days, but in severe initial infections this may have to be extended.
In severely immunocompromised patients (e.g. after marrow transplant) or in patients with impaired absorption from the gut the dose can be doubled to 400 mg Asiviral or alternatively intravenous dosing could be considered.
Dosing should begin as early as possible after the start of an infection; for recurrent episodes this should preferably be during the prodromal period or when lesions first appear.
Suppression of herpes simplex infections in immunocompetent patients: 200 mg Asiviral should be taken four times daily at approximately six-hourly intervals.
Many patients may be conveniently managed on a regimen of 400 mg Asiviral twice daily at approximately twelve-hourly intervals.
Dosage titration down to 200 mg Asiviral taken thrice daily at approximately eight-hourly intervals or even twice daily at approximately twelve-hourly intervals may prove effective.
Some patients may experience break-through infection on total daily doses of 800 mg Asiviral.
Therapy should be interrupted periodically at intervals of six to twelve months, in order to observe possible changes in the natural history of the disease.
Prophylaxis of herpes simplex infections in immunocompromised patients: 200 mg Asiviral should be taken four times daily at approximately six-hourly intervals.
In severely immunocompromised patients (e.g. after marrow transplant) or in patients with impaired absorption from the gut, the dose can be doubled to 400 mg Asiviral, or alternatively, intravenous dosing could be considered.
The duration of prophylactic administration is determined by the duration of the period at risk.
Treatment of varicella and herpes zoster infections: 800 mg Asiviral should be taken five times daily at approximately four-hourly intervals, omitting the night time dose. Treatment should continue for seven days.
In severely immunocompromised patients (e.g. after marrow transplant) or in patients with impaired absorption from the gut, consideration should be given to intravenous dosing.
Dosing should begin as early as possible after the start of an infection: Treatment of herpes zoster yields better results if initiated as soon as possible after the onset of the rash. Treatment of chickenpox in immunocompetent patients should begin within 24 hours after onset of the rash.
Dosage in children
Treatment of herpes simplex infections, and prophylaxis of herpes simplex infections in the immunocompromised: Children aged two years and over should be given adult dosages and children below the age of two years should be given half the adult dose.
For treatment on neonatal herpes virus infections, intravenous aciclovir is recommended.
Treatment of varicella infection
|
6 years and over: |
800 mg Asiviral four times daily. |
|
2 — 5 years: |
400mg Asiviral four times daily. |
|
Under 2 years: |
200mg Asiviral four times daily. |
Treatment should continue for five days.
Dosing may be more accurately calculated as 20 mg/kg bodyweight (not to exceed 800 mg) Asiviral four times daily.
No specific data are available on the suppression of herpes simplex infections or the treatment of herpes zoster infections in immunocompetent children.
Dosage in the elderly:
The possibility of renal impairment in the elderly must be considered and the dosage should be adjusted accordingly (see Dosage in renal impairment below).
Adequate hydration of elderly patients taking high oral doses of aciclovir should be maintained.
Dosage in renal impairment:
Caution is advised when administering aciclovir to patients with impaired renal function. Adequate hydration should be maintained.
In the management of herpes simplex infections in patients with impaired renal function, the recommended oral doses will not lead to accumulation of aciclovir above levels that have been established safe by intravenous infusion. However for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/minute) an adjustment of dosage to 200 mg aciclovir twice daily at approximately twelve-hourly intervals is recommended.
In the treatment of herpes zoster infections it is recommended to adjust the dosage to 800 mg aciclovir twice daily at approximately twelve — hourly intervals for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/minute), and to 800 mg aciclovir three times daily at intervals of approximately eight hours for patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance in the range 10 — 25 ml/minute).
Contraindications
The information provided in Contraindications of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Contraindications in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Special warnings and precautions for use
The information provided in Special warnings and precautions for use of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Special warnings and precautions for use in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Use in patients with renal impairment and in elderly patients:
Asiviral is eliminated by renal clearance, therefore the dose must be adjusted in patients with renal impairment (see 4.2 Posology and Method of Administration).
Elderly patients are likely to have reduced renal function and therefore the need for dose adjustment must be considered in this group of patients. Both elderly patients and patients with renal impairment are at increased risk of developing neurological side effects and should be closely monitored for evidence of these effects. In the reported cases, these reactions were generally reversible on discontinuation of treatment (see 4.8 Undesirable Effects).
Prolonged or repeated courses of Asiviral in severely immune-compromised individuals may result in the selection of virus strains with reduced sensitivity, which may not respond to continued Asiviral treatment.
Hydration status: Care should be taken to maintain adequate hydration in patients receiving high oral doses of Asiviral.
The risk of renal impairment is increased by use with other nephrotoxic drugs.
The data currently available from clinical studies is not sufficient to conclude that treatment with Asiviral reduces the incidence of chickenpox-associated complications in immunocompetent patients.
Paediatric population:
Oral Asiviral should be used in paediatric population mainly for the treatment of non-severe skin and mucosa HSV infections. For the treatment of neonatal HSV and severe HSV infections in immunocompromised children IV Asiviral should be used.
Use in patients with renal impairment and in elderly patients:
Aciclovir is eliminated by renal clearance, therefore the dose must be adjusted in patients with renal impairment (see 4.2 Posology and Method of Administration). Elderly patients are likely to have reduced renal function and therefore the need for dose adjustment must be considered in this group of patients. Both elderly patients and patients with renal impairment are at increased risk of developing neurological side effects and should be closely monitored for evidence of these effects. In the reported cases, these reactions were generally reversible on discontinuation of treatment (see 4.8 Undesirable Effects). Prolonged or repeated courses of aciclovir in severely immune-compromised individuals may result in the selection of virus strains with reduced sensitivity, which may not respond to continued aciclovir treatment.
Hydration status: Care should be taken to maintain adequate hydration in patients receiving high oral doses of aciclovir.
The risk of renal impairment is increased by use with other nephrotoxic drugs.
The data currently available from clinical studies is not sufficient to conclude that treatment with aciclovir reduces the incidence of chickenpox-associated complications in immunocompetent patients.
Effects on ability to drive and use machines
The information provided in Effects on ability to drive and use machines of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Effects on ability to drive and use machines in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
There have been no studies to investigate the effect of Asiviral on driving performance or the ability to operate machinery. A detrimental effect on such activities cannot be predicted from the pharmacology of the active substance, but the adverse event profile should be borne in mind.
There have been no studies to investigate the effect of aciclovir on driving performance or the ability to operate machinery. A detrimental effect on such activities cannot be predicted from the pharmacology of the active substance, but the adverse event profile should be borne in mind.
Undesirable effects
The information provided in Undesirable effects of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Undesirable effects in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
).
Prolonged or repeated courses of Asiviral in severely immune-compromised individuals may result in the selection of virus strains with reduced sensitivity, which may not respond to continued Asiviral treatment.
Hydration status: Care should be taken to maintain adequate hydration in patients receiving high oral doses of Asiviral.
The risk of renal impairment is increased by use with other nephrotoxic drugs.
The data currently available from clinical studies is not sufficient to conclude that treatment with Asiviral reduces the incidence of chickenpox-associated complications in immunocompetent patients.
Paediatric population:
Oral Asiviral should be used in paediatric population mainly for the treatment of non-severe skin and mucosa HSV infections. For the treatment of neonatal HSV and severe HSV infections in immunocompromised children IV Asiviral should be used.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Asiviral is eliminated primarily unchanged in the urine via active renal tubular secretion. Any drugs administered concurrently that compete with this mechanism may increase Asiviral plasma concentrations.
Probenecid and cimetidine increase the AUC of Asiviral by this mechanism, and reduce Asiviral renal clearance. Similarly increases in plasma AUCs of Asiviral and of the inactive metabolite of mycophenolate mofetil, an immunosuppresant agent used in transplant patients have been shown when the drugs are co administered. However no dosage adjustment is necessary because of the wide therapeutic index of Asiviral.
An experimental study on five male subjects indicates that concomitant therapy with Asiviral increases AUC of totally administered theophylline with approximately 50%. It is recommended to measure plasma concentrations during concomitant therapy with Asiviral.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
The use of Asiviral should be considered only when the potential benefits outweigh the possibility of unknown risks. A post-marketing Asiviral pregnancy registry has documented pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to any formulation of Asiviral. The registry findings have not shown an increase in the number of birth defects amongst Asiviral exposed subjects compared with the general population, and any birth defects showed no uniqueness or consistent pattern to suggest a common cause. Systemic administration of Asiviral in internationally accepted standard tests did not produce embryotoxic or teratogenic effects in rabbits, rats or mice. In a non-standard test in rats, foetal abnormalities were observed but only following such high subcutaneous doses that maternal toxicity was produced. The clinical relevance of these findings is uncertain.
Caution should however be exercised by balancing the potential benefits of treatment against any possible hazard.
Breastfeeding
Following oral administration of 200 mg Asiviral five times a day, Asiviral has been detected in breast milk at concentrations ranging from 0.6 to 4.1 times the corresponding plasma levels. These levels would potentially expose nursing infants to Asiviral dosages of up to 0.3 mg/kg/day. Caution is therefore advised if Asiviral is to be administered to a nursing woman.
Fertility
There is no information on the effect of Asiviral on human female fertility.
In a study of 20 male patients with normal sperm count, oral Asiviral administered at doses of up to 1g per day for up to six months has been shown to have no clinically significant effect on sperm count, motility or morphology.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
There have been no studies to investigate the effect of Asiviral on driving performance or the ability to operate machinery. A detrimental effect on such activities cannot be predicted from the pharmacology of the active substance, but the adverse event profile should be borne in mind.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The frequency categories associated with the adverse events below are estimates. For most events, suitable data for estimating incidence were not available. In addition, adverse events may vary in their incidence depending on the indication.
The following convention has been used for the classification of undesirable effects in terms of frequency: Very common > 1/10, common > 1/100 and < 1/10, uncommon > 1/1000 and < 1/100, rare > 1/10,000 and < 1/1000, very rare < 1/10,000
Blood and the lymphatic system disorders:
Very rare: Anaemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Immune system disorders:
Rare: Anaphylaxis.
Psychiatric and nervous system disorders:
Common: Headache, dizziness.
Very rare: Agitation, confusion, tremor, ataxia, dysarthria, hallucinations, psychotic symptoms, convulsions, somnolence, encephalopathy, coma.
The above events are generally reversible and usually reported in patients with renal impairment or with other predisposing factors (see 4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use).
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Rare: Dyspnoea.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pains.
Hepato-biliary disorders:
Rare: Reversible rises in bilirubin and liver related enzymes.
Very rare: Hepatitis, jaundice.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Common: Pruritus, rashes (including photosensitivity).
Uncommon: Urticaria. Accelerated diffuse hair loss. Accelerated diffuse hair loss has been associated with a wide variety of disease processes and medicines, the relationship of the event to Asiviral therapy is uncertain.
Rare: Angioedema.
Renal and urinary disorders:
Rare: Increases in blood urea and creatinine.
Very rare: Acute renal failure, renal pain.
Renal pain may be associated with renal failure and crystalluria.
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Common: fatigue, fever.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the Yellow Card Scheme at: www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard.
). Prolonged or repeated courses of aciclovir in severely immune-compromised individuals may result in the selection of virus strains with reduced sensitivity, which may not respond to continued aciclovir treatment.
Hydration status: Care should be taken to maintain adequate hydration in patients receiving high oral doses of aciclovir.
The risk of renal impairment is increased by use with other nephrotoxic drugs.
The data currently available from clinical studies is not sufficient to conclude that treatment with aciclovir reduces the incidence of chickenpox-associated complications in immunocompetent patients.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Aciclovir is eliminated primarily unchanged in the urine via active renal tubular secretion. Any drugs administered concurrently that compete with this mechanism may increase aciclovir plasma concentrations. Probenecid and cimetidine increase the AUC of aciclovir by this mechanism, and reduce aciclovir renal clearance. Similarly increases in plasma AUCs of aciclovir and of the inactive metabolite of mycophenolate mofetil, an immunosuppresant agent used in transplant patients have been shown when the drugs are coadministered. However no dosage adjustment is necessary because of the wide therapeutic index of aciclovir.
An experimental study on five male subjects indicates that concomitant therapy with aciclovir increases AUC of totally administered theophylline with approximately 50%. It is recommended to measure plasma concentrations during concomitant therapy with aciclovir.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy:
The use of aciclovir should be considered only when the potential benefits outweigh the possibility of unknown risks.
A post-marketing aciclovir pregnancy registry has documented pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to any formulation of Asiviral.
Breast-feeding:
Following oral administration of 200 mg Asiviral five times a day, aciclovir has been detected in breast milk at concentrations ranging from 0.6 to 4.1 times the corresponding plasma levels. These levels would potentially expose nursing infants to aciclovir dosages of up to 0.3 mg/kg/day. Caution is therefore advised if aciclovir is to be administered to a nursing woman.
Fertility:
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
There have been no studies to investigate the effect of aciclovir on driving performance or the ability to operate machinery. A detrimental effect on such activities cannot be predicted from the pharmacology of the active substance, but the adverse event profile should be borne in mind.
4.8 Undesirable effects
The frequency categories associated with the adverse events below are estimates. For most events, suitable data for estimating incidence were not available. In addition, adverse events may vary in their incidence depending on the indication.
The following convention has been used for the classification of undesirable effects in terms of frequency:- Very common >1/10, common >1/100 and <1/10, uncommon >1/1000 and <1/100, rare >1/10,000 and <1/1000, very rare <1/10,000.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Very rare: Anaemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Immune system disorders:
Rare: Anaphylaxis.
Psychiatric and nervous system disorders:
Common: Headache, dizziness.
Very rare: Agitation, confusion, tremor, ataxia, dysarthria, hallucinations, psychotic symptoms, convulsions, somnolence, encephalopathy, coma.
The above events are generally reversible and usually reported in patients with renal impairment or with other predisposing factors (see 4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use).
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Rare: Dyspnoea.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pains.
Hepato-biliary disorders:
Rare: Reversible rises in bilirubin and liver related enzymes.
Very rare: Hepatitis, jaundice.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Common: Pruritus, rashes (including photosensitivity).
Uncommon: Urticaria. Accelerated diffuse hair loss. Accelerated diffuse hair loss has been associated with a wide variety of disease processes and medicines, the relationship of the event to aciclovir therapy is uncertain.
Rare: Angioedema.
Renal and urinary disorders:
Rare: Increases in blood urea and creatinine.
Very rare: Acute renal failure, renal pain.
Renal pain may be associated with renal failure and crystalluria.
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Common: Fatigue, fever.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the Yellow Card Scheme at:.
Overdose
The information provided in Overdose of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Overdose in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Symptoms and signs
Asiviral is only partly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Patients have ingested overdoses of up to 20g Asiviral on a single occasion, usually without toxic effects. Accidental, repeated overdoses of oral Asiviral over several days have been associated with gastrointestinal effects (such as nausea and vomiting) and neurological effects (headache and confusion).
Overdosage of intravenous Asiviral has resulted in elevations of serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen and subsequent renal failure. Neurological effects including confusion, hallucinations, agitation, seizures and coma have been described in association with intravenous overdosage.
Management
Patients should be observed closely for signs of toxicity. Haemodialysis significantly enhances the removal of Asiviral from the blood and may, therefore, be considered a management option in the event of symptomatic overdose.
Symptoms and signs:- Aciclovir is only partly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Patients have ingested overdoses of up to 20g aciclovir on a single occasion, usually without toxic effects. Accidental, repeated overdoses of oral aciclovir over several days have been associated with gastrointestinal effects (such as nausea and vomiting) and neurological effects (headache and confusion).
Overdosage of intravenous aciclovir has resulted in elevations of serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen and subsequent renal failure. Neurological effects including confusion, hallucinations, agitation, seizures and coma have been described in association with intravenous overdosage.
Management:- Patients should be observed closely for signs of toxicity. Haemodialysis significantly enhances the removal of aciclovir from the blood and may, therefore, be considered a management option in the event of symptomatic overdose.
Pharmacodynamic properties
The information provided in Pharmacodynamic properties of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Pharmacodynamic properties in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Direct acting antivirals, Nucleosides and nucleotides excl. reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
ATC code: J05AB01
Asiviral is a synthetic purine nucleoside analogue with in vitro and in vivo inhibitory activity against human herpes viruses, including herpes simplex virus (HSV) types I and II and varicella zoster virus (VZV).
The inhibitory activity of Asiviral for HSV I, HSV II and VZV is highly selective. The enzyme thymidine kinase (TK) of normal, uninfected cells does not use Asiviral effectively as a substrate, hence toxicity of mammalian host cells is low; however, TK encoded by HSV and VZV converts Asiviral to Asiviral monophosphate, a nucleoside analogue which is further converted to the diphosphate and finally to the triphosphate by cellular enzymes. Asiviral triphosphate interferes with the viral DNA polymerase and inhibits viral DNA replication with resultant chain termination following its incorporation into the viral DNA.
Prolonged or repeated courses of Asiviral in severely immuno-compromised individuals may result in the selection of virus strains with reduced sensitivity, which may not respond to continued Asiviral treatment. Most of the clinical isolates with reduced sensitivity have been relatively deficient in viral TK, however, strains with altered viral TK or viral DNA polymerase have also been reported. In vitro exposure of HSV isolates to Asiviral can also lead to the emergence of less sensitive strains. The relationship between the in vitro-determined sensitivity of HSV isolates and clinical response to Asiviral therapy is not clear.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Direct acting antivirals, Nucleosides and nucleotides excl. reverse transcriptase inhibitors
ATC code: J05AB01.
Aciclovir is a synthetic purine nucleoside analogue with in vitro and in vivo inhibitory activity against human herpes viruses, including herpes simplex virus (HSV) types I and II and varicella zoster virus (VZV).
The inhibitory activity of aciclovir for HSV I, HSV II and VZV is highly selective. The enzyme thymidine kinase (TK) of normal, uninfected cells does not use aciclovir effectively as a substrate, hence toxicity of mammalian host cells is low; however, TK encoded by HSV and VZV converts aciclovir to aciclovir monophosphate, a nucleoside analogue which is further converted to the diphosphate and finally to the triphosphate by cellular enzymes. Aciclovir triphosphate interferes with the viral DNA polymerase and inhibits viral DNA replication with resultant chain termination following its incorporation into the viral DNA.
Prolonged or repeated courses of aciclovir in severely immune-compromised individuals may result in the selection of virus strains with reduced sensitivity, which may not respond to continued aciclovir treatment. Most of the clinical isolates with reduced sensitivity have been relatively deficient in viral TK, however, strains with altered viral TK or viral DNA polymerase have also been reported. In vitro exposure of HSV isolates to aciclovir can also lead to the emergence of less sensitive strains. The relationship between the in vitro determined sensitivity of HSV isolates and clinical response to aciclovir therapy is not clear.
Pharmacokinetic properties
The information provided in Pharmacokinetic properties of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Pharmacokinetic properties in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Asiviral is only partially absorbed from the gut. Mean steady state peak plasma concentrations (Cssmax) following doses of 200 mg administered four-hourly were 3.1 microMol (0.7 micrograms/ml) and equivalent trough plasma levels (Cssmin) were 1.8 microMol (0.4 micrograms/ml). Corresponding Cssmax levels following doses of 400 mg and 800 mg administered four-hourly were 5.3 microMol (1.2 micrograms/ml) and 8 microMol (1.8 micrograms/ml) respectively and equivalent Cssmin levels were 2.7 microMol (0.6 micrograms/ml) and 4 microMol (0.9 micrograms/ml).
In adults the terminal plasma half-life of Asiviral after administration of intravenous Asiviral is about 2.9 hours. Most of the drug is excreted unchanged by the kidney. Renal clearance of Asiviral is substantially greater than creatinine clearance, indicating that tubular secretion, in addition to glomerular filtration contributes to the renal elimination of the drug. 9-carboxymethoxymethylguanine is the only significant metabolite of Asiviral, and accounts for approximately 10 — 15% of the administered dose recovered from the urine. When Asiviral is given one hour after 1 gram of probenecid the terminal half-life and the area under the plasma concentration time curve is extended by 18% and 40% respectively.
In adults, mean steady state peak plasma concentrations (Cssmax) following a one hour infusion of 2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg were 22.7 microMol (5.1 micrograms/ml), 43.6 microMol (9.8 micrograms/ml) and 92 microMol (20.7 micrograms/ml), respectively. The corresponding trough levels (Cssmin) 7 hours later were 2.2 microMol (0.5 micrograms/ml), 3.1 microMol (0.7 micrograms/ml), and 10.2 microMol (2.3 micrograms/ml), respectively.
In children over 1 year of age similar mean peak (Cssmax) and trough (Cssmin) levels were observed when a dose of 250 mg/m2 was substituted for 5 mg/kg and a dose of 500 mg/m2 was substituted for 10 mg/kg. In neonates and young infants (0 to 3 months of age) treated with doses of 10 mg/kg administered by infusion over a one-hour period every 8 hours the Cssmax was found to be 61.2 microMol (13.8 micrograms/ml) and Cssmin to be 10.1 microMol (2.3 micrograms/ml). The terminal plasma half-life in these patients was 3.8 hours. A separate group of neonates treated with 15 mg/kg every 8 hours showed approximate dose proportional increases, with a Cmax of 83.5 micromolar (18.8 microgram/ml) and Cmin of 14.1 micromolar (3.2 microgram/ml).
In the elderly, total body clearance falls with increasing age associated with decreases in creatinine clearance although there is little change in the terminal plasma half-life.
In patients with chronic renal failure the mean terminal half-life was found to be 19.5 hours. The mean Asiviral half-life during haemodialysis was 5.7 hours. Plasma Asiviral levels dropped approximately 60% during dialysis.
Cerebrospinal fluid levels are approximately 50% of corresponding plasma levels. Plasma protein binding is relatively low (9 to 33%) and drug interactions involving binding site displacement are not anticipated.
Aciclovir is only partially absorbed from the gut. Mean steady state peak plasma concentrations (Cssmax) following doses of 200 mg administered four-hourly were 3.1 microMol (0.7 micrograms/ml) and equivalent trough plasma levels (Cssmin) were 1.8 microMol (0.4 micrograms/ml). Corresponding Cssmax levels following doses of 400 mg and 800 mg administered four-hourly were 5.3 microMol (1.2 micrograms/ml) and 8 microMol (1.8 micrograms/ml) respectively and equivalent Cssmin levels were 2.7 microMol (0.6 micrograms/ml) and 4 microMol (0.9 micrograms/ml).
In adults the terminal plasma half-life of aciclovir after administrations of intravenous aciclovir is about 2.9 hours. Most of the drug is excreted unchanged by the kidney. Renal clearance of aciclovir is substantially greater than creatinine clearance, indicating that tubular secretion, in addition to glomerular filtration contributes to the renal elimination of the drug. 9-carboxymethoxymethylguanine is the only significant metabolite of aciclovir, and accounts for approximately 10 — 15% of the administered dose recovered from the urine. When aciclovir is given one hour after 1 gram of probenecid the terminal half-life and the area under the plasma concentration time curve is extended by 18% and 40% respectively.
In adults, mean steady state peak plasma concentrations (Cssmax) following a one hour infusion of 2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg were 22.7 microMol (5.1 micrograms/ml), 43.6 microMol (9.8 micrograms/ml) and 92 microMol (20.7 micrograms/ml), respectively. The corresponding trough levels (Cssmin) 7 hours later were 2.2 microMol (0.5 micrograms/ml), 3.1 microMol (0.7 micrograms/ml), and 10.2 microMol (2.3 micrograms/ml), respectively.
In children over 1 year of age similar peak (Cssmax) and trough (Cssmin) levels were observed when a dose of 250 mg/m2 was substituted for 5 mg/kg and a dose of 500 mg/m2 was substituted for 10 mg/kg. In neonates and young infants (0 to 3 months of age) treated with doses of 10 mg/kg administered by infusion over a one-hour period every 8 hours the Cssmax was found to be 61.2 microMol (13.8 micrograms/ml) and Cssmin to be 10.1 microMol (2.3 micrograms/ml). The terminal plasma half-life in these patients was 3.8 hours. A separate group of neonates treated with 15 mg/kg every 8 hours showed approximate dose proportional increases, with a Cmax of 83.5 micromolar (18.8 microgram/ml) and Cmin of 14.1 micromolar (3.2 microgram/ml). In the elderly, total body clearance falls with increasing age associated with decreases in creatinine clearance although there is little change in the terminal plasma half-life.
In patients with chronic renal failure the mean terminal half-life was found to be 19.5 hours. The mean aciclovir half-life during haemodialysis was 5.7 hours. Plasma aciclovir levels dropped approximately 60% during dialysis.
Cerebrospinal fluid levels are approximately 50% of corresponding plasma levels. Plasma protein binding is relatively low (9 to 33%) and drug interactions involving binding site displacement are not anticipated.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
The information provided in Pharmacotherapeutic group of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Pharmacotherapeutic group in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Direct acting antivirals, Nucleosides and nucleotides excl. reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
Preclinical safety data
The information provided in Preclinical safety data of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Preclinical safety data in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Mutagenicity:
The results of a wide range of mutagenicity tests in vitro and in vivo indicate that Asiviral is unlikely to pose a genetic risk to man.
Carcinogenicity:
Asiviral was not found to be carcinogenic in long term studies in the rat and the mouse.
Teratogenicity:
Systemic administration of Asiviral in internationally accepted standard tests did not produce embryotoxic or teratogenic effects in rats, rabbits or mice.
In a non-standard test in rats, foetal abnormalities were observed, but only following such high subcutaneous doses that maternal toxicity was produced. The clinical relevance of these findings is uncertain.
Fertility:
Largely reversible adverse effects on spermatogenesis in association with overall toxicity in rats and dogs have been reported only at doses of Asiviral greatly in excess of those employed therapeutically. Two generation studies in mice did not reveal any effect of Asiviral on fertility.
Mutagenicity:- The results of a wide range of mutagenicity tests in vitro and in vivo indicate that aciclovir is unlikely to pose a genetic risk to man.
Carcinogenicity:- Aciclovir was not found to be carcinogenic in long term studies in the rat and the mouse.
Teratogenicity:- Systemic administration of aciclovir in internationally accepted standard tests did not produce embryotoxic or teratogenic effects in rats, rabbits or mice.
In a non-standard test in rats, foetal abnormalities were observed, but only following such high subcutaneous doses that maternal toxicity was produced. The clinical relevance of these findings is uncertain.
Fertility:- Largely reversible adverse effects on spermatogenesis in association with overall toxicity in rats and dogs have been reported only at doses of aciclovir greatly in excess of those employed therapeutically. Two generation studies in mice did not reveal any effect of aciclovir on fertility.
Incompatibilities
The information provided in Incompatibilities of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Incompatibilities in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Not applicable.
None known.
Special precautions for disposal and other handling
The information provided in Special precautions for disposal and other handling of Asiviral
is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Asiviral.
. Be careful and be sure to specify the information on the section Special precautions for disposal and other handling in the instructions to the drug Asiviral directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Cream for external use; Cream for local and external use; Eye ointment; Lyophilizate for the preparation of a solution for infusions; Ointment for external use; Ointment for topical and topical application; Pills; Substance-powder
Cream
Not applicable.
No special requirements.
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Administrative Data
Asiviral price
We have no data on the cost of the drug.
However, we will provide data for each active ingredient
The approximate cost of Aciclovir 800 mg per unit in online pharmacies is from 0.69$ to 1.08$, per package is from 38$ to 73$.
The approximate cost of Aciclovir 200 mg per unit in online pharmacies is from 0.53$ to 1.2$, per package is from 30$ to 40$.
The approximate cost of Aciclovir 400 mg per unit in online pharmacies is from 0.62$ to 0.62$, per package is from 35$ to 35$.
Available in countries
Find in a country:
| Dosage form |
Tab |
|---|---|
| Pack size |
25 |
| Potency |
200 Mg |
| Manufacturer |
Terra |
| Origin |
Turkey |
| Generic Name (Ingredient) |
It Contains 200 Mg Acyclovir. |
Assuming your emergency circumstances for this product, visit Urgent Quotation page. Besides, for any pharmaceutical questions, please ask us in the comments section.
-
Comments
-
Report / Upload
-
Disclaimer
Use the form below to report an error
Please answer the questions as thoroughly and accurately as possible. Your answers will help us better understand what kind of mistakes happen, why and where they happen, and in the end the purpose is to build a better archive to guide researchers and professionals around the world.
The information on this page is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. always seek the advice for your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Always remember to
- Ask your own doctor for medical advice.
- Names, brands, and dosage may differ between countries.
- When not feeling well, or experiencing side effects always contact your own doctor.
Cyberchondria
The truth is that when we’re sick, or worried about getting sick, the internet won’t help.
According to Wikipedia, cyberchondria is a mental disorder consisting in the desire to independently make a diagnosis based on the symptoms of diseases described on Internet sites.
Why you can’t look for symptoms on the Internet
If diagnoses could be made simply from a textbook or an article on a website, we would all be doctors and treat ourselves. Nothing can replace the experience and knowledge of specially trained people. As in any field, in medicine there are unscrupulous specialists, differences of opinion, inaccurate diagnoses and incorrect test results.
| Trade Name | Asiviral |
| Generic | Aciclovir |
| Type | |
| Therapeutic Class | Therapeutic Group: Anti Viral |
| Manufacturer | |
| Available Country | Turkey |
| Last Updated: | September 19, 2023 at 7:00 am |
Asiviral
Asiviral is the brand name of Asiviral, a synthetic purine nucleoside with inhibitory activity against herpes simplex virus(HSV-1 & HSV-2) and varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The activity of Asiviral is highly selective due to its affinity for the enzyme thymidine kinase encoded by HSV and VZV. This viral enzyme converts Asiviral into Asiviral monophosphate, a nucleotide analogue. The monophosphate is further converted into diphosphate and finally triphosphate by a number of cellular enzymes. In vitro, Asiviral triphosphate stops replication of herpes viral DNA. This is accomplished in 3 ways: 1) Competitive inhibition of viral DNA polymerase, 2) Incorporation into and termination of the growing viral DNA chain and 3) Inactivation of the viral DNA polymerase.
Uses
• Herpes Zoster
• Genital Herpes
• Chickenpox
• Herpes Simplex Infections
• Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
Asiviral
Table Of contents
- Asiviral
- Uses
- Dosage
- Side Effect
- Precautions
- Interactions
- Uses during Pregnancy
- Uses during Breastfeeding
- Accute Overdose
- Food Interaction
- Half Life
- Volume of Distribution
- Clearance
- Interaction With other Medicine
- Contradiction
- Storage
Dosage
Asiviral dosage
The total daily dosage of Asiviral should be based on the type or severity of infection and given in equally divided doses based on consideration of degree of susceptibility of the pathogens, renal function and body-weight.
Asiviral Tablet
• Acute Herpes Zoster:
800 mg every 4 hours, 5 times daily for 7 to 10 days.
• Genital Herpes:
Initial Genital Herpes: 200 mg every 4 hours, 5 times daily for 10 days.
Chronic suppressive therapy for recurrent disease: 400 mg 2 times daily for up to 12 months.
Intermittent therapy: 200 mg every 4 hours, 5 times daily for 5 days.
• Chickenpox:
Children (2 years of age and older): 20 mg/kg/dose 4 times daily (80 mg/kg/day) for 5 days.
Adults and Children (>40 kg): 800 mg 4 times daily for 5 days.
Asiviral IV
The required dose of Asiviral IV should be administered by slow intravenous infusion over a one-hour period.
• Herpes Simplex (HSV-1 and HSV-2) Infections:
Adults and Adolescents (≥12 years): 5 mg/kg, 8 hourly for 7 days.
Pediatrics (<12 years): 10 mg/kg 8 hourly for 7 days.
• Severe Initial Herpes Genitalis:
Adults and Adolescents (≥12 years): 5 mg/kg 8 hourly for 5 days.
• Herpes Simplex Encephalitis:
Adults and Adolescents (≥12 years): 10 mg/kg 8 hourly for 10 days.
Pediatrics (3 months to 12 years of age): 20 mg/kg 8 hourly for 10 days.
• Neonatal Herpes Simplex (Birth to 3 months):
10 mg/kg 8 hourly for 10 days.
• Varicella Zoster:
Adults and Adolescents (≥12 years): 10 mg/kg 8 hourly for 7 days.
Pediatrics (<12 years): 20 mg/kg 8 hourly for 7 days.
Dose adjustment of Tablet for patients with acute or chronic renal impairment, based on Creatinine Clearance, Cr Cl (mL/min/1.73 m2):
For Cr Cl= > 25 : 800 mg 4 hourly 5 times daily
For Cr Cl = 10 to 25 : 200 mg 4 hourly 5 times daily or 400 mg 12 hourly or 800 mg 8 hourly
For Cr Cl = 0 to 10 : 200 mg 12 hourly or 400 mg 12 hourly or 800 mg 12 hourly
Dose adjustment of IV for patients with acute or chronic renal impairment, based on Creatinine Clearance, Cr Cl (mL/min/1.73 m2):
For Cr Cl = > 50 : 100% of recommended dose, 8 hourly
For Cr Cl = 25 to 50 : 100% of recommended dose, 12 hourly
For Cr Cl = 10 to 25 : 100% of recommended dose, 24 hourly
For Cr Cl = 0 to 10 : 50% of recommended dose, 24 hourly
Caution: Rapid or bolus intravenous injection must be avoided. Intramuscular or subcutaneous injection must be avoided.
Reconstitution procedure of IV infusion
Vial containing 250 mg Asiviral will be reconstituted with 50 ml infusion solution and vial containing 500 mg Asiviral will be reconstituted with 100 ml infusion solution. Besides, Vial containing 1 gm Asiviral will be reconstituted with 250 ml infusion solution. 10 ml of the infusion solution will be added to the vial containing 250 mg, 500 mg and 1 gm Asiviral. Shake well and transfer the required amount of solution to the infusion container. The final concentration of Asiviral will be not more than 5 mg/ml.
The reconstituted solution should be used within 12 hours. Refrigeration of reconstituted solution may result in the formation of a precipitate which will re-dissolve at room temperature.
Compatible infusion fluids
Sodium Chloride Intravenous Infusion BP (0.45% and 0.9% w/v)
Sodium Chloride (0.18% w/v) and Glucose (4% w/v) Intravenous Infusion BP
Sodium Chloride (0.45% w/v) and Glucose (2.5% w/v) Intravenous Infusion BP
Hartmann\\\’s Solution
Side Effects
Rash, gastro-intestinal disturbances, rises in bilirubin and liver-related enzymes, increase in blood urea and creatinine, decreases in hematological indices, headache, neurological reactions, fatigue.
Precaution
Asiviral should be administered with caution in patient with renal impairment and doses should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance.
Pregnancy & Breastfeeding use
Pregnancy category B & caution should be exercised when it is administered to a lactating mother.
Interaction with other Medicine
Probenecid reduces Asiviral excretion and so increases plasma concentration and risk of toxicity.
Storage Condition
Keep in a cool & dry place away from light. Keep drugs out of the reach of children.
Innovators Monograph
You find simplified version here Asiviral
FAQ
What is Asiviral used for?
Asiviral is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following transplant and severe complications of Epstein–Barr virus infection.
How safe is Asiviral?
It is concluded that long-term suppression with Asiviral is safe and effective for patients with recurrent genital herpes.
How does Asiviral work?
Asiviral works by preventing viruses from multiplying, and this reduces the severity of the infection and stops it from spreading.
What are the common side effect of Asiviral?
Common side effects of Asiviral include:
- headaches.
- feeling dizzy.
- feeling or being sick (nausea or vomiting)
- diarrhea.
- skin being sensitive to sunlight.
Is Asiviral safe during pregnancy?
Use of Asiviral in the first trimester does not increase birth defects, and it should be the antiviral drug of choice in early pregnancy.
Is Asiviral safe during breastfeeding?
Asiviral does accumulate in breast milk but they also showed that there were no problems seen in the infants. The American Academy of Pediatrics considers Asiviral to be safe during breastfeeding, according to the researchers
Can I drink alcohol with Asiviral?
Yes, you can drink alcohol while taking Asiviral.
Can I drive after taking Asiviral?
Some people feel dizzy when taking Asiviral tablets or liquid. This may make it more difficult to concentrate and react. Do not drive or use any tools or machines if you’re affected.
When should be taken of Asiviral ?
Asiviral are usually taken with or without food two to five times a day for 5 to 10 days, starting as soon as possible after your symptoms begin.
How long does Asiviral take to work?
Asiviral begins to work within 24 to 48 hours after you start taking it. It may take four or five days for symptoms to reduce, but you should continue consuming the medication until the prescribed course is complete.
How long does Asiviral stay in my system?
Asiviral has a half-life of 2.5 to 3.3 hours in people with normal renal function. This means that a single dose of Asiviral, after conversion into Asiviral by your body, will reduce in concentration every 2.5 hours to 3.3 hours.
How long can I take Asiviral?
Asiviral is usually taken two to five times a day for up to 12 months.
Who should not take Asiviral ?
You should not take acyclovir buccal tablets if you are allergic to milk proteins. Tell your doctor if you have ever had kidney disease; or. a weak immune system (caused by disease or by using certain medicine).
What happens if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose of Asiviral, take the missed dose as soon as you remember it, and take the remaining doses for the day at evenly spaced intervals. If it is time or almost time for your next dose, however, do not double dose. Get to the next dose and stay on schedule.
What happen If I stop taking Asiviral?
If you stop taking the Asiviral suddenly or don’t take it at all: The symptoms of your infection may not get better or may get worse.
What happen if I take too much Asiviral?
If you take too much you could have dangerous levels of the drug in your body. Symptoms of an overdose of this Asiviral can include more severe side effects, such as: headache, nausea.
Is it bad to take too much Asiviral?
Taking too much Asiviral by accident is unlikely to harm you, unless you take too much over several days. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you’re worried that you have had too much Asiviral.
Can Asiviral affects my kidney?
It can present in clinical practice as acute kidney injury, crystal-induced nephropathy, acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, and rarely, as tubular dysfunction.
Can Asiviral affects liver?
Despite widespread use, there is little evidence that when given orally causes significant liver injury. Serum enzyme levels generally do not change during oral acyclovir therapy.
Can Asiviral affect my heart?
Increased heart rate Seizures. Encephalopathy (a disorder of the brain) Decreased number of blood platelets.
Инструкция по применению Ацикловир таблетки 200 мг
Регистрационный номер: ЛС-001205
Торговое наименование: Ацикловир
Международное непатентованное наименование: ацикловир
Лекарственная форма: таблетки.
Состав:
на одну таблетку:
Действующее вещество:
Ацикловир — 200,0 мг.
Вспомогательные вещества:
лактозы моногидрат — 137,0 мг, крахмал картофельный — 45,0 мг, сахароза — 16,0 мг, повидон К-17 — 7,6 мг, магния стеарат — 3,0 мг, натрия лаурилсульфат — 1,4 мг.
Описание:
Круглые плоскоцилиндрические таблетки белого или почти белого цвета с фаской и риской.
Фармакологическая группа: противовирусное средство.
Код АТХ: J05АВ01
Фармакологическое действие
Фармакологические свойства
Фармакодинамика
Механизм действия
Ацикловир – это синтетический аналог пуринового нуклеозида, который обладает способностью ингибировать invitro и invivo вирусы герпеса человека, включая вирус простого герпеса (ВПГ) 1-го и 2-го типов, вирус ветряной оспы и опоясывающего герпеса (варицелла-зостер вирус, Varicella zoster virus (ВЗВ)), вирус Эпштейна-Барр (ЭБВ) и цитомегаловирус (ЦМВ). В культуре клеток ацикловир обладает наиболее выраженной противовирусной активностью в отношении ВПГ-1, далее в порядке убывания активности следуют ВПГ-2, ВЗВ, ЭБВ и ЦМВ.
Ингибирующее действие ацикловира на вирусы герпеса (ВПГ-1, ВПГ-2, ВЗВ, ЭБВ и ЦМВ) имеет высокоизбирательный характер. Ацикловир не является субстратом для фермента тимидинкиназы неинфицированных клеток, поэтому ацикловир малотоксичен для клеток млекопитающих. Однако тимидинкиназа клеток, инфицированных вирусами ВПГ, ВЗВ, ЭБВ и ЦМВ, превращает ацикловир в ацикловира монофосфат – аналог нуклеозида, который затем последовательно превращается в дифосфат и трифосфат под действием клеточных ферментов. Включение ацикловира трифосфата в цепочку вирусной ДНК и последующий обрыв цепи блокируют дальнейшую репликацию вирусной ДНК.
У пациентов с выраженным иммунодефицитом длительные или повторные курсы терапии ацикловиром могут приводить к появлению резистентных штаммов, поэтому дальнейшее лечение ацикловиром может быть неэффективным. У большинства выделенных штаммов со сниженной чувствительностью к ацикловиру отмечалось относительно низкое содержание тимидинкиназы, а также нарушение структуры вирусной тимидинкиназы или ДНК-полимеразы. Воздействие ацикловира на штаммы вируса простого герпеса (ВПГ) invitro также может приводить к образованию менее чувствительных к нему штаммов. Не установлена корреляция между чувствительностью штаммов вируса простого герпеса (ВПГ) к ацикловиру invitro и клинической эффективностью препарата.
Фармакокинетика
Всасывание
Ацикловир только частично абсорбируется из кишечника. После приема 200 мг ацикловира каждые 4 часа средняя максимальная равновесная концентрация в плазме крови (Сssmax) составляла 3,1 мкМ (0,7 мкг/мл), а средняя равновесная минимальная концентрация в плазме крови (Сssmin) — 1,8 мкМ (0,4 мкг/мл). При приеме внутрь 400 мг и 800 мг ацикловира каждые 4 часа Сssmax составляла 5,3 мкМ (1,2 мкг/мл) и 8 мкМ (1,8 мкг/мл) соответственно, а Сssmin— 2,7 мкМ (0,6 мкг/мл) и 4 мкМ (0,9 мкг/мл), соответственно.
Распределение
Концентрация ацикловира в спинномозговой жидкости составляет приблизительно 50 % от его концентрации в плазме крови.
С белками плазмы крови ацикловир связывается в незначительной степени (9-33 %), поэтому лекарственные взаимодействия вследствие вытеснения из участков связывания с белками плазмы крови маловероятны.
Выведение
У взрослых после приема ацикловира внутрь период полувыведения из плазмы крови составляет около 3 ч. Большая часть препарата выводится почками в неизмененном виде. Почечный клиренс ацикловира значительно превышает клиренс креатинина, что свидетельствует о выведении ацикловира посредством не только клубочковой фильтрации, но и канальцевой секреции. 9-карбоксиметокси-метилгуанин является основным метаболитом ацикловира и составляет около 10-15% дозы, выводимой с мочой. При назначении ацикловира через 1 ч после приема 1 г пробенецида период полувыведения ацикловира и AUC (площадь под фармакокинетической кривой «концентрация — время») увеличивались на 18 и 40 %, соответственно.
Показания к применению
— Лечение инфекций кожи и слизистых оболочек, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, включая первичный и рецидивирующий генитальный герпес;
— профилактика рецидивов инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, у пациентов с нормальным иммунным статусом;
— профилактика инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, у пациентов с иммунодефицитом;
— лечение ветряной оспы и опоясывающего герпеса (раннее лечение опоясывающего герпеса ацикловиром оказывает анальгезирующий эффект и может снизить частоту возникновения постгерпетической невралгии).
Противопоказания
-
Повышенная чувствительность к ацикловиру или валацикловиру или любому другому компоненту препарата;
-
непереносимость лактозы, дефицит лактазы, глюкозо-галактозная мальабсорбция;
-
детский возраст до 3 лет.
С осторожностью
Беременность, период грудного вскармливания, пожилой возраст, почечная недостаточность, дегидратация, одновременное применение с другими нефротоксичными препаратами.
Применение при беременности и лактации.
Фертильность
Нет данных о влиянии ацикловира на женскую фертильность.
В исследовании с участием 20 пациентов мужского пола с нормальным количеством сперматозоидов было установлено, что применение ацикловира внутрь в дозе до 1 г в сутки в течение 6 месяцев не имело клинически значимого влияния на количество, подвижность или морфологию сперматозоидов.
Беременность
В пострегистрационном реестре беременностей при лечении ацикловиром собраны данные об исходах беременности у женщин, принимавших ацикловир в разных лекарственных формах. При анализе данных реестра не было отмечено увеличения количества врожденных дефектов у новорожденных, матери которых принимали ацикловир во время беременности, по сравнению с общей популяцией. Выявленные врожденные дефекты не отличались единообразием или закономерностью, позволяющими предположить общую причину их возникновения.
Однако следует соблюдать осторожность при назначении препарата Ацикловир женщинам в период беременности и оценивать предполагаемую пользу для матери и возможный риск для плода.
Период грудного вскармливания
После приема препарата Ацикловир внутрь в дозе 200 мг 5 раз в сутки ацикловир определялся в грудном молоке в концентрации, составляющей от 60 до 410 % плазменной концентрации. При таких концентрациях в грудном молоке дети, находящиеся на грудном вскармливании, могут получать ацикловир в дозе до 0,3 мг/кг/сут. Учитывая это, следует соблюдать осторожность при назначении препарата Ацикловир кормящим женщинам.
Способ применения и дозы
Препарат Ацикловир, таблетки можно принимать во время еды, поскольку прием пищи не нарушает в значительной степени его абсорбцию. Таблетки следует запивать полным стаканом воды.
Взрослые
Лечение инфекций кожи и слизистых оболочек, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, включая первичный рецидивирующий генитальный герпес
Для лечения инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, рекомендуемая доза препарата Ацикловир составляет
200 мг внутрь 5 раз в сутки (каждые 4 часа, за исключением периода ночного сна). Курс лечения составляет 5 дней, но может быть продлен при тяжелых первичных инфекциях.
В случае выраженного иммунодефицита (например, после трансплантации костного мозга) или при нарушении всасывания из кишечника доза препарата Ацикловир, может быть увеличена до 400 мг. В качестве альтернативы может быть рассмотрена возможность применения ацикловира в лекарственной форме лиофилизат для приготовления раствора для инфузий.
Лечение необходимо начинать как можно раньше после возникновения инфекции; при рецидивах препарат рекомендуется назначать уже в продромальном периоде или появлении первых элементов сыпи.
Профилактика рецидивов инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, у пациентов с нормальным иммунным статусом
Для профилактики рецидивов инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, у пациентов с нормальным иммунным статусом рекомендуемая доза препарата Ацикловир составляет 200 мг внутрь 4 раза в сутки (каждые 6 часов).
Многим пациентам подходит более удобная схема терапии 400 мг внутрь 2 раза в сутки (каждые 12 часов).
В ряде случаев оказываются эффективными более низкие дозы препарата Ацикловир: 200 мг внутрь 3 раза в сутки (каждые 8 часов) или 200 мг внутрь 2 раза в сутки (каждые 12 часов).
У некоторых пациентов может произойти обострение инфекции при приеме суммарной суточной дозы 800 мг.
Лечение препаратом Ацикловир следует прерывать через каждые 6-12 месяцев для выявления возможных изменений в течении заболевания.
Профилактика инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, у пациентов с иммунодефицитом
Для профилактики инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, у пациентов с иммунодефицитом рекомендуемая доза препарата Ацикловир составляет 200 мг внутрь 4 раза в сутки (каждые 6 часов).
В случае выраженного иммунодефицита (например, после трансплантации костного мозга) или при нарушении всасывания из кишечника доза препарата может быть увеличена до 400 мг внутрь. В качестве альтернативы может быть рассмотрена возможность применения ацикловира в лекарственной форме лиофилизат для приготовления раствора для инфузий.
Продолжительность профилактического курса терапии определяется длительностью периода, в течение которого существует риск инфицирования.
Лечение ветряной оспы и опоясывающего герпеса
Для лечения ветряной оспы и опоясывающего герпеса рекомендуемая доза препарата Ацикловир составляет 800 мг внутрь 5 раз в сутки (каждые 4 часа, за исключением периода ночного сна). Курс лечения составляет 7 дней.
Лечение опоясывающего герпеса следует начинать как можно раньше от момента первых проявлений заболевания, так как в этом случае лечение будет более эффективным.
Лечение ветряной оспы у пациентов с нормальным иммунным статусом следует начать в течение 24 часов с момента появления высыпаний.
У пациентов с тяжелым иммунодефицитом (например, после трансплантации костного мозга) или при нарушении всасывания из кишечника необходимо рассмотреть возможность назначения ацикловира в лекарственной форме лиофилизат для приготовления раствора для инфузий.
Особые группы пациентов
Дети в возрасте от 3 лет и старше
Лечение инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса; профилактика инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, у пациентов с иммунодефицитом
— в возрасте от 3 лет и старше – такие же дозы, как для взрослых.
Лечение ветряной оспы
— в возрасте от 6 лет и старше — 800 мг внутрь 4 раза в сутки;
— в возрасте от 3 до 6 лет — 400 мг внутрь 4 раза в сутки.
Более точно дозу можно определить из расчета 20 мг/кг массы тела (но не более 800 мг) внутрь 4 раза в сутки. Курс лечения составляет 5 дней.
Профилактика рецидивов инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, у пациентов с нормальным иммунным статусом; лечение опоясывающего герпеса
Данные о режиме дозирования отсутствуют.
Пациенты пожилого возраста
Необходимо учитывать вероятность наличия почечной недостаточности у пациентов пожилого возраста, дозы должны быть скорректированы в соответствии со степенью почечной недостаточности (см. подраздел «Пациенты с нарушением функции почек»).
Необходимо обеспечить поддержание адекватного водного баланса.
Пациенты с нарушением функции почек
Необходимо соблюдать осторожность при назначении препарата Ацикловир пациентам с нарушением функции почек.
Необходимо обеспечить поддержание адекватного водного баланса.
У пациентов с почечной недостаточностью прием ацикловира внутрь в рекомендуемых дозах с целью лечения и профилактики инфекций, вызванных вирусом простого герпеса, не приводит к кумуляции препарата до концентраций, превышающих установленные безопасные уровни. Однако у пациентов с клиренсом креатинина менее 10 мл/мин дозу препарата Ацикловир рекомендуется снижать до 200 мг внутрь 2 раза в сутки (каждые 12 часов).
При лечении ветряной оспы и опоясывающего герпеса рекомендуемые дозы препарата Ацикловир, таблетки составляют:
— при клиренсе креатинина менее 10 мл/мин— 800 мг внутрь 2 раза в сутки (каждые 12 часов);
— при клиренсе креатинина 10- 25 мл/мин — 800 мг внутрь 3 раза в сутки (каждые 8 часов).
Побочное действие
Приведенные ниже категории частоты нежелательных реакций являются оценочными. Для большинства нежелательных реакций необходимые данные для определения частоты встречаемости отсутствуют. Кроме того, частота встречаемости нежелательных реакций может варьировать в зависимости от показания.
Нежелательные реакции, представленные ниже, перечислены в соответствии с частотой встречаемости, определяемой следующим образом: очень часто (>1/10), часто (>1/100 и <1/10), нечасто (>1/1000 и <1/100), редко (>1/10000 и <1/1000), очень редко (<1/10 000).
Частота встречаемости нежелательных реакций
Нарушения со стороны крови и лимфатической системы
Очень редко: анемия, лейкопения, тромбоцитопения.
Нарушения со стороны иммунной системы
Редко: анафилаксия.
Нарушения со стороны нервной системы и психического статуса
Часто: головная боль, головокружение.
Очень редко: возбуждение, спутанность сознания, тремор, атаксия, дизартрия, галлюцинации, психотические
симптомы, судороги, сонливость, энцефалопатия, кома.
Обычно эти побочные эффекты наблюдались у пациентов с почечной недостаточностью или при наличии других провоцирующих факторов и были, в основном, обратимыми (см.раздел «Особые указания»).
Нарушения со стороны дыхательной системы, органов грудной клетки и средостения
Редко: одышка.
Нарушения со стороны желудочно-кишечного тракта
Часто: тошнота, рвота, диарея, боль в животе.
Нарушения со стороны печени и желчевыводящих путей
Редко: обратимое повышение концентрации билирубина и печеночных ферментов в крови.
Очень редко: гепатит, желтуха.
Нарушения со стороны кожи и подкожных тканей
Часто: зуд, сыпь, в том числе фотосенсибилизация.
Нечасто: крапивница, быстрое диффузное выпадение волос.
Поскольку быстрое диффузное выпадение волос наблюдается при различных заболеваниях и при терапии многими лекарственными средствами, связь егос приемом ацикловира не установлена.
Редко: ангионевротический отек.
Очень редко: токсический эпидермальный некролиз, мультиформная экссудативная эритема.
Нарушения со стороны почек и мочевыводящих путей
Редко: повышение концентрации мочевины и креатинина в сыворотке крови.
Очень редко: острая почечная недостаточность, почечная колика.
Почечная колика может быть связана с почечной недостаточностью и кристаллурией.
Общие расстройства и нарушения в месте введения
Часто: утомляемость, лихорадка.
Передозировка
Ацикловир лишь частично абсорбируется в желудочно-кишечном тракте. Как правило, при случайном однократном приеме ацикловира в дозе до 20 г токсические эффекты не были зарегистрированы. При повторных приемах внутрь в течение нескольких дней доз, превышающих рекомендованные, отмечались нарушения со стороны желудочно-кишечного тракта (тошнота, рвота) и нервной системы (головная боль и спутанность сознания). Иногда могут наблюдаться такие неврологические эффекты, как судорожные припадки, кома.
Пациенты нуждаются в тщательном медицинском наблюдении с целью выявления возможных симптомов интоксикации. Ацикловир выводится из организма с помощью гемодиализа, поэтому гемодиализ может быть использован для лечения передозировки.
Форма выпуска
Таблетки, 200 мг
По 10 таблеток в контурную ячейковую упаковку из пленки поливинилхлоридной и фольги алюминиевой печатной лакированной.
По 1, 2 или 3 контурные ячейковые упаковки вместе с инструкцией по применению помешают в пачку из картона.
Срок годности
3 года. Не использовать после истечения срока годности.
Условия хранения
В защищенном от влаги и света месте при температуре не выше 25°С.
Хранить в недоступном для детей месте.
Условия отпуска из аптек
По рецепту.
Наименование и адрес юридического лица, на имя которого выдано регистрационное удостоверение/ организация, принимающая претензии:
АО «АВВА РУС», Россия, 121614, г. Москва,
ул. Крылатские Холмы, д. 30, корп. 9.
Тел/факс: +7 (495) 956-75-54.
avva.com.ru
Адрес места производства:
АО «АВВА РУС», Россия, 610044, Кировская обл., г. Киров, ул. Луганская, д. 53а.
Тел.: +7 (8332) 25-12-29; +7 (495) 956-75-54.
Генеральный директор
АО «АВВА РУС» Егоров А.Г.