-
Uses
Temporarily relieves these symptoms associated with the common cold or flu:
- Headache
- Fever
- Sinus pressure
- Nasal congestion
- Minor body aches & pains
-
Dosage
12 years of age and older:
- 1 caplet/liquid-gel every 4 to 6 hours while symptoms persist. If symptoms do not respond to 1 caplet/liquid-gel, 2 may be used.
- Do not use more than 6 caplets/liquid-gels in 24 hours unless directed by a doctor.
Under 12 years of age:
- Do not take
-
Ingredients
Active ingredient:
- Solubilized ibuprofen equal to 200mg ibuprofen (NSAID)* (present as the free acid and potassium salt)
- Pseudoephedrine HCI 30 mg
- *Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Inactive Ingredients:
- D&C yellow no. 10, FD&C red no. 40, fractionated coconut oil, gelatin, pharmaceutical ink, polyethylene glycol, potassium hydroxide, purified water, sorbitan, sorbitol
Use as directed. Read complete warnings and information.
View full product labeling
-
Potential Health Effects
This product is indicated for adults and children ages 12 and older. Ask a doctor before giving to children under the age of 12. Do not take more than 6 capsules in 24 hours unless instructed to do so by a doctor. This product contains acetaminophen, which may cause severe liver damage if you take it with other drugs that contain acetaminophen, with 3 or more alcoholic drinks, or if you exceed maximum daily dosage. This product also contains ibuprofen, which may cause allergic reaction, especially in those allergic to aspirin.
See product label for full product information and warnings.
Symptoms & Tips
Sinuses and Congestion
What’s the Deal with Mucus?
Read Article
Sinuses and Congestion
How Advil Cold & Sinus Works
Read Article
Compare Advil Products
Count 300
Form Tablets
Key feature Easy to swallow
Ingredient Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 tablet every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 200
Form Capsules
Key feature Small and easy to swallow
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 160
Form Capsules
Key feature Fast-acting
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 200
Form Tablets
Key feature Easy open cap
Ingredient Ibuprofen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 tablet every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 144
Form Caplets
Key feature Long-lasting
Ingredient Ibuprofen / Acetaminophen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 8h
Dosage 2 caplets every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 caplets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 80
Form Capsules
Key feature Fast-acting
Ingredient Sulobilized Ibuprofen / Diphenhydramine
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage Take 2 capsules at bedtime. Do not take more than 2 capsules in 24h.
Count 160
Form Capsules
Key feature Fast-acting
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 144ct
Form Caplet
Key feature Targets Back Pain
Ingredient Ibuprofen + Acetaminophen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 8h
Dosage 2 caplets every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 caplets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 200
Form Capsules
Key feature Small and easy to swallow
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 200
Form Tablets
Key feature Easy open cap
Ingredient Ibuprofen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 tablet every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 144
Form Caplets
Key feature Long-lasting
Ingredient Ibuprofen / Acetaminophen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 8h
Dosage 2 caplets every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 caplets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 80
Form Capsules
Key feature Fast-acting
Ingredient Sulobilized Ibuprofen / Diphenhydramine
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage Take 2 capsules at bedtime. Do not take more than 2 capsules in 24h.
Count 160
Form Capsules
Key feature Fast-acting
Ingredient Liquid Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 capsule every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 capsules in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 300
Form Tablets
Key feature Easy to swallow
Ingredient Ibuprofen
Easy to swallow ✓
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 6h
Dosage 1 tablet every 4 — 6 hours. If symptoms persist, 2 may be used. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Count 144ct
Form Caplet
Key feature Targets Back Pain
Ingredient Ibuprofen + Acetaminophen
Fast-acting ✓
Duration Up to 8h
Dosage 2 caplets every 8 hours. Do not exceed 6 caplets in 24h unless directed by a doctor. Under 12 y/o: Ask a doctor.
Relief Finder
Not sure which Advil is right for you?
Advil treats a large variety of symptoms, so select one and we’ll help you narrow it down.
Advil can treat a variety of symptoms. Select one and we’ll help you narrow it down.
Advil can treat a variety of symptoms. Select one and we’ll help you narrow it down.
Advil can treat a variety of symptoms. Select one and we’ll help you narrow it down.
Advil can treat a variety of symptoms. Select one and we’ll help you narrow it down.
Advil can treat a variety of symptoms. Select one and we’ll help you narrow it down.
Топ 20 лекарств с такими-же компонентами:
Топ 20 лекарств с таким-же применением:
Название медикамента
Описание Название медикамента Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Advil холод
Состав
Описание Состав Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Ибупрофен, псевдоэфедрин
Терапевтические показания
Описание Терапевтические показания Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Симптоматическое облегчение заложенности носа / пазух носа с головными болями, лихорадкой и болью, связанной с простудой и гриппом. Advil Cold
Способ применения и дозы
Описание Способ применения и дозы Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Только для перорального введения и кратковременного применения.
Этот комбинированный продукт следует использовать, когда требуется как противозастойное действие псевдоэфедрина гидрохлорида, так и обезболивающее и/или противовоспалительное действие ибупрофена. Если преобладает симптом (либо заложенность носа, либо головная боль и/или лихорадка), предпочтительнее одноагентная терапия.
Взрослые, поляк и Porsche старше 12 лет:
Нежелательные эффекты могут быть сведены к минимуму, используя самую низкую эффективную дозу в течение кратчайшего срока, необходимого для контроля симптомов. Пациент должен обратиться к врачу, если симптомы сохраняются или ухудшаются, или если продукт требуется более 3 дней.
Posologie
Взрослые, пожилые люди и подростки старше 12 лет:
Принимайте по 1 или 2 таблетки каждые 4-6 часов до максимум 6 таблеток в течение 24 часов.
Педиатрическая популяция
Advil Cold
Почечная и печеночная недостаточность
У пациентов с легкой и умеренной дисфункцией почек или печениснижение дозы не требуется. Следует использовать самую низкую эффективную дозу.
Способ применения
Только для перорального введения. Таблетки следует принимать со стаканом воды.
Противопоказания
Описание Противопоказания Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
— Использование у детей в возрасте до 12 лет.
—
— Пациенты с аллергией на аспирин или другие нестероидные противовоспалительные препараты (НПВП) или с реакциями гиперчувствительности в анамнезе (например, астма, бронхоспазм, ринит, ангионевротический отек или крапивница) в ответ на ибупрофен, аспирин или НПВП.
-Желудочно-кишечное кровотечение или перфорация в анамнезе, связанные с предыдущей терапией НПВП.
— Активная или анамнез рецидивирующих язв желудка /кровотечений (два или более различных эпизода доказанных изъязвлений или кровотечений).
— Пациенты с феохромоцитомой, закрытой угловой глаукомой, диабетом или заболеваниями щитовидной железы.
— Пациенты с геморрагическим инсультом в предыстории.
— Пациенты с сердечными заболеваниями, проблемами кровообращения, гипертрофией предстательной железы, гипертонией, ишемической болезнью сердца, стенокардией, тахикардией или геморрагическим диатезом.
— Пациенты, принимающие другие НПВП, включая селективные ингибиторы циклооксигеназы-2, болеутоляющие средства или противозастойные средства.
— Пациенты, получающие трициклические антидепрессанты.
— Пациенты, которые в настоящее время получают ингибиторы моноаминоксидазы или получили их в течение последних двух недель.
— Пациенты с тяжелой сердечной недостаточностью (NYHA IV класса), почечной или печеночной недостаточностью.
— Во время беременности и грудного вскармливания..
Особые предупреждения и меры предосторожности
Описание Особые предупреждения и меры предосторожности Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
— Применение Advil Cold
— Нежелательные эффекты могут быть сведены к минимуму, используя минимальную эффективную дозу в течение кратчайшего срока, необходимого для контроля симптомов (см. GI и сердечно-сосудистые риски ниже).
— Если симптомы ухудшаются или продолжаются более 3 дней или у пациентов появляются другие симптомы, не связанные с первоначальным состоянием, лечение следует прекратить, если врач или медицинский работник не определят иное.
— Пожилые люди: пожилые люди имеют повышенную частоту побочных эффектов на НПВП, особенно желудочно-кишечное кровотечение и перфорацию, которые могут быть смертельными
-Желудочно-кишечное кровотечение, изъязвление и перфорация: кровотечение GI, изъязвление или перфорация, которые могут быть смертельными, сообщалось во всех НПВП в любое время во время лечения с предупреждающими симптомами или без них или серьезными событиями gi в истории.
— Риск кровотечения GI, изъязвления или перфорации выше с увеличением доз НПВП у пациентов с язвами в анамнезе, особенно при осложнениях с кровотечением или перфорацией, и у пожилых людей.)
— Пациенты с токсичностью gi в анамнезе, особенно у пожилых людей, должны сообщать о необычных абдоминальных симптомах (особенно кровотечение gi), особенно на начальных стадиях лечения.
-У пациентов, получающих сопутствующие препараты, которые могут увеличить риск изъязвления или кровотечения, такие как пероральные кортикостероиды, антикоагулянты, такие как варфарин, селективные ингибиторы обратного захвата серотонина или ингибиторы агрегации тромбоцитов, такие как аспирин, следует соблюдать осторожность.
— Когда кровотечение GI или изъязвления возникают у пациентов, которые Advil Cold
— НПВП следует назначать пациентам с желудочно-кишечными заболеваниями в анамнезе (например, язвенным колитом и нежелательными эффектами) с осторожностью.
— У пациентов с нарушениями функции сердца или почек следует соблюдать осторожность, так как применение НПВП может привести к ухудшению функции почек.
— Сердечно-сосудистые и цереброваскулярные эффекты:
Клинические исследования показывают, что применение некоторых НПВП (ибупрофен) может быть связано с низким повышенным риском артериальных тромботических событий (например, инфаркта миокарда или инсульта), особенно при высокой дозе (2400 мг/сут) и при длительном лечении. В целом, эпидемиологические исследования не показывают, что ибупрофен с низкой дозой (например, ⤠¤ 1200 мг / сут) связан с повышенным риском артериальных тромботических событий.
Больных с неконтролируемой гипертонией, застойной сердечной недостаточностью (NYHA II-III), установленной ишемической болезнью сердца, периферическим артериальным заболеванием и/или цереброваскулярным заболеванием следует лечить ибупрофеном только после тщательного взвешивания, а высоких доз (2400 мг/сут) следует избегать.
Перед началом длительного лечения больных с факторами риска развития сердечно-сосудистых событий (например, гипертония, гиперлипидемия, сахарный диабет и курение) также следует тщательно обдумать, особенно если требуются высокие дозы ибупрофена (2400 мг/сут).
— Серьезные кожные реакции, некоторые из которых смертельны, включая эксфолиативный дерматит, синдром Стивенса-Джонсона и токсический эпидермальный некролиз, очень редко сообщались в сочетании с использованием НПВП. Пациенты, по-видимому, подвергаются наибольшему риску этих реакций в начале курса терапии, причем начало реакции в большинстве случаев происходит в течение первого месяца лечения. Advil Cold
— Системная красная волчанка и смешанные заболевания соединительной ткани-повышенный риск асептического менингита.
— Поскольку НПВП могут влиять на функцию тромбоцитов, их следует использовать с осторожностью у пациентов с внутричерепным кровотечением и диатезом кровотечения.
— Пациенты, страдающие астмой, гипертонией, сердечными заболеваниями, диабетом, циррозом печени, нарушениями функции почек или печени, заболеваниями щитовидной железы или гипертрофией предстательной железы, должны проконсультироваться с врачом перед использованием этого продукта.
— У обезвоженных подростков или подростков в возрасте от 12 до 17 лет существует риск нарушения функции почек.
— Бронхоспазм может быть у пациентов с или с бронхиальной астмой или аллергическими заболеваниями в анамнезе.
— Использование НПВП может повлиять на женскую фертильность. Существуют ограниченные доказательства того, что лекарства, которые ингибируют синтез цикло-оксигеназы/простагландина, могут вызвать нарушение женской фертильности из-за влияния на овуляцию. Это обратимо при лишении лечения.
— Пациенты с редкими наследственными проблемами непереносимости фруктозы, мальабсорбции глюкозо-галактозы или недостаточности сукразы-изомальтазы не должны принимать это лекарство.
— Следует избегать употребления алкоголя во время лечения.
— Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид может вызвать положительную реакцию при тестах, проведенных во время антидопинговых проверок.
Влияние на способность управлять и использовать машины
Описание Влияние на способность управлять и использовать машины Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Advil Cold
Пациенты, у которых возникают головокружение, галлюцинации, необычные головные боли и проблемы со зрением или слухом, должны избегать вождения или использования машин. Однократное введение или кратковременное применение этого препарата обычно не оправдывает особых мер предосторожности.
Побочные эффекты
Описание Побочные эффекты Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Наиболее часто наблюдаемые нежелательные события носят желудочно-кишечный характер. Могут возникать язвы желудка, перфорации или кровотечения gi, иногда смертельные у пожилых людей. После введения сообщалось о тошноте, рвоте, диарее, вздутии живота, диспепсии, боли в животе, вздутии живота, язвах рта, мелаене, гематемезе, язвенном стоматите, обострении колита и болезни Крона. Реже наблюдался гастрит
После лечения ибупрофеном сообщалось о реакциях гиперчувствительности. Они могут состоять из,
а) неспецифическая аллергическая реакция и анафилаксия,
б) Дыхание: реактивность дыхательных путей, состоящая из астмы, обостренной астмы, бронхоспазма или одышки,
Кожа: различные кожные заболевания, в том числе сыпь различного рода, синяки прурит, крапивница, пурпура, ангиодема и реже эксфолиативные и буллезные дерматозы (в том числе эпидермальный некролиз и мультиформная эритема).
в) Очень редко-буллезные реакции, включая синдром Стивена Джонсона и токсический эпидермальный некролизис.
Клинические исследования показывают, что применение ибупрофена, особенно в высокой дозе (2400 мг/сут), может быть связано с низким повышенным риском артериальных тромботических событий (например, инфаркта миокарда или инсульта). Отек, высокое кровяное давление, стенокардия и сердечная недостаточность были сообщены в сочетании с лечением НПВП.
Следующий список побочных эффектов относится к тем, которые возникали при внебиржевых дозах ибупрофена и псевдоэфедрина гидрохлорида для кратковременного применения. При лечении хронических заболеваний при длительном лечении могут возникать дополнительные побочные эффекты.
Пациенты должны быть проинформированы о том, что они принимают Advil Cold
|
<Очень часто (>1/10)> |
|
<Общие (>1/100 к <1/10)> |
|
Вообще-т (>1/1000 к <1/100) > |
|
<Речь (>от 1/10000 до <1/1000)> |
|
<Очень редко (<1/10000)> |
|
<неизвестно (не оценивается из существующих данных)> |
|
Инфекции и заражение |
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
Обострение инфекционного воспаления (например, некротизирующий фасцит), асептический менингит( жесткость шеи, головная боль, тошнота, рвота, лихорадка или дезориентация у пациентов с ранее существовавшими аутоиммунными заболеваниями (СКВ, смешанные заболевания соединительной ткани) |
|
Заболевания кровеносной и лимфатической систем |
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
Кроветворные заболевания (например, анемия, лейкопения, тромбоцитопения, панцитопения, агранулоцитоз) |
|
Заболевания иммунной системы |
Ибупрофен |
Необычный |
Реакции гиперчувствительности при крапивнице, зуде и приступах астмы (при падении артериального давления) |
|
Ибупрофен и псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Очень редко |
Тяжелые генерализованные реакции гиперчувствительности, признаками могут быть отек лица, ангионевротический отек, одышка, тахикардия, падение артериального давления, анафилактический шок |
|
|
Психиатрические заболевания |
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
Психотические реакции, депрессия |
|
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Неизвестный |
Беспокойство, галлюцинация, беспокойство, поведенческие расстройства, Бессонница, возбудимость, раздражительность, Нервозность, беспокойство |
|
|
Заболевания нервной системы |
Ибупрофен |
Необычный |
Расстройства центральной нервной системы, такие как головная боль, головокружение, бессонница, беспокойство, раздражительность или усталость |
|
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Неизвестный |
Геморагический инсульт, ишемический инсульт, судороги, головная боль, бессонница, нервозность, беспокойство, беспокойство, тремор, галлюцинации. |
|
|
Глазные заболевания |
Ибупрофен |
Необычный |
Нарушение зрения |
|
Нарушения уха и лабиринта |
Ибупрофен |
Редкий |
Шум в ушах |
|
Ибупрофен |
Неизвестный |
Головокружение |
|
|
Сердечные заболевания |
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
Сердцебиение, сердечная недостаточность, инфаркт миокарда, отек, гипертония |
|
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Неизвестный |
Сердцебиение, тахикардия, боль в груди, арритмия |
|
|
Сосудистые заболевания |
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
артериальная гипертония |
|
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Неизвестный |
Гипертензия |
|
|
Респираторные, грудные и средостенные расстройства |
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Редкий |
Обострение астмы или реакция гиперчувствительности при бронхоспазме |
|
Желудочно-кишечные заболевания |
Ибупрофен |
Common |
Диспепсия, боли в животе, тошнота, рвота, вздутие живота, диарея, запор, анорексия, легкая желудочно-кишечная кровопотеря в редких случаях, приводящих к анемии |
|
Ибупрофен |
Необычный |
Язвенная болезнь желудка с кровотечениями и / или перфорацией, гастритом, язвенным стоматитом, обострением колита и болезни Крона |
|
|
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
Эзофагит, панкреатит, кишечная диафрагма-подобные стриктуры |
|
|
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Неизвестный |
Сухость во рту, жажда, тошнота, рвота |
|
|
Заболевания печени и желчи |
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
Дисфункция печени, повреждение печени, особенно при длительной терапии, печеночная недостаточность, острый гепатит |
|
Заболевания кожи и подкожной клетчатки |
Ибупрофен |
Необычный |
Различные сыпи |
|
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
Буллезная экзантема, такая как синдром Стивенса-Джонсона и токсический эпидермальный некролиз (синдром Лайелла), алопеция, тяжелые кожные инфекции, осложнения мягких тканей при ветряной инфекции |
|
|
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Неизвестный |
Сыпь, крапивница, зуд, гипергидроз. |
|
|
Заболевания почек и мочевых путей |
Ибупрофен |
Редкий |
Повреждение почечных тканей (некроз сосочков) и повышенные концентрации мочевой кислоты в крови |
|
Ибупрофен |
Очень редко |
Отеки (особенно у больных артериальной гипертензией или почечной недостаточностью), нефротический синдром, интерстициальный нефрит, острая почечная недостаточность |
|
|
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид |
Неизвестный |
Трудности с микцией (задержка мочи у мужчин с расстройствами предстательной железы уретры.) |
|
|
Исследования |
Ибупрофен |
неизвестный |
Haematokrit электро и электро гемоглобина |
Сообщение о предполагаемых побочных эффектах
Сообщение о предполагаемых побочных эффектах после приема препарата имеет важное значение. Это позволяет постоянно контролировать баланс пользы и риска препарата. Медицинским работникам предлагается сообщить о предполагаемых побочных эффектах через систему Yellow Card по адресу: www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard.
Передозировка
Описание Передозировка Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
У детей прием более 400 мг/кг вызывает симптомы. У взрослых эффект реакции дозы менее заметен. Период полураспада при передозировке составляет 1,5-3 часа.
Симптомы
Передозировка может вызвать нервозность, беспокойство, беспокойство, раздражительность, беспокойство, головокружение, тремор, головокружение, бессонницу, тошноту, боль в животе, рвоту, боль в желудке, диарею, брадикардию, сердцебиение, тахикардию, шум в ушах, головную боль и желудочно-кишечное кровотечение. Гиперкалиемия, метаболический ацидоз, высокое кровяное давление или гипотензия также являются возможными признаками передозировки. Токсичность может проявляться как сонливость, возбуждение, дезориентация или кома. У пациента могут развиться судороги. Функция печени может быть ненормальной. Может произойти метаболический ацидоз, и протромбиновое время / INR может быть продлено. Могут возникать острая почечная недостаточность и повреждение печени. У астматиков возможно обострение астмы.
Управление
Из-за быстрого поглощения двух активных ингредиентов из желудочно-кишечного тракта эметики и промывание желудка должны быть начаты в течение четырех часов после передозировки, чтобы быть эффективными. Древесный уголь эффективен только в том случае, если его вводят в течение часа. Состояние сердца следует контролировать и измерять электролиты сыворотки.
При признаках сердечной токсичности пропанолол можно вводить внутривенно. При падении уровня калия в сыворотке крови следует начать медленную инфузию разбавленного раствора хлорида калия. Несмотря на гипокалиемию, маловероятно, что пациент с низким содержанием калия, поэтому необходимо избегать перегрузки. Дальнейший контроль калия в сыворотке крови целесообразен в течение нескольких часов после введения соли. При делирии или судорогах показано внутривенное введение диазепама.
Фармакодинамика
Описание Фармакодинамика Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Ибупрофен
Фармакотерапевтическая группа: производные пропионовой кислоты.
Код УВД: M01AE51
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид
Фармакотерапевтическая группа: носовые противозастойные средства системного применения, симпатомиметрия.
Код УВД: R01BA52
Ибупрофен — нестероидное противовоспалительное средство, относящееся к классу пропионовой кислоты лекарственных средств. Обладает обезболивающими, жаропонижающими и противовоспалительными свойствами. Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид является симпатомиметиком, который вызывает вазоконстрикцию слизистой оболочки носа и тем самым уменьшает ринорею и заложенность носа.
Экспериментальные данные показывают, что ибупрофен может конкурентно ингибировать влияние аспирина с низкой дозой (ацетилсалициловой кислоты) на агрегацию тромбоцитов при одновременной дозировке. Некоторые фармакодинамические исследования показывают, что при разовых дозах 400 мг ибупрофена в течение 8 ч до или в течение 30 мин после немедленного высвобождения аспирина (ацетилсалициловой кислоты) (81 мг) снижение влияния АСД на образование тромбоксана или агрегации тромбоцитов происходило в течение 8 ч.. Хотя существует неопределенность в отношении экстраполяции этих данных на клиническую ситуацию, нельзя исключать возможность того, что регулярное долгосрочное использование ибупрофена уменьшит кардиопротекторное действие ацетилсалициловой кислоты с низкой дозой. При случайном использовании ибупрофена ни один клинически релевантный эффект не считается вероятным
Фармакокинетика
Описание Фармакокинетика Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
У взрослых ибупрофен всасывается из желудочно-кишечного тракта из твердой пероральной дозировки, а пиковые концентрации в плазме происходят примерно через 1-2 часа после приема. Ибупрофен в основном метаболизируется в печени до 2-гидроксиибупрофена и 2 — карбоксиибупрофена. Ибупрофен на 90-99% связан с белками плазмы и имеет период полураспада плазмы около 2 часов. Он быстро выводится с мочой в основном в виде метаболитов и их конъюгатов. Около 1% выводится с мочой в виде неизмененного ибупрофена и около 14% — в виде конъюгированного ибупрофена.
В ограниченных исследованиях ибупрофен появляется в очень низких концентрациях в грудном молоке.
Псевдоэфедрин гидрохлорид быстро всасывается из желудочно-кишечного тракта с пиковыми уровнями плазмы через 1-3 часа. Он, как и большинство симпатомиметиков, частично метаболизируется в печени, но в основном выводится с мочой в неизмененном виде.
Фармокологическая группа
Описание Фармокологическая группа Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Производные пропионовой кислоты.
Доклинические данные по безопасности
Описание Доклинические данные по безопасности Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Исследования токсичности с повторной дозой комбинаций ибупрофена и псевдоэфедрина не проводились. Комбинация не была мутагенной.
Субхронные и хронические исследования токсичности проводились только на ибупрофене с 6-месячным НОАЭЛЕМ 60 мг/кг у крыс. Токсичность проявлялась в виде поражений и изъязвлений в желудочно-кишечном тракте. Ибупрофен не мутаген и не был канцерогенным в хронических грызунов bioassays.
Subchronische или хроническая токсичность исследования не проводились с псевдо эфедрин в одиночку. Сочетание ибупрофена и псевдоэфедрина не было мутагеном. Исследование скрининга человека с участием более 3000 пользователей псевдоэфедрина не показало увеличения рака в течение 7,5 лет
Исследования репротоксичности на животных с отдельными ингредиентами показали, что они не были тератогенными, однако следует избегать использования продукта во время беременности, если это возможно.
Особые меры предосторожности при утилизации и другой обработке
Описание Особые меры предосторожности при утилизации и другой обработке Advil Cold & Sinusявляется автоматическим переводом с языка оригинала.
Ни в коем случае не используйте эту информацию для любых медицинских назначений или манипуляций.
Обязательно изучайте оригинальную инструкцию лекарства из упаковки.
В данном описании могут присутствовать многочисленные ошибки из-за автоматического перевода!
Учитывайте это и не используйте это описание!
more…
Никаких особых требований.
Доступно в странах
Найти в стране:
А
Б
В
Г
Д
Е
З
И
Й
К
Л
М
Н
О
П
Р
С
Т
У
Ф
Х
Ч
Ш
Э
Ю
Я
Advil Cold and Sinus Prescribing Information
Package insert / product label
Generic name: ibuprofen, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride
Dosage form: tablet, coated
Drug class: Upper respiratory combinations
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 24, 2023.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Warnings
- Dosage and Administration
ACTIVE INGREDIENTS (IN EACH CAPLET)
Ibuprofen 200 mg (NSAID)*
Pseudoephedrine HCl 30 mg
*nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
PURPOSES
Pain reliever/fever reducer
Nasal decongestant
Indications and Usage for Advil Cold and Sinus
temporarily relieves these symptoms associated with the common cold or flu:
- •
- headache
- •
- fever
- •
- sinus pressure
- •
- nasal congestion
- •
- minor body aches and pains
Warnings
Allergy alert:
Ibuprofen may cause a severe allergic reaction, especially in people allergic to aspirin. Symptoms may include:
- •
- hives
- •
- facial swelling
- •
- asthma (wheezing)
- •
- shock
- •
- skin reddening
- •
- rash
- •
- blisters
If an allergic reaction occurs, stop use and seek medical help right away.
Stomach bleeding warning:
This product contains an NSAID, which may cause severe stomach bleeding. The chance is higher if you:
- •
- are age 60 or older
- •
- have had stomach ulcers or bleeding problems
- •
- take a blood thinning (anticoagulant) or steroid drug
- •
- take other drugs containing prescription or nonprescription NSAIDs [aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, or others]
- •
- have 3 or more alcoholic drinks every day while using this product
- •
- take more or for a longer time than directed
Heart attack and stroke warning
NSAIDs, except aspirin, increase the risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke. These can be fatal. The risk is higher if you use more than directed or for longer than directed.
Do not use
- •
- in children under 12 years of age
- •
- if you have ever had an allergic reaction to any other pain reliever/fever reducer
- •
- right before or after heart surgery
- •
- if you are now taking a prescription monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) (certain drugs for depression, psychiatric, or emotional conditions, or Parkinson’s disease), or for 2 weeks after stopping the MAOI drug. If you do not know if your prescription drug contains an MAOI, ask a doctor or pharmacist before taking this product.
Ask a doctor before use if
- •
- stomach bleeding warning applies to you
- •
- you have problems or serious side effects from taking pain relievers or fever reducers
- •
- you have a history of stomach problems, such as heartburn
- •
- you have high blood pressure, heart disease, liver cirrhosis, kidney disease, asthma, thyroid disease, diabetes, have trouble urinating due to an enlarged prostate gland, or had a stroke
- •
- you are taking a diuretic
Ask a doctor or pharmacist before use if you are
- •
- under a doctor’s care for any serious condition
- •
- taking any other product that contains pseudoephedrine or any other nasal decongestant
- •
- taking aspirin for heart attack or stroke, because ibuprofen may decrease this benefit of aspirin
- •
- taking any other drug
When using this product
- •
- take with food or milk if stomach upset occurs
Stop use and ask a doctor if
- •
- you experience any of the following signs of stomach bleeding:
- •
- feel faint
- •
- vomit blood
- •
- have bloody or black stools
- •
- have stomach pain that does not get better
- •
- you have symptoms of heart problems or stroke:
- •
- chest pain
- •
- trouble breathing
- •
- weakness in one part or side of body
- •
- slurred speech
- •
- leg swelling
- •
- fever gets worse or lasts more than 3 days
- •
- nasal congestion lasts for more than 7 days
- •
- symptoms continue or get worse
- •
- redness or swelling is present in the painful area
- •
- you get nervous, dizzy, or sleepless
- •
- any new symptoms appear
If pregnant or breast-feeding,
ask a health professional before use. It is especially important not to use ibuprofen during the last 3 months of pregnancy unless definitely directed to do so by a doctor because it may cause problems in the unborn child or complications during delivery.
Keep out of reach of children.
In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center right away.
Advil Cold and Sinus Dosage and Administration
- •
- do not take more than directed
- •
- the smallest effective dose should be used
- •
- adults and children 12 years of age and over:
- •
- take 1 caplet every 4 to 6 hours while symptoms persist. If symptoms do not respond to 1 caplet, 2 caplets may be used.
- •
- do not use more than 6 caplets in any 24-hour period unless directed by a doctor
- •
- children under 12 years of age: do not use
OTHER INFORMATION
- •
- store at 20-25°C (68-77°F). Avoid excessive heat above 40°C (104°F).
- •
- read all warnings and directions before use. Keep carton.
INACTIVE INGREDIENTS
acetylated monoglycerides, carnauba wax, colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, croscarmellose sodium, methylparaben, microcrystalline cellulose, pharmaceutical glaze, pharmaceutical ink, povidone, pregelatinized starch, propylparaben, sodium benzoate, sodium lauryl sulfate, stearic acid, sucrose, synthetic iron oxides, titanium dioxide
QUESTIONS OR COMMENTS?
Call toll free 1-800-88-ADVIL
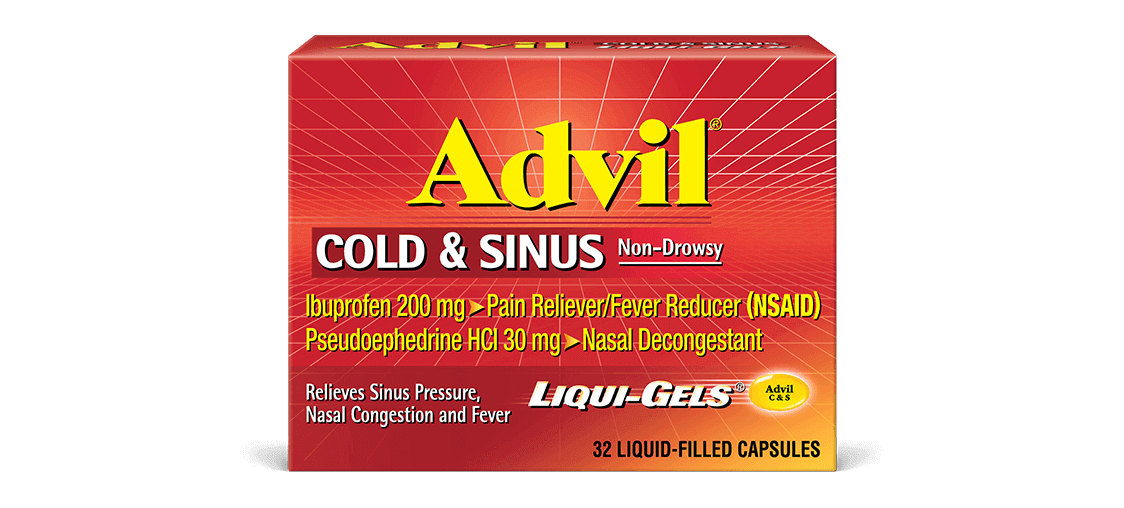
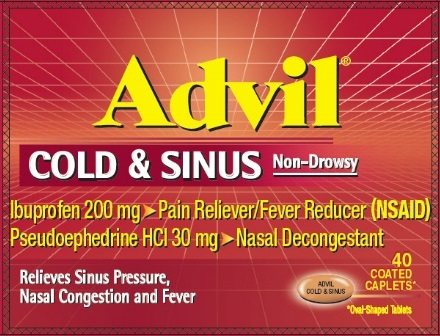
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Advil®
COLD & SINUS Non-Drowsy
Ibuprofen 200 mg ‣ Pain Reliever/Fever Reducer (NSAID)
Pseudoephedrine HCl 30 mg ‣ Nasal Decongestant
Relieves Sinus Pressure,
Nasal Congestion and Fever
40
COATED
CAPLETS*
*Oval-Shaped Tablets
| ADVIL COLD AND SINUS ibuprofen and pseudoephedrine hydrochloride tablet, coated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Labeler — GlaxoSmithKline Consumer Healthcare Holdings (US) LLC
(079944263)
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Company | 829390975 | ANALYSIS(0573-0180) , MANUFACTURE(0573-0180) |
Medical Disclaimer
Адвил — инструкция по применению
Форма выпуска и состав
Лекарственное средство выпускается в виде двояковыпуклых, покрытых пленочными красновато-коричневыми оболочками, таблеток. На их гладкой блестящей поверхности нанесена черная маркировка. Первичная упаковка — компактный пластиковый флакон с навинчивающейся крышкой с защитой от случайного вскрытия. Он находится в картонной коробке вместе с инструкцией по применению. Производит препарат германская фармацевтическая компания Пфайзер Инновации.
Активный состав лекарственного средства представлен только ибупрофеном из клинико-фармакологической группы нестероидных противовоспалительных средств. Для формирования таблетированной основы с пленочной оболочкой производитель воспользовался следующими вспомогательными веществами:
- кукурузным крахмалом;
- прежелатинизированным крахмалом;
- кроскармелозой натрия;
- двуокисью кремния коллоидной;
- кислотой стеариновой;
- натрия лаурилсульфатом;
- гипромеллозой;
- макроголом;
- двуокисью титана;
- окисью железа красной;
- тальком;
- опакодом черным.
Благодаря подобному сочетанию дополнительных ингредиентов ибупрофен быстро, но постепенно высвобождается из таблетированной основы, оказывая длительное обезболивающее и жаропонижающее воздействие (на протяжении восьми часов и более). За счет наличия прочной пленочной оболочки он не разрушается соляной кислотой в желудке, а проникает в тонкий кишечник, где и происходит его усвоение.
Принцип действия Адвила
В основе механизма фармакологического действия лекарственного средства — блокирование фермента циклооксигеназы. Он ответственен за запуск биосинтеза провоспалительных медиаторов, провоцирующих появление почти всех дискомфортных ощущений при обострении артрита или артроза, внедрении в дыхательные пути инфекционных возбудителей. Также активное вещество препятствует слипанию тромбоцитов и их агрегации на внутренних стенках кровеносных сосудов, что несколько облегчает течение заболеваний. Оно проявляет и другие фармакологические эффекты:
- снижает концентрацию лейкоцитов и макрофагов в области воспалительного очага, стимулируя рассасывание отека;
- предупреждает повторное обострение заболевания за счет купирования воспалительного процесса;
- нормализует терморегуляцию;
- способствует более быстрому восстановлению стенок капилляров и улучшению их проницаемости.
Под воздействием основного компонента снижается выраженность припухлости кожи над пораженным суставом или позвоночным сегментом, исчезает скованность движений, ускоряется восстановления поврежденных мягкотканных структур.
Показания для лечения
Болевые ощущения легкой или умеренной выраженности и любой локализации становятся показаниями к приему лекарственного средства. Оно также используется и в комплексной терапии болезней, проявляющихся подъемом температуры. Врачи включают препарат в лечебные схемы пациентов, страдающих такими патологиями:
- артралгиями;
- головными болями;
- мигренями;
- зубной болью;
- невралгией;
- миалгией;
- лихорадочным состоянием, в том числе с ознобом и холодной испариной;
- альгодисменореей — болями в малом тазу во время менструации.
Применяется Адвил и в травматологической практике для устранения болевого синдрома на фоне разрывов связок и (или) сухожилий, мышечных растяжений. Препарат востребован в послеоперационном периоде для снижения выраженности последствий хирургического вмешательства. За счет антипиретического действия таблетки применяются для снижения температуры, обычно превышающей субфебрильные значения.
Как правильно принимать Адвил
Если врач не назначил лечение в индивидуальных дозах, то придерживаются рекомендаций инструкции по применению. Препарат принимать внутрь по таблетке до трех раз в день таким образом, чтобы между приемами было не менее четырех часов. Оптимальное время — во время еды. Таблетку нельзя разжевывать, так как оболочка защищает активное вещество от едкого желудочного сока. Ее необходимо проглотить целиком, запивая достаточным количеством воды.
При отсутствии должного жаропонижающего эффекта в течение трех дней препарат обязательно заменяется аналогом с другим активным компонентом. В качестве анальгетического средства использовать его разрешается не более десяти дней.
Перечень ограничений
Препарат запрещено использовать при индивидуальной непереносимости ибупрофена или одного из вспомогательных компонентов. Нельзя принимать таблетки пациентам с такими заболеваниями и патологическими состояниями:
- сопутствующими или предшествующими эрозивно-язвенными заболеваниями или перфорацией пищеварительных органов;
- заболеваниями крови, в том числе проявляющиеся нарушениями ее свертываемости;
- тяжело протекающей печеночной и почечной недостаточностью;
- тяжело протекающей неконтролируемой сердечной недостаточностью.
Помимо этого в перечень абсолютных противопоказаний включены запланированные или уже проведенные хирургические вмешательства на сердечных структурах и курсовой прием препаратов из той же клинико-фармакологической группы. В педиатрии таблетки используются с двенадцати лет. Их применение в третьем триместре вынашивания беременности запрещено. Производитель не предоставил доказательств безопасности препарата для этой группы пациентов.
Под врачебным контролем и с осторожностью следует принимать лекарственное средство больным детского и пожилого возраста, пациентам с сердечной недостаточностью, артериальной гипертензией, ишемической болезнью сердца, цирроз, течение которого осложняет портальная гипертензия, печеночной и/или почечной недостаточностью, нефротическим синдромом. А также с гипербилирубинемией, язвенными поражениями пищеварительных органов в прошлом, гастритами, энтеритами, колитами, заболеваниями крови неясного генеза (лейкопенией и анемией), цереброваскулярными заболеваниями, дислипидемией, гиперлипидемией, сахарным диабетом, заболеваниями периферических артерий.
Побочные эффекты
В процессе лечения побочные эффекты отмечаются достаточно редко и чаще при несоблюдении режима дозирования. Системные реакции проявляются следующим образом:
- болями в животе, тошнотой, рвотой, изжогой, диспепсией, угнетением аппетита, диареей, повышенным газообразованием, запором;
- изъязвлением слизистых пищеварительных органов;
- сухостью во рту, изъязвлением его слизистых, афтозным стоматитом;
- панкреатитом;
- вздутием живота, гастритом, гематемезисом, меленой;
- снижением почечной и печеночной функциональной активности;
- ощущением нехватки воздуха при вдохе, бронхоспазмами, обострениями астмы, хрипами, стридором;
- вертиго, слуховыми расстройствами;
- зрительными расстройствами;
- головными болями, головокружениями, расстройствами сна, тревожностью, нервозностью и раздражительностью, психомоторным возбуждением, депрессивным состоянием;
- стенокардией, тахикардией, повышенным кровяным давлением, отеками;
- воспалительными или дегенеративными почечными поражениями;
- анемией;
- системными аллергическими реакциями.
Местные побочные реакции характеризуются раздражением кожи, ощущением жжения, зудом. Следует отменить прием таблеток и обратиться к врачу. Может потребоваться прием препаратов для устранения симптомов, в том числе с противоаллергическим действием.
Взаимодействие
Настоятельно не рекомендуется принимать лекарственное средство с такими препаратами и представителями следующих клинико-фармакологических групп:
- антигипертензивными средствами;
- литием;
- сердечными гликозидами;
- Метотрексатом;
- антацидами;
- глюкокортикостероидами;
- ингибиторами обратного захвата серотонина;
- Циклоспорином;
- Мифепристоном;
- диуретиками;
- Зидовудином;
- индукторами и ингибиторами микросомального окисления;
- кофеином;
- Цефамандолом, Цефоперазоном, Цефотетаном, вальпроевой кислотой, Пликамицином;
- миелотоксическими препаратами;
- Циклоспорином;
- урикозурическими лекарственными средствами;
- антиагрегантами, фибринолитиками, тромболитиками.
Нежелательно принимать Адвил вместе со средствами, состав которых представлен компонентами с аналогичным фармакологическим действием, если это не рекомендовано врачом.
Рекомендации
Рекомендуется соблюдать осторожность во время лечения при управлении автотранспортными средствами, выполнении технически сложных работ, требующих особой концентрации внимания и скорости реакций.
Аналоги
При непереносимости лекарственного средства оно заменяется курирующим врачом препаратами с похожим фармакологическим действием — Нимесулидом, Диклофенаком, Кетотифеном, Ортофеном и другими. В Aptstore можно купить Адвил и любые его аналоги. Здесь они продаются в различных лекарственных формах.
Срок годности, условия хранения
Срок годности — три года. Таблетки следует хранить при комнатной температуре в темных местах. Беречь от детей.
Отпуск из аптек
Купить в Интернет-аптеке Aptstore Адвил можно без рецепта от врача.
Где купить Адвил
Клиенты Aptstore сразу ответят на вопрос, где купить Адвил — только в филиалах этой аптечной сети. Наши сотрудники ежедневно контролируют хранение лекарств, соблюдение температурного режима, обязательно отслеживают сроки годности. Именно поэтому все реализуемые в Aptstore препараты, биологически активные добавки, лечебная косметика самого высокого качества. Здесь можно заказать Адвил заранее, если курсовая терапия только планируется, неплохо при этом сэкономив. А также приобрести лекарственные средства и изделия медицинского назначения, назначенные врачом одновременно — бандажи, ортезы, согревающие мази и другое.
Цена в аптеке Адвил вполне демократична. Впрочем, как и стоимость его импортных и российских аналогов. Во время акций приобрести у нас Адвил можно очень дешево.
Как купить Адвил в интернет-аптеке Aptstore
На сайте Aptstore можно в любое время суток узнать, сколько стоит Адвил, как правильно принимать таблетки от боли и жара. Здесь удобно сортировать препараты по назначению, фармакологическим свойствам. На сайте есть информация о скидках на Адвил и другие лекарства. Отыскать его в нашей онлайн-аптеке можно так:
- ввести в поисковую строку слова «Адвил»;
- использовать алфавит, сместив курсор до букв «Адв» (Адвил);
- поэтапно открыть в каталоге: Лекарственные препараты — Обезболивающие препараты — Адвил;
- если Адвил был приобретен здесь ранее, то из избранного отправить его в корзину для оформления заказа.
В нашем интернет-магазине лекарств купить Адвил можно по сниженной цене. Дешевле стоят таблетки, заказ на которые создан за 2-3 дня. Столько длится доставка Адвила в ближайшую аптеку Aptstore с нашего склада.
Доставка заказа Москва
Заказывая на aptstore.ru, можно выбрать доставку в удобную для вас аптеку рядом с домом или по дороге на работу.
Самовывоз из аптеки
Самовывоз из постамата
aminolevulinic acid oral, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid administering other phototoxic drugs with aminolevulinic acid oral for 24 hr during perioperative period.
ibuprofen, aminolevulinic acid topical.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Each drug may increase the photosensitizing effect of the other.
amitriptyline increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
amoxapine increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
ibuprofen and apixaban both increase anticoagulation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
ibuprofen decreases effects of aspirin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Comment: Ibuprofen decreases the antiplatelet effects of low-dose aspirin by blocking the active site of platelet cyclooxygenase. Administer ibuprofen 8 h before aspirin or at least 2-4 h after aspirin. The effect of other NSAIDs on aspirin is not established.ibuprofen increases toxicity of aspirin by anticoagulation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. increases risk of bleeding.
ibuprofen decreases effects of aspirin rectal by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Comment: Ibuprofen decreases the antiplatelet effects of aspirin by blocking the active site of platelet cyclooxygenase. The effect of other NSAIDs on aspirin is not established.
ibuprofen decreases effects of aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Comment: Ibuprofen decreases the antiplatelet effects of aspirin by blocking the active site of platelet cyclooxygenase. The effect of other NSAIDs on aspirin is not established.
ibuprofen, benazepril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
cabergoline, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Additive vasospasm; risk of hypertension.
ibuprofen, captopril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
clomipramine increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
cocaine topical increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
desipramine increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
desvenlafaxine increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
doxapram increases effects of pseudoephedrine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Additive pressor effect.
doxepin increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
duloxetine increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
ibuprofen, enalapril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of erdafitinib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration with strong CYP2C9 inhibitors, monitor closely for adverse reactions and consider decreasing dose accordingly. If strong CYP2C9 inhibitor is discontinued, consider increasing erdafitinib dose in the absence of any drug-related toxicities.
ibuprofen, fosinopril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
imipramine increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of iobenguane I 123 by receptor binding competition. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If clinically appropriate, discontinue drugs that compete for NE receptor sites for at least 5 half-lives; may cause false-negative imaging results. Do not administer pseudoephedrine until at least 7 days after each iobenguane dose.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of iobenguane I 131 by receptor binding competition. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If clinically appropriate, discontinue drugs that compete for NE receptor sites for at least 5 half-lives; may cause false-negative imaging results. Do not administer pseudoephedrine until at least 7 days after each iobenguane dose.
isoflurane increases toxicity of pseudoephedrine by Mechanism: unknown. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of V tach, HTN.
ibuprofen, ketorolac.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
ibuprofen, ketorolac intranasal.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
levomilnacipran increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
ibuprofen, lisinopril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
lofepramine, pseudoephedrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
maprotiline, pseudoephedrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
ibuprofen increases levels of methotrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant administration of NSAIDs with high dose methotrexate has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and GI toxicity. NSAIDs may reduce tubular secretion of methotrexate and enhance toxicity. .
methoxyflurane increases toxicity of pseudoephedrine by Mechanism: unknown. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of V tach, HTN.
ibuprofen, methyl aminolevulinate.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Each drug may increase the photosensitizing effect of the other.
milnacipran increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
ibuprofen, moexipril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of naproxen by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Therapeutic duplicationibuprofen and naproxen both increase anticoagulation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Therapeutic duplicationibuprofen and naproxen both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Therapeutic duplication
nortriptyline increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of oxaprozin by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Therapeutic duplicationibuprofen and oxaprozin both increase anticoagulation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Therapeutic duplicationibuprofen and oxaprozin both increase serum potassium. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Therapeutic duplication
ozanimod increases toxicity of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Because the active metabolite of ozanimod inhibits MAO-B in vitro, there is a potential for serious adverse reactions, including hypertensive crisis. Therefore, coadministration of ozanimod with drugs that can increase norepinephrine or serotonin is not recommended. Monitor for hypertension with concomitant use.
ibuprofen increases levels of pemetrexed by unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Especially in pts. w/mild moderate renal insufficiency. D/C NSAIDs 2 5 d before and 2 d after pemetrexed administration.
ibuprofen, perindopril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
ibuprofen and pexidartinib both increase Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Pexidartinib can cause hepatotoxicity. Avoid coadministration of pexidartinib with other products know to cause hepatoxicity.
ibuprofen, pretomanid.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Comment: Pretomanid regimen associated with hepatotoxicity. Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic agents, including herbal supplements and drugs other than bedaquiline and linezolid.
protriptyline increases effects of pseudoephedrine by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
ibuprofen, quinapril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
ibuprofen, ramipril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
sevoflurane increases toxicity of pseudoephedrine by Mechanism: unknown. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of V tach, HTN.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of siponimod by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of siponimod with drugs that cause moderate CYP2C9 AND a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibition is not recommended. Caution if siponimod coadministered with moderate CYP2C9 inhibitors alone.
ibuprofen, tacrolimus.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Comment: Concomitant administration increases risk of nephrotoxicity.
ibuprofen, trandolapril. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may result in a significant decrease in renal function. NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. The mechanism of these interactions is likely related to the ability of NSAIDs to reduce the synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins.
trazodone, pseudoephedrine. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Comment: Tricyclic antidepressants increase or decrease effects of sympathomimetics, by blocking reuptake of NE, or blocking uptake of indirect sympathomimetics into the adrenergic neuron.
acebutolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of acebutolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
aceclofenac and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.aceclofenac and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
acemetacin and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.acemetacin and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
acetazolamide will increase the level or effect of pseudoephedrine by passive renal tubular reabsorption — basic urine. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and agrimony both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
albuterol and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and albuterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and alfalfa both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of alfuzosin by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen decreases effects of alfuzosin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen will decrease the level or effect of aliskiren by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or with compromised renal function, coadministration of NSAIDs with drugs that affect RAAS may increase the risk of renal impairment (including acute renal failure) and cause loss of antihypertensive effect. Monitor renal function periodically.
ibuprofen and alteplase both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased risk of bleeding, caution is advised.
ibuprofen and American ginseng both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
aluminum hydroxide will increase the level or effect of pseudoephedrine by passive renal tubular reabsorption — basic urine. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution advised with frequent or high dose antacids
ibuprofen increases levels of amikacin by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. Interaction mainly occurs in preterm infants.
amiloride and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
ammonium chloride decreases effects of pseudoephedrine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Urinary excretion of indirect acting alpha/beta agonists (eg, pseudoephedrine) may increase when administered concomitantly with urinary acidifying agents, resulting in lower serum concentrations.
antithrombin alfa and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
antithrombin III and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
arformoterol and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and arformoterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
argatroban and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
benzphetamine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen decreases effects of asenapine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
aspirin and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.aspirin and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
aspirin rectal and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.aspirin rectal and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.aspirin/citric acid/sodium bicarbonate and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
atenolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of atenolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
azficel-T, ibuprofen. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: Patients taking NSAIDS may experience increased bruising or bleeding at biopsy and/or injection sites. Concomitant use of NSAIDs is not recommended.
ibuprofen, azilsartan.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.ibuprofen decreases effects of azilsartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. NSAIDs decrease synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins, and thus affect fluid homeostasis and may diminish antihypertensive effect.
bemiparin and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
benazepril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
ibuprofen increases and bendroflumethiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
betaxolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of betaxolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen, betrixaban.
Either increases levels of the other by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
bimatoprost, ibuprofen. unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. There are conflicting reports from studies of either increased or decreased IOP when ophthalmic prostaglandins are coadministered with NSAIDs (either systemic or ophthalmic).
bisoprolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of bisoprolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
bivalirudin and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
bromocriptine, pseudoephedrine.
Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Hypertension, V tach.
ibuprofen, budesonide.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
ibuprofen increases and bumetanide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of bumetanide by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
candesartan and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of candesartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. NSAIDs decrease synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins, and thus affect fluid homeostasis and may diminish antihypertensive effect.candesartan, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
captopril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor plasma levels when used concomitantly
ibuprofen increases and carbenoxolone decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
carvedilol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of carvedilol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
celecoxib and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.celecoxib and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
celiprolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of celiprolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen increases and chlorothiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
chlorpromazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider avoiding use of pseudoephedrine in patients receiving phenothiazines (especially thioridazine) due to the potential risk of cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death. Monitor for evidence of ventricular arrhythmias during concomitant use.
ibuprofen increases effects of chlorpropamide by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypoglycemia.
ibuprofen increases and chlorthalidone decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and choline magnesium trisalicylate both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and choline magnesium trisalicylate both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and cinnamon both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen, ciprofloxacin. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Comment: Mechanism: unknown. Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
citalopram, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. If possible, avoid concurrent use.
clomipramine, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. Clomipramine inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
clopidogrel, ibuprofen.
Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Clopidogrel and NSAIDs both inhibit platelet aggregation.
ibuprofen and cordyceps both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen, cortisone.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
ibuprofen increases and cyclopenthiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen, cyclosporine.
Either increases toxicity of the other by nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis, increasing the risk of nephrotoxicity.
dabigatran and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution is advised, both drugs have the potential to cause bleeding. Concomitant use may increase risk of bleeding.
dalteparin and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
deferasirox, ibuprofen. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: Combination may increase GI bleeding, ulceration and irritation. Use with caution.
defibrotide increases effects of ibuprofen by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Defibrotide may enhance effects of platelet inhibitors.
ibuprofen, deflazacort.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
ibuprofen, dexamethasone.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
dexfenfluramine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
dexmethylphenidate and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
dextroamphetamine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
dichlorphenamide, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Both drugs can cause metabolic acidosis.
diclofenac and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.diclofenac and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
diethylpropion and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
diflunisal and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.diflunisal and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and digoxin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
dobutamine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and dobutamine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and dong quai both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
dopamine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
dopexamine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and dopexamine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen decreases effects of doxazosin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.pseudoephedrine decreases effects of doxazosin by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of dronabinol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Dronabinol is a CYP2C9 substrate.
pseudoephedrine and droxidopa both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor. May increase risk for supine hypertension
drospirenone and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
duloxetine, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
edoxaban, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Both drugs have the potential to cause bleeding, monitor closely. Promptly evaluate any signs or symptoms of blood loss.
efavirenz will increase the level or effect of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
eltrombopag increases levels of ibuprofen by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. UGT inhibition; significance of interaction unclear.
ibuprofen increases levels of eluxadoline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. As a precautionary measure due to incomplete information on the metabolism of eluxadoline, use caution when coadministered with strong CYP2C9/10 inhibitors.
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by decreasing renal clearance. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Toxicity may result from coadministration of emtricitabine and tenofovir with other drugs that are also primarily excreted by glomerular filtration and/or active tubular secretion including high-dose or multiple-dose NSAIDs; alternatives to NSAIDs should be considered.
emtricitabine, ibuprofen.
Either increases levels of the other by decreasing renal clearance. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Toxicity may result from coadministration of emtricitabine with other drugs that are also primarily excreted by glomerular filtration and/or active tubular secretion including high-dose or multiple-dose NSAIDs; alternatives to NSAIDs should be considered.
enalapril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
enoxaparin and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
ibuprofen increases and ephedrine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.ephedrine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ephedrine, pseudoephedrine.
Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
epinephrine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and epinephrine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
pseudoephedrine, epinephrine inhaled.
Either increases effects of the other by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen increases and epinephrine racemic decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
epinephrine racemic and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and epoprostenol both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
eprosartan and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of eprosartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. NSAIDs decrease synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins, and thus affect fluid homeostasis and may diminish antihypertensive effect.eprosartan, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
escitalopram, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
esketamine intranasal, pseudoephedrine.
Either increases toxicity of the other by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor. Closely monitor blood pressure with concomitant use of esketamine nasal with stimulants. .
esmolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of esmolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen increases and ethacrynic acid decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
etodolac and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.etodolac and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
fenfluramine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and fennel both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
fenoprofen and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.fenoprofen and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and feverfew both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
fish oil triglycerides will increase the level or effect of ibuprofen by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Prolonged bleeding reported in patients taking antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants and oral omega-3 fatty acids. Periodically monitor bleeding time in patients receiving fish oil triglycerides and concomitant antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants.
ibuprofen, fludrocortisone.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
fluoxetine will increase the level or effect of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.fluoxetine, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
fluphenazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider avoiding use of pseudoephedrine in patients receiving phenothiazines (especially thioridazine) due to the potential risk of cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death. Monitor for evidence of ventricular arrhythmias during concomitant use.
flurbiprofen and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.flurbiprofen and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
fluvoxamine, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding; SSRIs inhib. srotonin uptake by platelets.
fondaparinux and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
formoterol and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and formoterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and forskolin both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
hydralazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sympathomimetics can antagonize the activity of some antihypertensive agents.
fosinopril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
ibuprofen increases and furosemide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and garlic both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
gemifloxacin, ibuprofen. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Comment: Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
ibuprofen increases and gentamicin decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and ginger both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and ginkgo biloba both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen increases effects of glimepiride by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypoglycemia.
ibuprofen increases effects of glipizide by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypoglycemia.
ibuprofen increases effects of glyburide by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypoglycemia.ibuprofen increases levels of glyburide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP2C9 inhibitors may decrease glyburide metabolism.
green tea, ibuprofen. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: Combination may increase risk of bleeding.
heparin and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
ibuprofen and horse chestnut seed both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen decreases effects of hydralazine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen increases and hydrochlorothiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen, hydrocortisone.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
ibrutinib will increase the level or effect of ibuprofen by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Ibrutinib may increase the risk of hemorrhage in patients receiving antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapies and monitor for signs of bleeding.
icosapent, ibuprofen.
Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Icosapent may prolong bleeding time. Periodically monitor if coadministered with other drugs that affect bleeding.
imatinib will increase the level or effect of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.imatinib, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Comment: Imatinib may cause thrombocytopenia; bleeding risk increased when imatinib is coadministered with anticoagulants, NSAIDs, platelet inhibitors, and thrombolytic agents.
ibuprofen increases and indapamide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and indomethacin both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and indomethacin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of insulin degludec by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Sympathomimetics increase blood glucose by stimulating alpha and beta receptors; this action results in increased hepatic glucose production, glycogenolysis, and decreased insulin secretion.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of insulin degludec/insulin aspart by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Sympathomimetics increase blood glucose by stimulating alpha and beta receptors; this action results in increased hepatic glucose production, glycogenolysis, and decreased insulin secretion.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of insulin detemir by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Sympathomimetics increase blood glucose by stimulating alpha and beta receptors; this action results in increased hepatic glucose production, glycogenolysis, and decreased insulin secretion.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of insulin glargine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Sympathomimetics increase blood glucose by stimulating alpha and beta receptors; this action results in increased hepatic glucose production, glycogenolysis, and decreased insulin secretion.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of insulin inhaled by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Sympathomimetics increase blood glucose by stimulating alpha and beta receptors; this action results in increased hepatic glucose production, glycogenolysis, and decreased insulin secretion.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of insulin regular human by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Sympathomimetics increase blood glucose by stimulating alpha and beta receptors; this action results in increased hepatic glucose production, glycogenolysis, and decreased insulin secretion.
irbesartan and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of irbesartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antihypertensive effect of angiotensin receptor blockers may be attenuated by NSAIDs; monitor renal function and blood pressure periodically.irbesartan, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
isoproterenol and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and isoproterenol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and ketoprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and ketoprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
levalbuterol and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and ketorolac both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and ketorolac both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and ketorolac intranasal both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and ketorolac intranasal both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
labetalol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of labetalol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs diminish antihypertensive effects of beta-blockers.
ibuprofen increases levels of lacosamide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider decreasing lacosamide dose when coadministered with strong CYP2C9 inhibitors.
latanoprost, ibuprofen. unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. There are conflicting reports from studies of either increased or decreased IOP when ophthalmic prostaglandins are coadministered with NSAIDs (either systemic or ophthalmic).
latanoprostene bunod ophthalmic, ibuprofen. unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. There are conflicting reports from studies of either increased or decreased IOP when ophthalmic prostaglandins are coadministered with NSAIDs (either systemic or ophthalmic).
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of lesinurad by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
ibuprofen increases and levalbuterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
levofloxacin, ibuprofen. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Comment: Risk of CNS stimulation/seizure. Mechanism: Displacement of GABA from receptors in brain.
levomilnacipran, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. SNRIs may further impair platelet activity in patients taking antiplatelet or anticoagulant drugs.
lisdexamfetamine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
lisinopril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
ibuprofen increases levels of lithium by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and lornoxicam both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and lornoxicam both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
losartan and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of losartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. NSAIDs decrease synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins, and thus affect fluid homeostasis and may diminish antihypertensive effect.losartan, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
lumacaftor/ivacaftor will decrease the level or effect of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Ibuprofen it a substrate of CYP2C9. Lumacaftor has the potential to induce CYP2C9 substrates.
meclofenamate and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.meclofenamate and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and mefenamic acid both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and mefenamic acid both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
melatonin increases effects of ibuprofen by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Melatonin may decrease prothrombin time.
ibuprofen and meloxicam both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and meloxicam both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
mesalamine, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive nephrotoxicity.
ibuprofen increases and metaproterenol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.metaproterenol and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
methamphetamine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen increases and methyclothiazide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor. .
methenamine decreases effects of pseudoephedrine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Urinary excretion of indirect acting alpha/beta agonists (eg, pseudoephedrine) may increase when administered concomitantly with urinary acidifying agents, resulting in lower serum concentrations.
methyldopa increases effects of pseudoephedrine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor.
methylenedioxymethamphetamine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen, methylprednisolone.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
ibuprofen increases and metolazone decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
metoprolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of metoprolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
midodrine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
milnacipran, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
mipomersen, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: Both drugs have potential to increase hepatic enzymes; monitor LFTs.
ibuprofen increases and mistletoe decreases anticoagulation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
moexipril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
moxifloxacin, ibuprofen. Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
Comment: Increased risk of CNS stimulation and seizures with high doses of fluoroquinolones.
ibuprofen decreases effects of moxisylyte by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of mycophenolate by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and nabumetone both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and nabumetone both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
nadolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of nadolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of nateglinide by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may reduce nateglinide’s hypoglycemic action.
nebivolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of nebivolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
nefazodone, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
ibuprofen increases and nettle decreases anticoagulation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
norepinephrine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and norepinephrine decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
olmesartan and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of olmesartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. NSAIDs decrease synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins, and thus affect fluid homeostasis and may diminish antihypertensive effect.olmesartan, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
pseudoephedrine and olodaterol inhaled both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution with coadministration of adrenergic drugs by any route because of additive sympathetic effects
ibuprofen increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen, ospemifene.
Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
oxytocin increases effects of pseudoephedrine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and panax ginseng both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and parecoxib both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and parecoxib both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
paroxetine, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
ibuprofen and pau d’arco both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
pegaspargase increases effects of ibuprofen by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of bleeding events.
peginterferon alfa 2b decreases levels of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. When patients are administered peginterferon alpha-2b with CYP2C9 substrates, the therapeutic effect of these drugs may be altered.
penbutolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of penbutolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
perindopril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
perphenazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider avoiding use of pseudoephedrine in patients receiving phenothiazines (especially thioridazine) due to the potential risk of cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death. Monitor for evidence of ventricular arrhythmias during concomitant use.
phendimetrazine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenindione and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
ibuprofen decreases effects of phenoxybenzamine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
phentermine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen decreases effects of phentolamine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
phenylephrine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenylephrine PO and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and phytoestrogens both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
pindolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of pindolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen increases and pirbuterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.pirbuterol and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and piroxicam both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and piroxicam both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
potassium phosphate decreases effects of pseudoephedrine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Urinary excretion of indirect acting alpha/beta agonists (eg, pseudoephedrine) may increase when administered concomitantly with urinary acidifying agents, resulting in lower serum concentrations.
pivmecillinam, ibuprofen.
Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Use Caution/Monitor.pivmecillinam, ibuprofen.
Either increases levels of the other by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and potassium acid phosphate both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
ibuprofen and potassium chloride both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
ibuprofen and potassium citrate both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
potassium iodide and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen increases levels of pralatrexate by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs may delay pralatrexate clearance, increasing drug exposure. Adjust the pralatrexate dose as needed.
ibuprofen, prasugrel.
Either increases effects of the other by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Chronic use of NSAIDs with prasugrel may increase bleeding risk.
ibuprofen decreases effects of prazosin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen, prednisolone.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
ibuprofen, prednisone.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of GI ulceration.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of probenecid by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
prochlorperazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider avoiding use of pseudoephedrine in patients receiving phenothiazines (especially thioridazine) due to the potential risk of cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death. Monitor for evidence of ventricular arrhythmias during concomitant use.
promazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death, more likely w/thioridazine than other phenothiazines. Interaction more likely in certain predisposed pts. only.
promethazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death, more likely w/thioridazine than other phenothiazines. Interaction more likely in certain predisposed pts. only.
propranolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of propranolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
propylhexedrine and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
protamine and ibuprofen both increase anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
quinapril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
ramipril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
ibuprofen and reishi both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and reteplase both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased risk of bleeding, caution is advised.
rivaroxaban, ibuprofen. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: NSAIDs are known to increase bleeding. Bleeding risk may be increased when NSAIDs are used concomitantly with rivaroxaban. Monitor for signs/symptoms of blood loss.
rivastigmine increases toxicity of ibuprofen by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor patients for symptoms of active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding.
sacubitril/valsartan and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.sacubitril/valsartan, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.ibuprofen decreases effects of sacubitril/valsartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. NSAIDs decrease synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins, and thus affect fluid homeostasis and may diminish antihypertensive effect.
pseudoephedrine and safinamide both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor patients for hypertension if safinamide is prescribed concomitantly with prescription or nonprescription sympathomimetics, including nasal, oral, or ophthalmic decongestants and cold remedies.
ibuprofen and salicylates (non-asa) both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and salicylates (non-asa) both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
salmeterol and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen increases and salmeterol decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and salsalate both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and salsalate both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate and pseudoephedrine both decrease sedation. Use Caution/Monitor.serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
saw palmetto increases toxicity of ibuprofen by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. May increase risk of bleeding.
sertraline, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
ibuprofen and Siberian ginseng both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen decreases effects of silodosin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.pseudoephedrine decreases effects of silodosin by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
sodium bicarbonate will increase the level or effect of pseudoephedrine by passive renal tubular reabsorption — basic urine. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution advised with frequent or high dose antacids
ibuprofen, sodium picosulfate/magnesium oxide/anhydrous citric acid.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May be associated with fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
sodium citrate/citric acid will increase the level or effect of pseudoephedrine by passive renal tubular reabsorption — basic urine. Use Caution/Monitor.
sodium lactate will increase the level or effect of pseudoephedrine by passive renal tubular reabsorption — basic urine. Use Caution/Monitor.
sodium phosphates, IV decreases effects of pseudoephedrine by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Urinary excretion of indirect acting alpha/beta agonists (eg, pseudoephedrine) may increase when administered concomitantly with urinary acidifying agents, resulting in lower serum concentrations.
sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride increases toxicity of ibuprofen by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: Coadministration with medications that cause fluid and electrolyte abnormalities may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmias, and renal impairment.
ibuprofen, sodium sulfate/potassium chloride/magnesium sulfate/polyethylene glycol. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: Caution when bowel preps are used with drugs that cause SIADH or NSAIDs; increased risk for water retention or electrolyte imbalance.
sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate increases toxicity of ibuprofen by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: Coadministration with medications that cause fluid and electrolyte abnormalities may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmias, and renal impairment.
pseudoephedrine and solriamfetol both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
sotalol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of sotalol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen and sparsentan both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of NSAIDS, including selective COX-2 inhibitors, may result in deterioration of kidney function (eg, possible kidney failure). Monitor for signs of worsening renal function with concomitant use with NSAIDs.
spironolactone and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.spironolactone decreases effects of pseudoephedrine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and succinylcholine both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of tamsulosin by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and sulfasalazine both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and sulfasalazine both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and sulindac both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and sulindac both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
tafluprost, ibuprofen. unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. There are conflicting reports from studies of either increased or decreased IOP when ophthalmic prostaglandins are coadministered with NSAIDs (either systemic or ophthalmic).
telmisartan and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of telmisartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. NSAIDs decrease synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins, and thus affect fluid homeostasis and may diminish antihypertensive effect.telmisartan, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
temocillin, ibuprofen.
Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Use Caution/Monitor.temocillin, ibuprofen.
Either increases levels of the other by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and tenecteplase both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased risk of bleeding, caution is advised.
tenofovir DF, ibuprofen.
Either increases levels of the other by decreasing renal clearance. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Toxicity may result from coadministration of tenofovir DF with other drugs that are also primarily excreted by glomerular filtration and/or active tubular secretion including high-dose or multiple-dose NSAIDs; alternatives to NSAIDs should be considered.
pseudoephedrine decreases effects of terazosin by sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of terazosin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of terbinafine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
terbutaline and pseudoephedrine both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen increases and terbutaline decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
thioridazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider avoiding use of pseudoephedrine in patients receiving phenothiazines (especially thioridazine) due to the potential risk of cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death. Monitor for evidence of ventricular arrhythmias during concomitant use.
ticagrelor, ibuprofen.
Either increases effects of the other by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of bleeding with use of ticagrelor and chronic NSAID use. .
ticarcillin, ibuprofen.
Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Use Caution/Monitor.ticarcillin, ibuprofen.
Either increases levels of the other by decreasing renal clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
ticlopidine will increase the level or effect of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.ticlopidine increases toxicity of ibuprofen by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
timolol and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of timolol by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Long term (>1 wk) NSAID use. NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis.
tobramycin inhaled and ibuprofen both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid concurrent or sequential use to decrease risk for ototoxicity
ibuprofen increases effects of tolazamide by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypoglycemia.
ibuprofen increases effects of tolbutamide by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypoglycemia.
ibuprofen and tolfenamic acid both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and tolfenamic acid both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and tolmetin both increase anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen and tolmetin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen and tolvaptan both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen increases and torsemide decreases serum potassium. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
trandolapril, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
travoprost ophthalmic, ibuprofen. unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. There are conflicting reports from studies of either increased or decreased IOP when ophthalmic prostaglandins are coadministered with NSAIDs (either systemic or ophthalmic).
trazodone, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
ibuprofen, triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of NSAIDS and corticosteroids increases the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. .
triamterene and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
trifluoperazine, pseudoephedrine. Mechanism: unknown. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider avoiding use of pseudoephedrine in patients receiving phenothiazines (especially thioridazine) due to the potential risk of cardiac arrhythmia or sudden death. Monitor for evidence of ventricular arrhythmias during concomitant use.
ibuprofen and valoctocogene roxaparvovec both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Medications that may cause hepatotoxicity when combined with valoctogene roxaparvovec may potentiate the risk of elevated liver enzymes. Closely monitor these medications and consider alternative medications in case of potential drug interactions.
valsartan and ibuprofen both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.ibuprofen decreases effects of valsartan by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. NSAIDs decrease synthesis of vasodilating renal prostaglandins, and thus affect fluid homeostasis and may diminish antihypertensive effect.valsartan, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor.
Comment: May result in renal function deterioration, particularly in elderly or volume depleted individuals.
venlafaxine, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of upper GI bleeding. SSRIs inhib. serotonin uptake by platelets.
ibuprofen increases and vitamin K1 (phytonadione) decreases anticoagulation. Effect of interaction is not clear, use caution. Use Caution/Monitor.
voclosporin, ibuprofen.
Either increases toxicity of the other by nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with drugs associated with nephrotoxicity may increase the risk for acute and/or chronic nephrotoxicity.
ibuprofen, vorapaxar.
Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive antiplatelet effect may occur.
ibuprofen, vortioxetine.
Either increases effects of the other by anticoagulation. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen, warfarin.
Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Drugs with antiplatelet properties may increase anticoagulation effect of warfarin.
pseudoephedrine and xylometazoline both increase sympathetic (adrenergic) effects, including increased blood pressure and heart rate. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen, zanubrutinib.
Either increases effects of the other by anticoagulation. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Zanubrutinib-induced cytopenias increases risk of hemorrhage. Coadministration of zanubritinib with antiplatelets or anticoagulants may further increase this risk.
Обобщенные научные материалы по действующему веществу препарата Адвил (таблетки, покрытые пленочной оболочкой, 400 мг)
Дата последней актуализации: 01.06.2021
Особые отметки:
Содержание
- Действующее вещество
- ATX
- Владелец РУ
- Условия хранения
- Срок годности
- Источники информации
- Фармакологическая группа
- Характеристика
- Фармакология
- Показания к применению
- Нозологическая классификация (МКБ-10)
- Противопоказания
- Ограничения к применению
- Применение при беременности и кормлении грудью
- Побочные действия
- Взаимодействие
- Передозировка
- Способ применения и дозы
- Меры предосторожности
- Аналоги (синонимы) препарата Адвил
Действующее вещество
ATX
Владелец РУ
Пфайзер Инновации ООО
Условия хранения
При температуре не выше 30 °C.
Хранить в недоступном для детей месте.
Срок годности
3 года.
Не применять по истечении срока годности, указанного на упаковке.
Источники информации
www.drugs.com, www.fda.gov, 2021.
Фармакологическая группа
Характеристика
Белый или не совсем белый кристаллический порошок, практически нерастворимый в воде, хорошо растворимый в органических растворителях (этанол, ацетон). Молекулярная масса 206,28.
Фармакология
Механизм действия
НПВС из группы производных пропионовой кислоты. Ингибирует ЦОГ-1 и ЦОГ-2, катализирующих образование ПГ.
ПГ являются медиаторами воспаления, сенсибилизируют афферентные нервы и потенцируют действие брадикинина при возникновении боли у животных моделей. Ибупрофен является сильным ингибитором синтеза ПГ in vitro. Концентрация ибупрофена, достигаемая во время терапии, вызывает эффект in vivo.
Фармакодинамика
Оказывает противовоспалительный, обезболивающий и жаропонижающий эффекты.
Обеспечивает закрытие артериального протока у недоношенных новорожденных путем ингибирования синтеза ПГ.
Фармакокинетика
Хорошо всасывается при пероральном приеме, Tmax составляет обычно 1–2 ч, а начало обезболивающего и жаропонижающего эффектов проявляется через 1 ч.
Связывание с белками плазмы составляет >99%.
Большее количество ибупрофена подвергается метаболизму и выводится с мочой в виде метаболитов. T1/2 составляет 1,8–2,4 ч, при этом у новорожденных T1/2 в 10 раз продолжительнее, чем у взрослых.
Клиническая фармакология
Взрослые. В ходе клинических исследований 560 пациентов принимали ибупрофен, из них 438 — при боли и 122 — при лихорадке. В исследованиях боли ибупрофен назначали в дозе 400 или 800 мг каждые 6 ч в течение 3 дней. При лихорадке — в дозах 100, 200 или 400 мг каждые 4 или 6 ч в течение 3 дней. Наиболее частым типом побочных реакций, возникающих при пероральном приеме ибупрофена, является нарушение со стороны ЖКТ.
Дети. В общей сложности 143 пациента в возрасте 6 мес и старше получали ибупрофен в контролируемых клинических исследованиях. Наиболее распространенными побочными реакциями (частота возникновения ≥2%) у педиатрических пациентов были боль в месте инфузии, рвота, тошнота, анемия и головная боль.
Показания к применению
Воспалительные заболевания (симптоматическая терапия) (остеоартрит, ревматоидный артрит, ювенильный ревматоидный артрит у детей, уменьшение боли, лихорадки и воспаления при перикардите (при наличии инфаркта миокарда отдают предпочтение ацетисалициловой кислоте); слабая или умеренная боль у взрослых и детей, связанная с простудой, гриппом; боль в горле; головная боли (включая мигрень); зубная боль; мышечная боль; боли в спине; боль при артрите; дисминорея (симптоматическое лечение первичной дисминореи, временное облегчение незначительных болей, связанных с менструальными спазмами); лихорадка (снижение температуры у взрослых и детей (пероральный прием).
Открытый артериальный проток (ОАП): ибупрофен имеет статус орфанного препарата для терапии ОАП и используется у недоношенных новорожденных с весом 500–1500 г и гестационным возрастом ≤32 нед, когда обычное медицинское лечение неэффективно.
Нозологическая классификация (МКБ-10)
Список кодов МКБ-10
- G54.1 Поражения пояснично-крестцового сплетения
- G54.5 Невралгическая амиотрофия
- J00 Острый назофарингит [насморк]
- J01 Острый синусит
- J02.9 Острый фарингит неуточненный
- J03.9 Острый тонзиллит неуточненный (ангина агранулоцитарная)
- J04.0 Острый ларингит
- K08.8.0* Боль зубная
- M06.9 Ревматоидный артрит неуточненный
- M10 Подагра
- M15-M19 Артрозы
- M45 Анкилозирующий спондилит
- M47 Спондилез
- M65 Синовиты и тендосиновиты
- M71 Другие бурсопатии
- M77.9 Энтезопатия неуточненная
- M79.0 Ревматизм неуточненный
- M79.1 Миалгия
- M79.2 Невралгия и неврит неуточненные
- M79.3 Панникулит неуточненный
- N70 Сальпингит и оофорит
- N94.6 Дисменорея неуточненная
- R50 Лихорадка неясного происхождения
- R51 Головная боль
- R52.0 Острая боль
- R52.2 Другая постоянная боль
- T14.0 Поверхностная травма неуточненной области тела
- T14.3 Вывих, растяжение и повреждение капсульно-связочного аппарата сустава неуточненной области тела
Противопоказания
Гиперчувствительность; бронхиальная астма, крапивница и другие аллергические реакции в анамнезе, вызванные применением ацетилсалициловой кислоты или других НПВС; состояние после операции аортокоронарного шунтирования.
При лечении открытого артериального протока — известная или предполагаемая нелеченная инфекция; кровотечение, особенно внутричерепное кровоизлияние или желудочно-кишечное кровотечение; тромбоцитопения, недостаточность коагуляции; некротический энтероколит, почечная недостаточность; врожденный порок сердца, если проходимость артериального протока необходима для легочного или системного кровотока (например, легочная атрезия, тяжелая тетралогия Фалло, тяжелая коарктация аорты).
Ограничения к применению
С осторожностью: желудочно-кишечное кровотечение, изъязвление, перфорация; инфаркт миокарда, гипертензия, сердечная недостаточность, отеки, почечная недостаточность, печеночная недостаточность, бронхиальная астма, аспириновая триада (гиперчувствительность, аспириновая астма, полипоз носа).
Применение при беременности и кормлении грудью
Применение НПВС, в т.ч. ибупрофена, в III триместре беременности увеличивает риск преждевременного закрытия артериального протока плода. Следует избегать применения ибупрофена у беременных женщин, начиная с 30-й нед беременности (III триместр). Адекватных и контролируемых исследований влияния ибупрофена на ход беременности в I и II триместре не проводилось. Применение ибупрофена при беременности связано с потенциальным риском для плода.
Исследований по изучению влиянии ибупрофена на лактацию не проводилось, однако имеются сообщения о незначительном присутствии его в грудном молоке (от 0,06 до 0,6% суточной дозы). Сообщений о неблагоприятном воздействии ибупрофена на грудного ребенка и влиянии на выработку молока нет, тем не менее при кормлении грудью необходимо оценивать соотношение польза-риск для матери и ребенка.
Побочные действия
При пероральном применении ибупрофена возможны головокружение, боль в эпигастрии, изжога, тошнота, сыпь, рвота.
Взаимодействие
Ингибиторы АПФ, АРА II, бета-адреноблокаторы. При совместном применении с ибупрофеном может наблюдаться снижение действия на АД.
Дигоксин. При совместном применении может увеличиватся сывороточная концентрация и удлиниться T1/2 дигоксина.
Алкоголь. Употребление алкоголя увеличивает риск развития кровотечений в ЖКТ.
Антациды не влияниют на всасывание ибупрофена при совместном применении.
Ацетилсалициловая кислота. При совместном применении с ибупрофеном наблюдается антагонизм антиагрегационной активности и может снизиться кардиопротективный эффект ацетилсалициловой кислоты, повышается риск ульцерогенного действия и других осложнений со стороны ЖКТ.
Диуретики (фуросемид, тиазидные диуретики). Возможно снижение натриуретического эффекта.
Н2-антигистаминные ЛС (циметидин, ранитидин) не влияют на сывороточную концентрацию ибупрофена.
Литийсодержащие ЛС. Концентрация в плазме крови солей лития возрастает при приеме ибупрофена.
Метотрексат. При совместном применения с ибупрофеном может изменяться фармакокинетика метотрексата.
ЛС, нарушающие гемостаз (варфарин, ацетилсалициловая кислота, неселективные ингибиторы обратного захвата моноаминов/СИОЗС). Имеются сообщения о развитии кровотечения при совместном применении ибупрофена с ЛС, ингибирующими гемостаз.
Передозировка
Симптомы: летаргия, сонливость, тошнота, рвота и боль в эпигастрии. Данные симптомы, как правило, обратимы при поддерживающей терапии. Возможно возникновение желудочно-кишечного кровотечения. Так же есть вероятность возникновения гипертензии, острой почечной недостаточности, угнетения дыхания и комы, однако сообщения о них были редкими.
Лечение: в случае передозировки необходимо обеспечить симптоматическую и поддерживающую терапию. Специфических антидотов нет. На первом этапе рекомендуется вызвать рвоту и/или применить активированной уголь. Спустя 4 ч после передозировки при сохранении симптомов или у пациентов с большой передозировкой (от 5 до 10 раз выше МРДЧ) рекомендуется применение осмотических слабительных. Принудительный диурез, ощелачивание мочи, гемодиализ или гемоперфузия могут быть бесполезными из-за высокого связывания ибупрофена с белками плазмы крови.
Способ применения и дозы
Реклама: ООО «РЛС-Библиомед», ИНН 7714758963, erid=4CQwVszH9pUmKjt23pm
Внутрь, при наличии проблем с ЖКТ рекомендуется принимать во время еды или запивая молоком. Чтобы свести к минимуму потенциальный риск развития неблагоприятных сердечно-сосудистых и/или желудочно-кишечных побочных реакций, следует использовать самую низкую эффективную дозу и короткую продолжительность применения в соответствии с целями лечения пациента. Режим дозирования зависит от возраста и показания и определяется врачом.
Меры предосторожности
Гепатотоксичность
Следует прекратить прием ибупрофена, если отклонения в показателях работы печени сохраняются или ухудшаются, или если развиваются клинические признаки и симптомы заболевания печени.
Гипертония
У пациентов, принимающие некоторые гипотензивные ЛС, может быть снижена эффективность лечения гипертензии при одновременном приеме с НПВС. Необходим контроль АД.
Сердечная недостаточность и отеки
Следует избегать применения ибупрофена у пациентов с тяжелой сердечной недостаточностью, за исключением случаев, когда ожидаемая польза перевешивает риск обострения сердечной недостаточности.
Влияние на почки
Необходимо контролировать функцию почек у пациентов с почечной или печеночной недостаточностью, сердечной недостаточностью, обезвоживанием или гиповолемией. Следует избегать применения ибупрофена у пациентов с запущенным заболеванием почек, за исключением случаев, когда ожидаемая польза перевешивает риск.
Анафилактические реакции
При возникновении анафилактической реакции необходимо обратиться за неотложной помощью.
Серьезные кожные реакции
Следует прекратить прием ибупрофена при первом появлении кожной сыпи или других признаков развития гиперчувствительности.
Преждевременное закрытие артериального протока плода
Следует избегать применения ибупрофена у беременных женщин начиная с 30-й нед беременности.
Гематологическая токсичность
Необходимо контролировать уровень Hb или гематокрит у пациентов с любыми признаками или симптомами анемии.