Акьюлар ЛС (Akyular LS)
💊 Состав препарата Акьюлар ЛС
✅ Применение препарата Акьюлар ЛС
⚠️ Государственная регистрация данного препарата отменена
Описание активных компонентов препарата
Акьюлар ЛС
(Akyular LS)
Приведенная научная информация является обобщающей и не может быть использована для принятия
решения о возможности применения конкретного лекарственного препарата.
Дата обновления: 2020.05.18
Владелец регистрационного удостоверения:
Лекарственная форма
| Акьюлар ЛС |
Капли глазные 0.4%: фл.-капельница 5 мл рег. №: ЛП-001529 |
Форма выпуска, упаковка и состав
препарата Акьюлар ЛС
Капли глазные в виде прозрачного бесцветного раствора.
Вспомогательные вещества: натрия хлорид – 7.9 мг, динатрия эдетат – 0.15 мг, октоксинол 40 – 0.03 мг, бензалкония хлорид – 0.06 мг, 1М раствор хлористоводородной кислоты до pH 7.3 -7.5, 1М раствор натрия гидроксида до pH 7.3 – 7.5, вода очищенная — до 1 мл.
5 мл — флаконы-капельницы (1) — пачки картонные.
Фармакологическое действие
НПВС, оказывает выраженное анальгезирующее действие, обладает также противовоспалительным и умеренным жаропонижающим действием.
Механизм действия связан с неселективным угнетением активности ферментов ЦОГ-1 и ЦОГ-2, главным образом в периферических тканях, следствием чего является торможение биосинтеза простагландины – модуляторов болевой чувствительности, воспаления и терморегуляции. Кеторолак представляет собой рацемическую смесь R(+) и S(-)-энантиомеров, при этом анальгезирующее (обезболивающее) действие обусловлено S(-)-энантиомером.
Фармакокинетика
При инстилляции раствора кеторолака трометамола в виде глазных капель системная абсорбция низкая.
Кеторолак активно распределяется в тканях глаза, при этом большая часть задерживается в тканях роговицы и склеры. Cmax кеторолака в тканях определяется через 0.5-1 ч после применения, за исключением радужной оболочки и ресничного тела, где Cmax обнаруживается через 4 ч после применения.
Метаболизируется в печени. Метаболитами кеторолака трометамола являются: p-гидроксикеторолак, полярные метаболиты, а также глюкуронидный конъюгат кеторолака и ряд неизвестных метаболитов.
Большая часть кеторолака выводится почками и незначительная — через кишечник.
Показания активных веществ препарата
Акьюлар ЛС
Симптоматическое лечение боли, ощущения инородного тела, жжения в глазу, фотофобии, слезотечения после рефракционной операции на роговице.
Режим дозирования
Способ применения и режим дозирования конкретного препарата зависят от его формы выпуска и других факторов. Оптимальный режим дозирования определяет врач. Следует строго соблюдать соответствие используемой лекарственной формы конкретного препарата показаниям к применению и режиму дозирования.
Местно, закапывают в конъюнктивальный мешок оперированного глаза 4 раза/сут по мере необходимости для устранения клинических симптомов в течение не более 4 дней после проведения рефракционной операции на роговице.
Побочное действие
Со стороны органа зрения: часто — гиперемия конъюнктивы, инфильтраты роговицы, отек тканей глаза и боль в глазах, временное ощущение покалывания и жжения в месте введения, отек роговицы, воспаление радужной оболочки глаза, воспаление слизистой оболочки глаза, раздражение слизистой оболочки глаза, поверхностный кератит, поверхностные глазные инфекции; редко — язва роговицы, сухость слизистой оболочки глаза, нарушение зрения (нечеткость зрения); частота неизвестна — эрозия роговицы, перфорация роговицы, истончение и размягчение роговицы, разрушение эпителия.
Со стороны нервной системы: часто — головная боль.
Аллергические реакции: частота неизвестна — бронхоспазм или обострение бронхиальной астмы.
Противопоказания к применению
Повышенная чувствительность к кеторолаку, III триместр беременности, детский возраст до 3 лет.
С осторожностью
Повышенная чувствительности к ацетилсалициловой кислоте, производным фенилуксусной кислоты и другим НПВС ввиду возможной перекрестной чувствительности с кеторолаком; I и II триместры беременности и в период грудного вскармливания; при склонности к кровотечениям и при сопутствующем приеме препаратов, увеличивающих время кровотечения; у пациентов с офтальмологическими осложнениями в послеоперационном периоде, с нарушением иннервации роговицы, дефектами эпителия роговицы, сахарным диабетом, заболеваниями слизистой оболочки глаз (например, синдромом «сухого глаза»), с сопутствующим ревматоидным артритом, а также при небольших промежутках между повторными офтальмологическими операциями ввиду высокого риска развития нежелательных реакций со стороны роговицы, которые могут угрожать потерей зрения.
Применение при беременности и кормлении грудью
Противопоказано применение в III триместре беременности.
С осторожностью применять в I и II триместрах беременности.
Ввиду низкой системной абсорбции кеторолака при местном применении, влияние кеторолака на детей, находящихся на грудном вскармливании, не ожидается. Тем не менее, у женщин в период грудного вскармливания следует применять с осторожностью, в связи с отсутствием данных по экскреции кеторолака с грудным молоком при местном применении. При системном и пероральном введении кеторолак выделяется с грудным молоком.
Применение у детей
Противопоказание: детский возраст до 3 лет.
Применение у пожилых пациентов
Не установлено различий эффективности и безопасности препарата у пациентов пожилого возраста и пациентов молодого возраста.
Особые указания
Ввиду наличия у некоторых НПВС влияния на агрегацию тромбоцитов, что может увеличивать время кровотечения, применение глазных форм НПВС после офтальмологических хирургических вмешательств может повышать риск кровотечения в тканях глаза, в т.ч. способствовать возникновению гифемы.
При длительном местном применении НПВС возможно развитие кератита, истончение и разрушение роговичного эпителия, эрозии, язвенного поражения роговицы или ее перфорации. Перечисленные явления могут угрожать потерей зрения. У пациентов с признаками разрушения роговичного эпителия следует немедленно отменить прием препарата и тщательно контролировать состояние роговицы.
Пострегистрационный опыт свидетельствует о том, что применение местных НПВС в течение 24 ч и более перед хирургической операцией на роговице и более 14 дней после нее может повышать риск осложнений со стороны роговицы и их тяжесть.
Не рекомендуется к применению у лиц, которые используют контактные линзы. Следует избегать касания наконечником флакона глаза или поверхности вокруг глаз, так как это может привести к загрязнению наконечника микроорганизмами, которые вызывают глазные инфекции. Серьезное повреждение глаза и последующая потеря зрения могут стать следствием использования контаминированных растворов.
В случае возникновения интеркуррентных состояний со стороны органа зрения (например, травма или инфекция) или проведения офтальмологической операции, следует немедленно обратиться к врачу-офтальмологу для решения вопроса о возможности дальнейшего лечения.
Лекарственное взаимодействие
Все препараты группы НПВС, включая кеторолак, могут замедлять заживление ран в послеоперационном периоде. Также известно, что местные ГКС замедляют или пролонгируют заживление. Сопутствующее применение глазных форм НПВС и ГКС может в большей степени удлинять период заживления ран.
Если вы хотите разместить ссылку на описание этого препарата — используйте данный код
Top 20 medicines with the same components:
Top 20 medicines with the same treatments:
Ketorolac trometamol 5 mg/ml.
Excipient(s) with known effect: benzalkonium chloride 0.1 mg/ml.
Eye drops, solution.
Clear, colourless to pale yellow aqueous solution.
ACULAR is indicated for the prophylaxis and reduction of inflammation and associated symptoms following ocular surgery.
ACULAR is indicated in adults.
Posology
Post-operative inflammation:
One drop instilled into the eye three times daily starting 24 hours pre-operatively and continuing for up to three weeks post-operatively.
Paediatric population
There is no relevant use of ACULAR in the paediatric population in the indication: For the prophylaxis and reduction of inflammation following cataract surgery.
Method of administration
Ocular use.
Instil one drop of the solution into the inferior conjunctival sac of the eye to be treated, while pulling the lower eyelid gently downwards and looking upwards.
If ACULAR is used concomitantly with other topical eye medications there must be an interval of at least 5 minutes between the two medications.
The potential exists for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. ACULAR is contraindicated in individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs.
It is recommended that ACULAR be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications which may prolong bleeding time.
In common with other anti-inflammatory drugs, ACULAR may mask the usual signs of infection.
All non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow down or delay wound healing. Concomitant use of NSAIDs and topical steroids can increase the potential for healing problems.
Concomitant use of ACULAR and topical corticosteroids should be exercised with caution in patients susceptible to corneal epithelial breakdown.
Use of topical NSAIDS may result in keratitis. In some patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g. dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time, as they may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events which may become sight threatening.
Post marketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggest that use more than 24 hours prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post surgery may increase patient risk for the occurrence and severity of corneal adverse events.
The preservative in ACULAR, benzalkonium chloride, may cause eye irritation. Contact lenses must be removed prior to application, with at least a 15-minute wait before reinsertion. Benzalkonium chloride is known to discolour soft contact lenses. Contact with soft contact lenses must be avoided.
There have been post-marketing reports of bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma in patients, who have either a known hypersensitivity to aspirin/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or a past medical history of asthma associated with the use of ACULAR, which may be contributory. Caution is recommended in the use of ACULAR in these individuals.
Patients should be instructed to avoid allowing the tip of the dispensing container to contact the eye or surrounding structures to avoid injury and contamination of eye drops.
Undesirable effects may be minimised by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms.
Transient blurring of vision may occur on instillation of eye drops. Do not drive or use hazardous machinery unless vision is clear.
The most frequent adverse events reported with the use of ACULAR are transient stinging and burning on instillation.
The frequency of adverse reactions documented during clinical trials of ketorolac trometamol and through post-marketing experience is given below and is defined as follows:
Very Common (> 1/10); Common (>1/100 to <1/10); Uncommon (>1/1,000 to <1/100); Rare (>1/10,000 to <1/1,000); Very Rare (<1/10,000); Not Known (cannot be estimated from available data).
Immune system disorders
Common: Hypersensitivity including localised allergic reactions
Nervous system disorders
Common: Headache
Eye Disorders
Very Common: Eye irritation (including burning sensation)
Eye pain (including stinging)
Common: Superficial (punctate) keratitis
Eye and/or eyelid oedema
Ocular pruritus
Conjunctival hyperaemia
Eye infection
Eye inflammation
Iritis
Keratic precipitates
Retinal haemorrhage
Cystoid macular oedema
Eye trauma
Increased intraocular pressure
Blurred and/or diminished vision
Uncommon: Corneal ulcer
Corneal infiltrates
Eye dryness
Epiphora
Not known: Corneal damage, e.g. thinning, erosion, epithelial breakdown and perforation*
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Not known: Bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma**
*Occasional post marketing reports of corneal damage including corneal thinning, corneal erosion, epithelial breakdown and corneal perforation have been received. These occurred mainly in patients using concomitant topical corticosteroids and/or with predisposing co-morbidity.
**There have been post-marketing reports of bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma, in patients, who have either a known hypersensitivity to aspirin/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or a past medical history of asthma, associated with the use of ACULAR which may be contributory.
None of the typical adverse reactions reported with the systemic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (including ketorolac trometamol) have been observed at the doses used in topical ophthalmic therapy.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via:
Yellow Card Scheme
Website: www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard
No case of overdose has been reported. Overdose is unlikely to occur via the recommended method of administration.
If accidentally ingested, drink fluids to dilute.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Anti-inflammatory agents, non-steroids
ATC code: S01BC 05.
ACULAR (ketorolac trometamol) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent demonstrating analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity. Ketorolac trometamol inhibits the cyclo-oxygenase enzyme essential for biosynthesis of prostaglandins. ACULAR has been shown to reduce prostaglandin levels in the aqueous humour after topical ophthalmic administration.
Ketorolac trometamol given systemically does not cause pupil constriction. Results from clinical studies indicate that ACULAR has no significant effect on intra-ocular pressure.
a) General characteristics
Absorption
|
Rabbit aqueous humor bioavailability: |
|
|
Mean concentration of total radioactivity |
0.856 µg-equiv./ml @ 0.5 hr |
|
1.607 µg-equiv./ml @ 2 hr |
|
|
Tmax |
3.38 hr |
|
Cmax |
1.905 µg-equiv./ml |
|
AUC (0-8 hr) |
9.39 µg-equiv. hr/ml |
|
Total AUC |
13.53 µg-equiv. hr/ml |
|
Half-life |
3.77 hr |
|
Absolute ocular bioavailability |
3.7% |
After topical ocular doses in the rabbit the half life of total radioactivity in aqueous humor was longer than after intracameral injection. This suggests that topical dosing may lead to a «reservoir» effect in the corneal epithelium and continued flux of drug from the reservoir into the aqueous humor.
Distribution
After ophthalmic doses were administered to rabbits, peak concentrations of radioactivity were achieved within 1 hour in the ocular tissues and were highest in the cornea (6.06 mcg-eq/ml). At 1 hour, the majority of the radioactivity (0.9% of administered dose) was recovered from the sclera (0.58%) and cornea (0.24%), and smaller amounts were recovered from the aqueous humor (0.026%), vitreous humor (0.023%), retina-choroid (0.018%), iris-ciliary body (0.007%) and lens (0.002%).
Relative to plasma AUC values, the AUC’s in rabbits were higher for cornea (104 fold), sclera (27 fold), iris-ciliary body (5.8 fold), retina-choroid (5.6 fold), aqueous humor (3.3 fold) and approximately one-half in the vitreous humor and lens. After ophthalmic administration, concentrations of drug-related radioactivity were higher in the ocular tissues and lower in plasma compared with those after IV dosing.
Systemic Absorption
After ophthalmic doses in the rabbit, ketorolac was absorbed rapidly into the systemic circulation (Tmax, 15 min). Plasma half-lives after ophthalmic doses (6.6 — 6.9 hr) were longer than those after IV administration (1.1 hr), suggesting that removal of drug from eye into the venous circulation may be rate-limiting. By comparison of drug levels in aqueous humor after intracameral injection vs. plasma levels after IV administration, ketorolac was shown to clear more rapidly from plasma (6 ml/min) than from the anterior chamber (11 mcl/min).
In the cynomolgus monkey, peak plasma levels of ketorolac occurred at 1.1 hr after the ophthalmic dose. The plasma half-life of ketorolac was similar after ophthalmic (1.8 hr) and IV doses (1.6 hr).
The majority of the ophthalmic dose was excreted in urine (66% in rabbit and 75% in monkey) and a small amount in faeces (11% in rabbit and 2% in monkey). The extent of systemic absorption after ophthalmic dosing averaged 73% in the rabbit and 76% in the cynomolgus monkey.
Metabolism
After ophthalmic administration in rabbits, ketorolac represented the major component (more than 90%) of radioactivity in aqueous humor and plasma and the p-hydroxy metabolite accounted for 5% of radioactivity in plasma. Ketorolac was also the major component (96%) of plasma radioactivity after ophthalmic dosing in monkeys.
After ophthalmic dosing in the rabbit, 72%, 17% and 6% of the total radioactivity in urine was comprised of intact ketorolac, p-hydroxy ketorolac and other polar metabolites, respectively. After IV dosing, the relative proportions of total radioactivity in urine averaged 6% as intact ketorolac, 68% as p-hydroxy ketorolac and 22% as polar metabolites.
In the monkey, intact ketorolac and its polar metabolite accounted for 32% and 65% of the total radioactivity in urine, respectively, after ophthalmic dosing, and 50% and 49% of the radioactivity in urine, respectively, after IV dosing. Thus, the metabolism of ketorolac was qualitatively similar after ophthalmic and IV administration in the monkey and rabbit.
b) Characteristics in patients
Ketorolac tromethamine solutions (0.1% or 0.5%) or vehicle were instilled into the eyes of patients approximately 12 hours and 1 hour prior to surgery. Concentrations of ketorolac in aqueous humor sampled at the time of surgery were at the lower limit of detection (40 ng/ml) in 1 patient and below the quantitation limit in 7 patients dosed with 0.1% ketorolac tromethamine. The average aqueous humor level of ketorolac in patients treated with 0.5% ketorolac tromethamine was 95 ng/ml. Concentrations of PGE2 in aqueous humor were 80 pg/ml, 40 pg/ml and 28 pg/ml in patients treated with vehicle, 0.1% ketorolac tromethamine and 0.5% ketorolac tromethamine, respectively.
In the 21-day multiple dose (TID) tolerance study in healthy subjects, only 1 of 13 subjects had a detectable plasma level pre-dose (0.021 µg/ml). In another group of 13 subjects, only 4 subjects showed very low plasma levels of ketorolac (0.011 to 0.023 µg/ml) 15 minutes after the ocular dose.
Thus, higher levels of ketorolac in the aqueous humor and very low or no detectable plasma levels after ophthalmic doses, suggest that the use of ketorolac tromethamine by the ophthalmic route in treatment of ocular disorders results in quite low systemic absorption in patients.
Anti-inflammatory agents, non-steroids
Non-clinical data reveal no special hazard for humans based on conventional studies of safety pharmacology, repeated dose toxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenic potential, toxicity to reproduction and development.
Acute, sub-acute and chronic studies of ACULAR in experimental animals have established the safety of the drug. In addition, octoxinol 40 was separately evaluated for its ocular safety. ACULAR was found to be non-irritating, it did not demonstrate a local anaesthetic effect, it did not influence the healing of experimental corneal wounds in rabbits, it did not enhance the spread of experimental ocular infections of Candida albicans, Herpes simplex virus type one, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa in rabbits, and it did not increase the ocular pressure of normal rabbit eyes.
Sodium chloride
Benzalkonium chloride
Disodium edetate
Octoxinol 40
1N Sodium hydroxide or 1N Hydrochloric acid, to adjust pH
Purified water
Unopened: 2 years.
Use within 28 days of first opening.
Low density polyethylene dropper bottles (with LDPE dropper tips) containing 3 ml, 5 ml or 10 ml of solution. The drop size is 35 microlitres. Each bottle has a medium impact polystyrene (MIPS) screw-cap.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
No special requirements.
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Allergan Ltd.
Marlow International
The Parkway
Marlow
Bucks SL7 1YL
United Kingdom
30th October 2014. Version 3.
Acular price
We have no data on the cost of the drug.
However, we will provide data for each active ingredient
The approximate cost of Ketorolac 0.5 % per unit in online pharmacies is from 4.33$ to 11.28$, per package is from 43$ to 130$.
The approximate cost of Ketorolac 0.50 % per unit in online pharmacies is from 8.79$ to 9.79$, per package is from 44$ to 49$.
The approximate cost of Ketorolac 10 mg per unit in online pharmacies is from 0.67$ to 1.1$, per package is from 67$ to 110$.
Available in countries
Find in a country:
Rebel Distributors Corp.
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
- Principal Display Panel
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
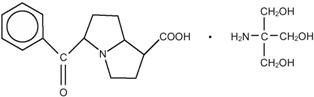
ACULAR® (ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution) is a member of the pyrrolo-pyrrole group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for ophthalmic use. Its chemical name is (±)-5-benzoyl-2, 3-dihydro-1H pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid, compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol (1:1) and it has the following structure:
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is supplied as a sterile isotonic aqueous 0.5% solution, with a pH of 7.4. ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is a racemic mixture of R-(+) and S-(-)- ketorolac tromethamine. Ketorolac tromethamine may exist in three crystal forms. All forms are equally soluble in water. The pKa of ketorolac is 3.5. This white to off-white crystalline substance discolors on prolonged exposure to light. The molecular weight of ketorolac tromethamine is 376. 41. The osmolality of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is 290 mOsml/kg.
Each mL of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution contains: Active: ketorolac tromethamine 0.5%. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%. Inactives: edetate disodium 0.1%; octoxynol 40; purified water; sodium chloride; and hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ketorolac tromethamine is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug which, when administered systemically, has demonstrated analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-pyretic activity. The mechanism of its action is thought to be due to its ability to inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Ketorolac tromethamine given systemically does not cause pupil constriction.
Prostaglandins have been shown in many animal models to be mediators of certain kinds of intraocular inflammation. In studies performed in animal eyes, prostaglandins have been shown to produce disruption of the blood-aqueous humor barrier, vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, leukocytosis, and increased intraocular pressure. Prostaglandins also appear to play a role in the miotic response produced during ocular surgery by constricting the iris sphincter independently of cholinergic mechanisms.
Two drops (0.1 mL) of 0.5% ACULAR® ophthalmic solution instilled into the eyes of patients 12 hours and 1 hour prior to cataract extraction achieved measurable levels in 8 of 9 patients’ eyes (mean ketorolac concentration 95 ng/mL aqueous humor, range 40 to 170 ng/mL). Ocular administration of ketorolac tromethamine reduces prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels in aqueous humor. The mean concentration of PGE2 was 80 pg/mL in the aqueous humor of eyes receiving vehicle and 28 pg/mL in the eyes receiving ACULAR® 0.5% ophthalmic solution.
One drop (0.05 mL) of 0.5% ACULAR® ophthalmic solution was instilled into one eye and one drop of vehicle into the other eye TID in 26 normal subjects. Only 5 of 26 subjects had a detectable amount of ketorolac in their plasma (range 10.7 to 22.5 ng/mL) at Day 10 during topical ocular treatment. When ketorolac tromethamine 10 mg is administered systemically every 6 hours, peak plasma levels at steady state are around 960 ng/mL.
Two controlled clinical studies showed that ACULAR® ophthalmic solution was significantly more effective than its vehicle in relieving ocular itching caused by seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
Two controlled clinical studies showed that patients treated for two weeks with ACULAR® ophthalmic solution were less likely to have measurable signs of inflammation (cell and flare) than patients treated with its vehicle.
Results from clinical studies indicate that ketorolac tromethamine has no significant effect upon intraocular pressure; however, changes in intraocular pressure may occur following cataract surgery.
Uses
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is indicated for the temporary relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is also indicated for the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formulation.
WARNINGS
There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, phenylacetic acid derivatives, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Therefore, caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs.
With some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphemas) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
PRECAUTIONS
General:
All topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDS and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems.
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events which may become sight threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 24 hours prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post-surgery may increase patient risk for the occurrence and severity of corneal adverse events.
It is recommended that ACULAR® ophthalmic solution be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications which may prolong bleeding time.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequent adverse events reported with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions have been transient stinging and burning on instillation. These events were reported by up to 40% of patients participating in clinical trials.
Other adverse events occurring approximately 1% — 10% of the time during treatment with ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions included allergic reactions, corneal edema, iritis, ocular inflammation, ocular irritation, superficial keratitis, and superficial ocular infections.
Other adverse events reported rarely with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions included: corneal infiltrates, corneal ulcer, eye dryness, headaches, and visual disturbance (blurry vision).
Clinical Practice: The following events have been identified during postmarketing use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5% in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The events, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to topical ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5%, or a combination of these factors, include corneal erosion, corneal perforation, corneal thinning and epithelial breakdown (see PRECAUTIONS, General).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is one drop (0.25 mg) four times a day for relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
For the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction, one drop of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution should be applied to the affected eye(s) four times daily beginning 24 hours after cataract surgery and continuing through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period.
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution has been safely administered in conjunction with other ophthalmic medications such as antibiotics, beta blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cycloplegics, and mydriatics.
HOW SUPPLIED
ACULAR® (ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution) is supplied sterile in opaque white LDPE plastic bottles with white droppers with gray high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps as follows:
5mL in 10mL bottle — NDC 21695-463-05
Store at 15°C — 25°C (59°F- 77°F) with protection from light.
Rx Only
© 2004 Allergan, Inc.
Irvine, CA 92612, U.S.A.
ACULAR® (a registered trademark of Roche Palo Alto L.L.C.) is manufactured and distributed by Allergan under license from its developer, Roche Palo Alto L.L.C., Palo Alto, California, U.S.A.
® Marks owned by Allergan, Inc.
U.S. Pat. 5,110,493
8344X
71590US11P
Repackaged by:
Rebel Distributors Corp.
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Information for Patients:
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution should not be administered while wearing contact lenses.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility:
Ketorolac tromethamine was not carcinogenic in rats given up to 5 mg/kg/day orally for 24 months (151 times the maximum recommended human topical ophthalmic dose, on a mg/kg basis, assuming 100% absorption in humans and animals) nor in mice given 2 mg/kg/day orally for 18 months (60 times the maximum recommended human topical ophthalmic dose, on a mg/kg basis, assuming 100% absorption in humans and animals).
Ketorolac tromethamine was not mutagenic in vitro in the Ames assay or in forward mutation assays. Similarly, it did not result in an in vitro increase in unscheduled DNA synthesis or an in vivo increase in chromosome breakage in mice. However, ketorolac tromethamine did result in an increased incidence in chromosomal aberrations in Chinese hamster ovary cells.
Ketorolac tromethamine did not impair fertility when administered orally to male and female rats at doses up to 272 and 484 times the maximum recommended human topical ophthalmic dose, respectively, on a mg/kg basis, assuming 100% absorption in humans and animals.
Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C. Ketorolac tromethamine, administered during organogenesis, was not teratogenic in rabbits or rats at oral doses up to 109 times and 303 times the maximum recommended human topical ophthalmic dose, respectively, on a mg/kg basis assuming 100% absorption in humans and animals. When administered to rats after Day 17 of gestation at oral doses up to 45 times the maximum recommended human topical ophthalmic dose, respectively, on a mg/kg basis, assuming 100% absorption in humans and animals, ketorolac tromethamine resulted in dystocia and increased pup mortality. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. ACULAR® ophthalmic solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects: Because of the known effects of prostaglandin-inhibiting drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of the ductus arteriosus), the use of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution during late pregnancy should be avoided.
Nursing Mothers:
Caution should be exercised when ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use:
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients below the age of 3 have not been established.
Geriatric Use:
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
Principal Display Panel
ACULAR
KETOROLAC TROMETHAMINE SOLUTION
Product Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Human prescription drug label | Item Code (Source) | NDC:21695-463(NDC:0023-2181) |
| Route of Administration | OPHTHALMIC | DEA Schedule |
Active Ingredient/Active Moiety |
||
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Basis of Strength | Strength |
| KETOROLAC TROMETHAMINE KETOROLAC | 5 mg |
Inactive Ingredients |
|
|---|---|
| Ingredient Name | Strength |
| EDETATE DISODIUM | |
| octoxynol-40 | |
| water | |
| SODIUM CHLORIDE | |
| benzalkonium chloride | |
| SODIUM HYDROXIDE | |
| HYDROCHLORIC ACID |
Packaging |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Item Code | Package Description | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| 1 | NDC:21695-463-05 | 5 in 1 BOTTLE |
Marketing Information |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA019700 | 1992-11-09 |
Generic name: KETOROLAC TROMETHAMINE 5mg in 1mL
Dosage form: ophthalmic solution
Drug class: Ophthalmic anti-inflammatory agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on May 22, 2023.
Recommended Dosing
Patient Dosing
The recommended dose of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is one drop four times a day to the affected eye(s) for relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
For the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction, one drop of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution should be applied to the affected eye four times daily beginning 24 hours after cataract surgery and continuing through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period.
Use with Other Topical Ophthalmic Medications
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution has been safely administered in conjunction with other ophthalmic medications such as antibiotics, alpha-agonists, beta blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cycloplegics, and mydriatics. Drops should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Medical Disclaimer
What Is Acular?
Acular (ketorolac tromethamine) Ophthalmic Solution is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to relieve eye itching caused by seasonal allergies. Acular is also used to reduce swelling, pain, and burning or stinging after cataract surgery or corneal refractive surgery. Acular is available in generic form.
What Are Side Effects of Acular?
Common side effects of Acular include:
- temporary stinging,
- burning, or
- itching of the eyes for 1-2 minutes when applied.
Other side effects of Acular include:
- eye redness,
- swollen or puffy eyelids, and
- headache.
Tell your doctor if you have unlikely but serious side effects of Acular including:
- eye swelling,
- eye discharge,
- vision changes,
- eye pain, or
- bleeding inside the eye.
Seek medical care or call 911 at once if you have the following serious side effects:
- Serious eye symptoms such as sudden vision loss, blurred vision, tunnel vision, eye pain or swelling, or seeing halos around lights;
- Serious heart symptoms such as fast, irregular, or pounding heartbeats; fluttering in your chest; shortness of breath; and sudden dizziness, lightheartedness, or passing out;
- Severe headache, confusion, slurred speech, arm or leg weakness, trouble walking, loss of coordination, feeling unsteady, very stiff muscles, high fever, profuse sweating, or tremors.
This document does not contain all possible side effects and others may occur. Check with your physician for additional information about side effects.
Dosage for Acular
The recommended dose of Acular ophthalmic solution is one drop (0.25 mg) four times a day for relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. For the treatment of postoperative inflammation in cataract surgery patients, one drop should be applied to the affected eye(s) four times daily beginning 24 hours after surgery and continued for 2 weeks postoperatively.
What Drugs, Substances, or Supplements Interact with Acular?
Acular may interact with blood thinners. Other drugs may interact with Acular ophthalmic. Tell your doctor all prescription and over-the-counter medications and supplements you use.
Acular During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Acular should be used only when prescribed during the first 6 months of pregnancy. Avoid use during the last 3 months of pregnancy due to the potential for harm to the fetus. It is unknown if this drug passes into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
Additional Information
Our Acular (ketorolac tromethamine) Side Effects Drug Center provides a comprehensive view of available drug information on the potential side effects when taking this medication.
DESCRIPTION
ACULAR® (ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is a member of the pyrrolopyrrole group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for ophthalmic use. Its chemical name is (±)-5-Benzoyl-2, 3-dihydro-1H pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol (1:1) and it has the following structure:
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is supplied as a sterile isotonic aqueous 0.5% solution, with a pH of 7.4. ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is a racemic mixture of R-(+) and S-(-)- ketorolac tromethamine. Ketorolac tromethamine may exist in three crystal forms. All forms are equally soluble in water. The pKa of ketorolac is 3.5. This white to off-white crystalline substance discolors on prolonged exposure to light. The molecular weight of ketorolac tromethamine is 376.41. The osmolality of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is 290 mOsmol/kg.
Each mL of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution contains: Active: ketorolac tromethamine 0.5%. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.01%. Inactives: edetate disodium 0.1%; octoxynol 40; purified water; sodium chloride; hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH.
INDICATIONS
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is indicated for the temporary relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is also indicated for the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosing
Patient Dosing
The recommended dose of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution is one drop four times a day to the affected eye(s) for relief of ocular itching due to seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
For the treatment of postoperative inflammation in patients who have undergone cataract extraction, one drop of ACULAR® ophthalmic solution should be applied to the affected eye four times daily beginning 24 hours after cataract surgery and continuing through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period.
Use With Other Topical Ophthalmic Medications
ACULAR® ophthalmic solution has been safely administered in conjunction with other ophthalmic medications such as antibiotics, alpha-agonists, beta blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cycloplegics, and mydriatics. Drops should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
HOW SUPPLIED
Dosage Forms And Strengths
10 mL size bottle filled with 5 mL of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution, 0.5% (5 mg/mL)
Storage And Handling
ACULAR® (ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution) 0.5% is supplied sterile, in white opaque plastic LDPE bottles with white droppers, with gray high impact polystyrene (HIPS) caps as follows:
5 mL in 10 mL bottle NDC 0023-2181-05
Storage
Store at 15°-25°C (59°-77°F). Protect from light.
ACULAR® is manufactured and distributed by Allergan, Inc. under license from its developer, Roche Palo Alto LLC, Palo Alto, CA, U.S.A. Revised: Dec 2011
Side Effects & Drug Interactions
SIDE EFFECTS
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Clinical Studies Experience
The most frequent adverse reactions reported with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions have been transient stinging and burning on instillation. These reactions were reported by up to 40% of patients participating in clinical trials.
Other adverse reactions occurring approximately 1 to 10% of the time during treatment with ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions included allergic reactions, corneal edema, iritis, ocular inflammation, ocular irritation, superficial keratitis, and superficial ocular infections.
Other adverse reactions reported rarely with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solutions included: corneal infiltrates, corneal ulcer, eye dryness, headaches, and visual disturbance (blurry vision).
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-marketing use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5% in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The reactions, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to topical ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.5% or a combination of these factors, include bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma, corneal erosion, corneal perforation, corneal thinning, and epithelial breakdown [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS].
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No Information provided
WARNINGS
Included as part of the PRECAUTIONS section.
PRECAUTIONS
Delayed Healing
Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems.
Cross-Sensitivity Or Hypersensitivity
There is the potential for cross-sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid, phenylacetic acid derivatives, and other NSAIDs. There have been reports of bronchospasm or exacerbation of asthma associated with the use of ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution in patients who have either a known hypersensitivity to aspirin/non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or a past medical history of asthma. Therefore, caution should be used when treating individuals who have previously exhibited sensitivities to these drugs.
Increased Bleeding Time
With some NSAIDs, there exists the potential for increased bleeding time due to interference with thrombocyte aggregation. There have been reports that ocularly applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause increased bleeding of ocular tissues (including hyphemas) in conjunction with ocular surgery.
It is recommended that ACULAR® ophthalmic solution be used with caution in patients with known bleeding tendencies or who are receiving other medications, which may prolong bleeding time.
Corneal Effects
Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration, or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs suggests that patients with complicated ocular surgeries, corneal denervation, corneal epithelial defects, diabetes mellitus, ocular surface diseases (e.g., dry eye syndrome), rheumatoid arthritis, or repeat ocular surgeries within a short period of time may be at increased risk for corneal adverse events which may become sight threatening. Topical NSAIDs should be used with caution in these patients.
Postmarketing experience with topical NSAIDs also suggests that use more than 1 day prior to surgery or use beyond 14 days post-surgery may increase patient risk for the occurrence and severity of corneal adverse events.
Contact Lens Wear
ACULAR® should not be administered while wearing contact lenses.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Ketorolac tromethamine was not carcinogenic in either rats given up to 5 mg/kg/day orally for 24 months or in mice given 2 mg/kg/day orally for 18 months. These doses are approximately 125 times and 50 times higher respectively than the maximum recommended human topical ophthalmic daily dose given as QID for itching to affected eyes on a mg/kg basis.
Ketorolac tromethamine was not mutagenic in vitro in the Ames assay or in forward mutation assays. Similarly, it did not result in an in vitro increase in unscheduled DNA synthesis or an in vivo increase in chromosome breakage in mice. However, ketorolac tromethamine did result in an increased incidence in chromosomal aberrations in Chinese hamster ovary cells.
Ketorolac tromethamine did not impair fertility when administered orally to male and female rats at doses up to 9 mg/kg/day and 16 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are respectively 225 and 400 times higher than the typical human topical ophthalmic daily dose.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects.
Pregnancy Category C
Ketorolac tromethamine, administered during organogenesis, was not teratogenic in rabbits and rats at oral doses of 3.6 mg/kg/day and 10 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are approximately 100 times and 250 times higher respectively than the maximum recommended human topical ophthalmic daily dose of 2 mg (5 mg/mL x 0.05 mL/drop, x 4 drops x 2 eyes) to affected eyes on a mg/kg basis. Additionally, when administered to rats after Day 17 of gestation at oral doses up to 1.5 mg/kg/day (approximately 40 times the typical human topical ophthalmic daily dose), ketorolac tromethamine resulted in dystocia and increased pup mortality. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. ACULAR® solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Because of the known effects of prostaglandin-inhibiting drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of the ductus arteriosus), the use of ACULAR® solution during late pregnancy should be avoided.
Nursing Mothers
Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ACULAR is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients below the age of 2 have not been established.
Geriatric Use
No overall clinical differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and other adult patients.
Overdose & Contraindications
OVERDOSE
No Information provided
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ACULAR® solution is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formulation.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism Of Action
Ketorolac tromethamine is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug which, when administered systemically, has demonstrated analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-pyretic activity. The mechanism of its action is thought to be due to its ability to inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis.
Pharmacokinetics
Two drops of 0.5% ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution instilled into the eyes of patients 12 hours and 1 hour prior to cataract extraction achieved a mean ketorolac concentration of 95 ng/mL in the aqueous humor of 8 of 9 eyes tested (range 40 to 170 ng/mL).
One drop of 0.5% ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution was instilled into 1 eye and 1 drop of vehicle into the other eye TID in 26 healthy subjects. Five (5) of 26 subjects had detectable concentrations of ketorolac in their plasma (range 11 to 23 ng/mL) at Day 10 during topical ocular treatment. The range of concentrations following TID dosing of 0.5% ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution are approximately 4 to 8% of the steady state mean minimum plasma concentration observed following four times daily oral administration of 10 mg ketorolac in humans (290 ± 70 ng/mL).
Clinical Studies
Two controlled clinical studies showed that ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution was significantly more effective than its vehicle in relieving ocular itching caused by seasonal allergic conjunctivitis.
Two controlled clinical studies showed that patients treated for two weeks with ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution were less likely to have measurable signs of inflammation (cell and flare) than patients treated with its vehicle.
Results from clinical studies indicate that ketorolac tromethamine has no significant effect upon intraocular pressure; however, changes in intraocular pressure may occur following cataract surgery.
PATIENT INFORMATION
Slow Or Delayed Healing
Patients should be informed of the possibility that slow or delayed healing may occur while using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Avoiding Contamination Of The Product
Patients should be instructed to avoid allowing the tip of the bottle to contact the eye or surrounding structures because this could cause the tip to become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions.
Also, to avoid the potential for cross-contamination, the patient should be advised to use one bottle for each eye following bilateral ocular surgery. The use of the same bottle of topical eye drops for both eyes following bilateral ocular surgery is not recommended.
Contact Lens Wear
Patients should be advised that ACULAR® solution should not be administered while wearing contact lenses.
Intercurrent Ocular Conditions
Patients should be advised that if they develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection) or have ocular surgery, they should immediately seek their physician’s advice concerning the continued use of ACULAR®.
Concomitant Topical Ocular Therapy
Patients should be advised that if more than one topical ophthalmic medication is being used, the medicines should be administered at least 5 minutes apart.
From 
Health Solutions From Our Sponsors
Report Problems to the Food and Drug Administration
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Акьюлар ЛС — раствор капель глазных, нестероидное противовоспалительное средство, с анальгезирующим и жаропонижающим действием. Применяется в офтальмологии для купирования умеренного и сильного болевого синдрома, ощущения в глазу инородного тела, светобоязни, слезотечения.
Состав и форма выпуска
Акьюлар ЛС – раствор капель глазных 0,4% прозрачный, стерильный, содержит:
- Основное вещество: кеторолакатрометамин – 4 мг.
Упаковка. Белые пластиковые флаконы с капельницей по 5 мл в пачке картонной.
Фармакологические свойства
Кеторолакатрометамин в составе раствора Акьюлар ЛС, является нестероидным противовоспалительным средством, производным пирролизин-карбоксиловой к-ты. Он обладает выраженным анальгезирующим действием, имеет противовоспалительное и умеренное жаропонижающее свойства, что связано с блокированием активности ЦОГ – главного из ферментов метаболизма арахидоновой к-ты. Данный фермент является предшественником простагландинов и играет основную роль в развитии воспалительного процесса, лихорадочных состояний, боли.
Показания к применению
- Кратковременное купирование в глазу боли, жжения, ощущения инородного тела, светобоязни.
- Слезотечение после оперативных вмешательств на роговице.
Способ применения и дозы
Раствор Акьюлар ЛС рекомендуется закапывать конъюнктивально по одной капле в пораженный глаз до 4 раз ежесуточно или по мере необходимости до полного устранения клинических симптомов. Продолжительность применения не должна превышать 4-х дней.
Противопоказания
- Индивидуальная непереносимость.
- Детский возраст.
- Беременность (III триместр).
Раствор Акьюлар ЛС назначают с осторожностью пациентам с ревматоидным артритом, сахарным диабетом, непереносимостью ацетилсалициловой к-ты, производных фенилуксусной к-ты и прочих НПВС, при осложнениях офтальмологических операций, повлекших нарушения иннервации роговицы либо дефекты ее эпителия, патологических процессах слизистой оболочки (синдром «сухого глаза»), а также в промежутках между назначенными офтальмологическими операциями, из-за риска развития возникновения негативных реакций роговицы, с угрозой потери зрения.
Женщинам в I — II триместры беременности, а также при грудном вскармливании, раствор Акьюлар ЛС может назначаться только по особым показаниям и под медицинским контролем. Также под контролем врача препарат назначается пациентам с риском развития кровотечений или принимающим лекарственные средства, увеличивающие время свертываемости крови.
Побочные действия
- Местные боли, покраснение конъюнктивы, отеки, инфильтрация роговицы.
- Затуманивание зрение (кратковременное).
- Головная боль.
- Кератит, истончение эпителия роговицы, язвенное поражение роговицы (при применении длительно).
Передозировка
Данных нет.
Лекарственные взаимодействия
Раствор Акьюлар ЛС может назначаться с любыми офтальмологическими препаратами, однако его одновременное применение с капельными глюкокортикостероидами нежелательно, вследствие возможности замедления заживления раневых поверхностей.
Особые указания
Раствор Акьюлар ЛС не рекомендуется применять лицам использующим контактные линзы.
Не прикасаться носиком дозатора к поверхности глаза во время закапывания.
При инстилляциях раствора нередко происходит кратковременное затуманивание зрения, в это время, лучше не садиться за руль и не работать с движущимися механизмами.
Хранят раствор Акьюлар ЛС при комнатной температуре. Берегут от детей.
Срок годности – 1,5 года. Раствор во вскрытом флаконе необходимо утилизировать через 4 недели.
Цена препарата Акьюлар ЛС
Стоимость препарата «Акьюлар ЛС» в аптеках Москвы начинается от 190 руб.
Аналоги Акьюлар ЛС
Альбуцид |
Витабакт |
Дексаметазон |
Фармадекс |
Обратившись в «Московскую Глазную Клинику», Вы сможете пройти обследование на самом современном диагностическом оборудовании, а по его результатам – получить индивидуальные рекомендации ведущих специалистов по лечению выявленных патологий.
Клиника работает семь дней в неделю без выходных, с 9 до 21 ч. Записаться на прием и задать специалистам все интересующие Вас вопросы можно по телефонам 8 (800) 777-38-81 и 8 (499) 322-36-36 или онлайн, воспользовавшись соответствующей формой на сайте.

Запишитесь на прием к врачу офтальмологу
Заполните форму и получите скидку 15 % на диагностику!